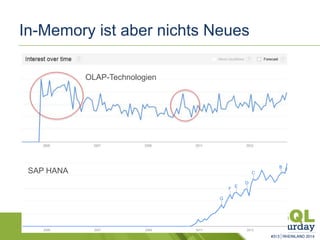
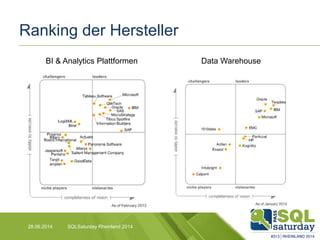
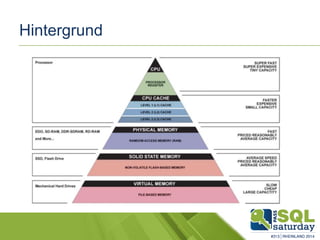
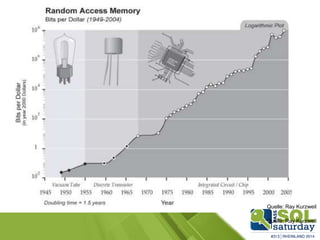
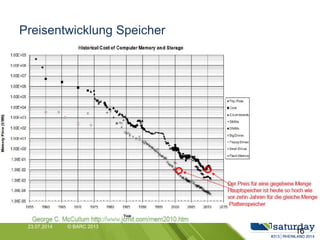
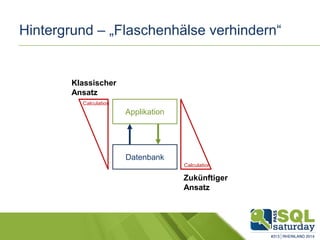
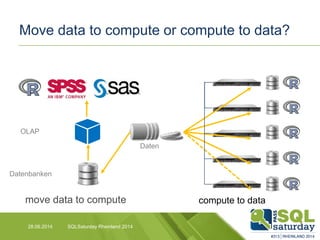
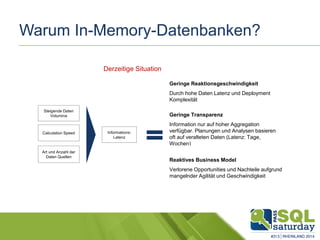
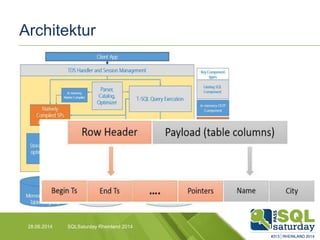
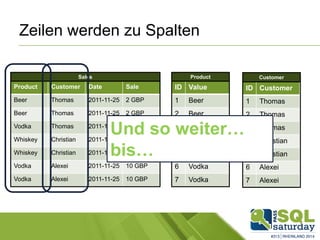
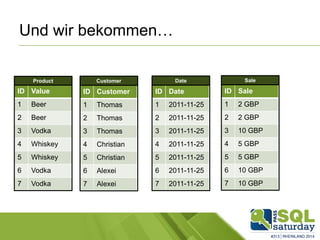
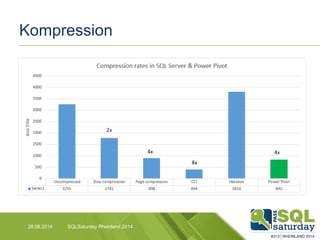
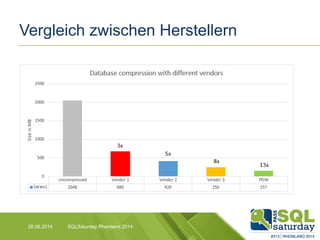
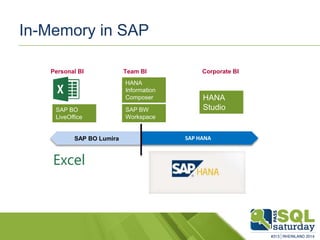
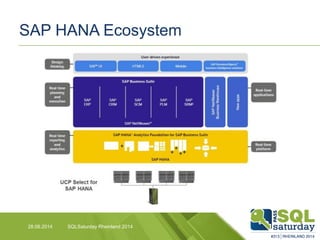
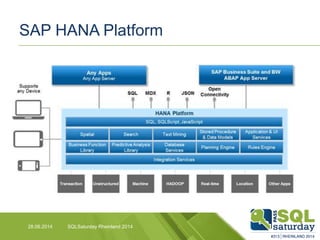
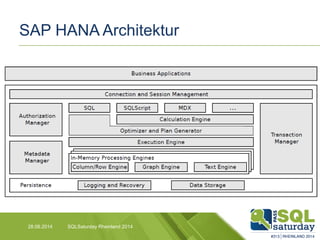
Das Dokument liefert einen Vergleich zwischen verschiedenen In-Memory-Technologien, insbesondere SAP HANA und Microsoft SQL Server, und analysiert deren Einsatzmöglichkeiten für OLAP und OLTP Workloads. Es werden die Vorteile von In-Memory-Computing hervorgehoben, wie schnellere Berechnungen und bessere Leistung bei großen Datenmengen. Abschließend wird festgestellt, dass beide Hersteller leistungsstarke Lösungen anbieten, jedoch unterschiedliche Architekturen und Funktionen besitzen.