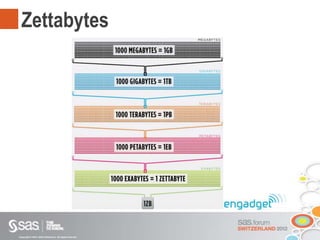
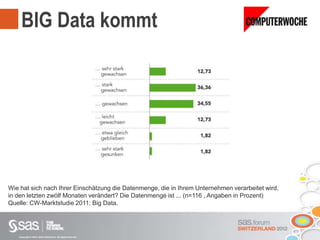
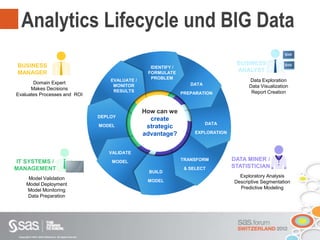
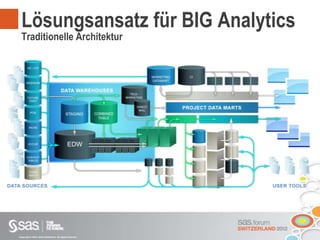
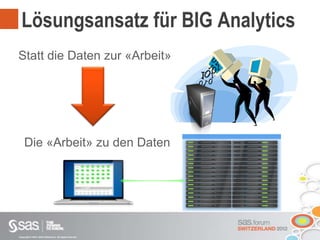
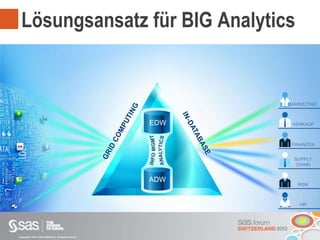
Das Dokument beschreibt Big Data als große Datenmengen, die mit herkömmlichen Datenmanagement-Tools schwer zu verarbeiten sind, und thematisiert die Herausforderungen in Bezug auf Erfassung, Speicherung und Analyse. Es wird die Relevanz von Big Data für Unternehmen hervorgehoben und auf Lösungen wie parallele Datenbanksysteme und Cloud Computing hingewiesen. Darüber hinaus wird ein strategischer Vorteil durch die effektive Nutzung von Big Data angedeutet, unterstützt durch moderne Technologien und Ansätze.