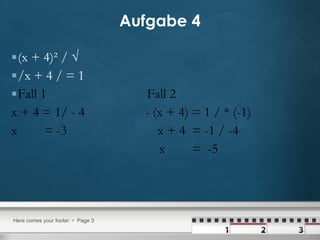
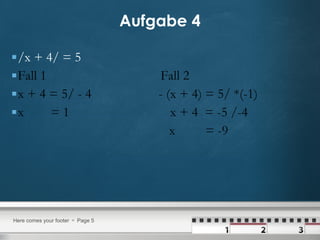
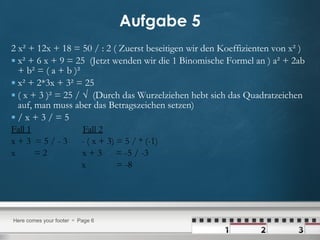
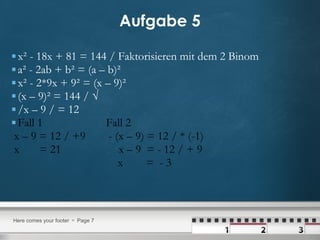
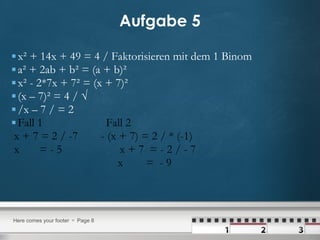
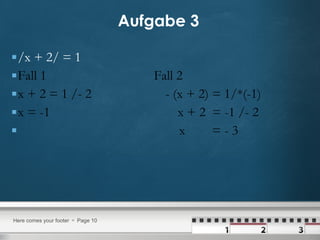
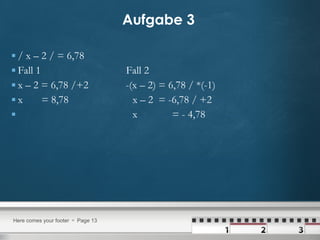
Das Dokument enthält Lösungen zu verschiedenen Aufgaben über quadratische Gleichungen, inklusive der Anwendung der quadratischen Ergänzung und der Binomformel. Es werden mehrere Aufgabenstellungen präsentiert, die jeweils Schritt für Schritt gelöst werden, um die Nullstellen der Gleichungen zu finden. Die Methoden wie die pq-Formel und das Faktorisieren werden ebenfalls mit Beispielen erklärt.