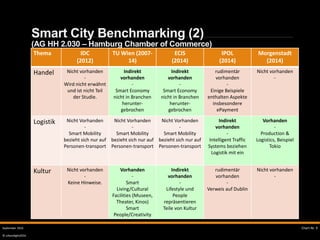
Das Dokument behandelt das Konzept der Smart City, einschließlich ihrer Schlüsselfaktoren wie Mobilität, Energie, Sicherheit und Bildung. Es beschreibt Herausforderungen, Zielsetzungen und Best Practices sowie Benchmarking-Daten zu verschiedenen Städten. Zudem wird die Bedeutung digitaler Dienste und Technologien hervorgehoben, die zur Verbesserung urbaner Lebensqualität beitragen.