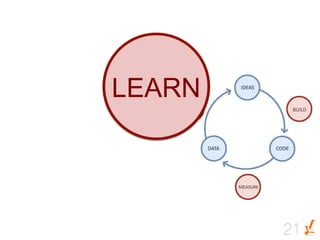
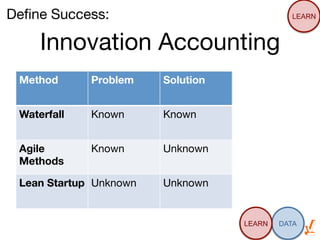
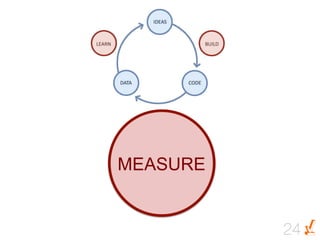
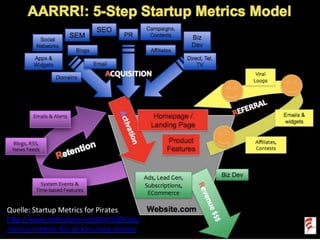
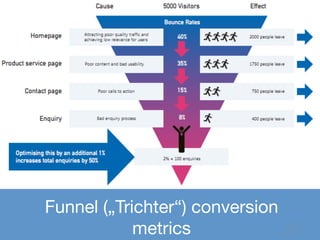
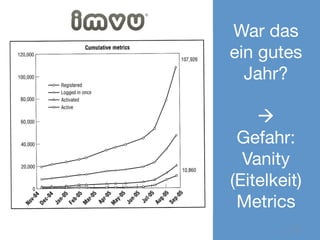
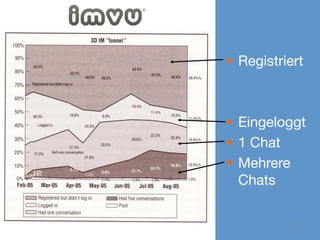
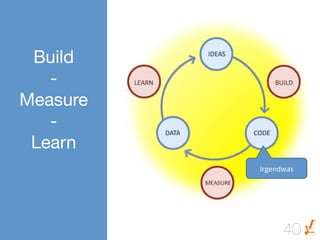
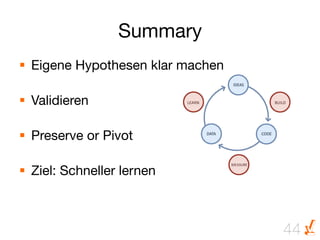
Das Dokument thematisiert die Grundlagen und Methoden des Lean Startups, einschließlich der Entwicklung eines Minimum Viable Product (MVP) und des kontinuierlichen Lernens durch die Build-Measure-Learn-Schleife. Es beschreibt, wie Unternehmer Annahmen testen und ihre Geschäftsmodelle anpassen können, um erfolgreich zu sein und Ressourcenverschwendung zu vermeiden. Zudem werden Metriken zur Bewertung des Fortschritts und der Erfolgschancen eines Startups diskutiert.












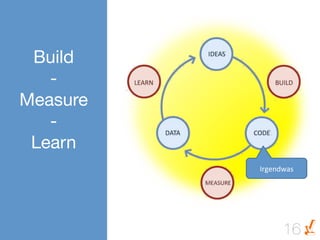
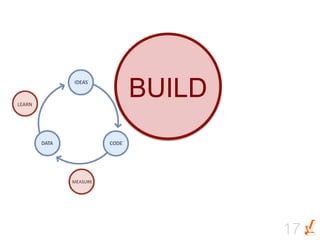
![BUILD
Minimum Viable Product
brauchbar
feasible
durchführbar
[biol.]
entwicklungsfähig
existenzfähig
gangbar
[med.]
lebensfähig
feasible
machbar
Klein feasible
prak>kabel
feasible
realisierbar
anfangen überlebensfähig
[biol.]
wachstumsfähig
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcka-leanstartup-120715111217-phpapp02/85/2012-07-Lean-Startup-at-bcka-by-Calpano-18-320.jpg)