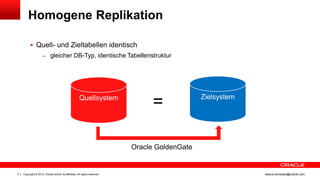
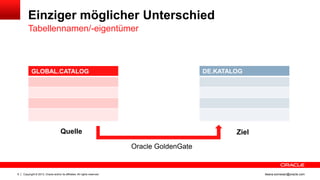
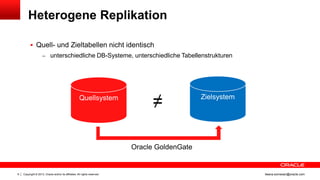
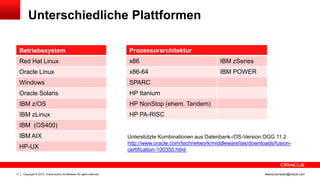
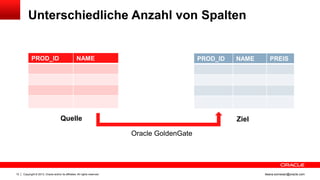
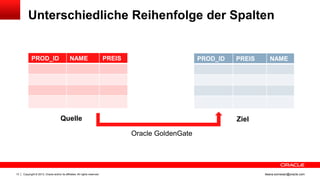
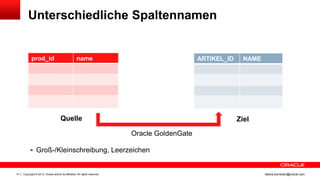
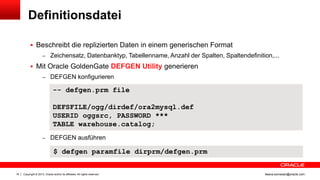
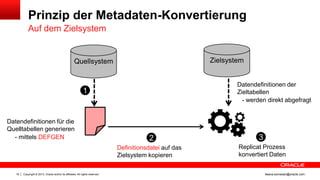
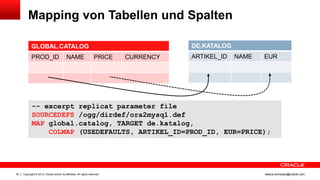
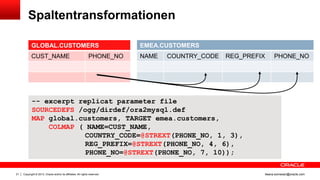
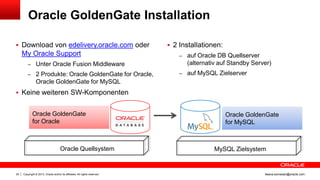
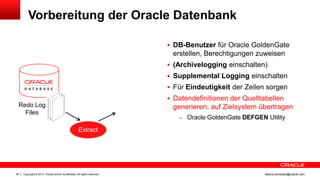
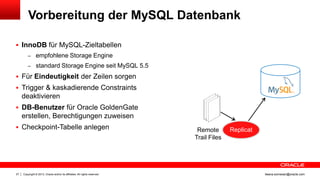
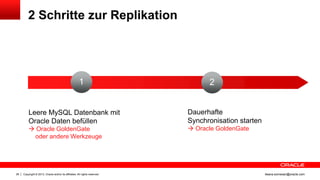
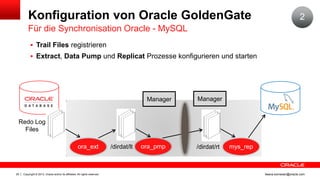
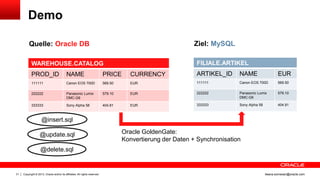
Das Dokument behandelt die Replikation im heterogenen Umfeld mithilfe von Oracle GoldenGate, insbesondere Beispiele für die Synchronisation unterschiedlicher Datenbanken und Anwendungs-Upgrades. Es erklärt die Unterschiede zwischen homogener und heterogener Replikation, einschließlich der erforderlichen Datenkonvertierungen und der Unterstützung verschiedener Datenbanksysteme. Zudem werden Anleitungen zur Installation und Konfiguration von Oracle GoldenGate sowie zur Vorbereitung der Quell- und Zieldatenbanken gegeben.