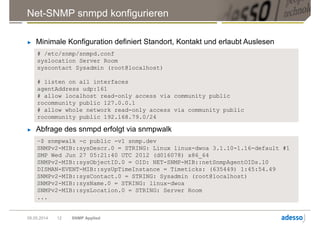
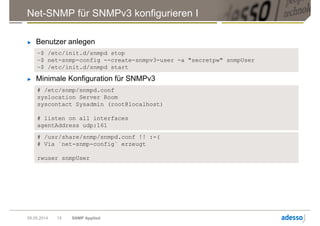
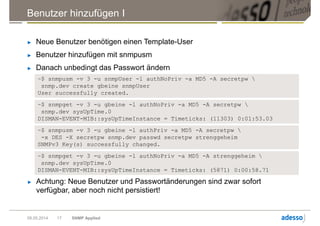
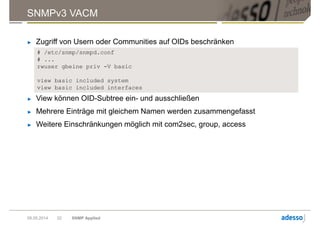
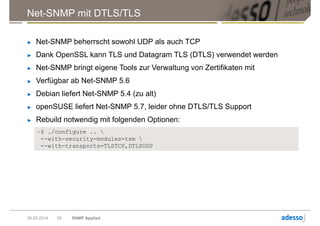
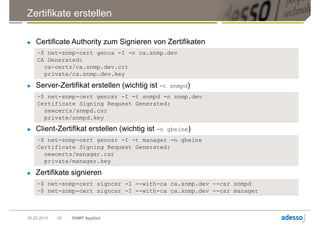
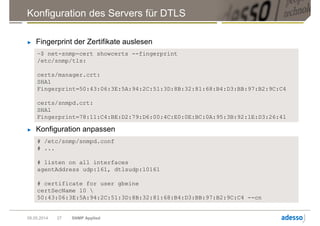
Das Dokument gibt einen Überblick über das Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) sowie dessen Versionen und Sicherheitsaspekte, insbesondere SNMPv3. Es behandelt die Konfiguration und Anwendung von net-snmp, einschließlich der Implementierung von Benutzer- und Zugriffsverwaltung, sowie die Verwendung von TLS/DTLS zur Sicherstellung einer sicheren Datenübertragung. Weiterhin wird die Bedeutung von OIDs, MIBs und den verschiedenen SNMP-Nachrichtentypen erläutert.










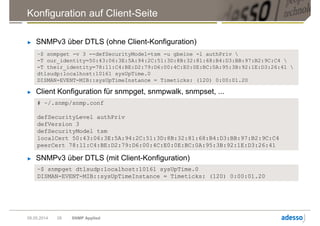
![Einfaches SNMP v1 get I
public class SimpleGet {
private static String hostName = "snmp.dev";
private static String port = "161";
// OID via snmptranslate -On -IR sysUpTime.0
private static String oid = ".1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0";
private static int snmpVersion = SnmpConstants.version1;
private static String community = "public";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Create Target Address object
CommunityTarget target = new CommunityTarget();
target.setAddress(new UdpAddress(hostName + "/" + port));
target.setVersion(snmpVersion);
target.setCommunity(new OctetString(community));
// Create the PDU object
PDU pdu = new PDU();
pdu.add(new VariableBinding(new OID(oid)));
pdu.setType(PDU.GET);
// Create TransportMapping and send SNMP get
TransportMapping<UdpAddress>transport = new DefaultUdpTransportMapping();
transport.listen();
Snmp snmp = new Snmp(transport);
ResponseEvent response = snmp.get(pdu, target);
snmp.close();
...
09.05.2014 SNMP Applied30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snmpapplied-140702023240-phpapp01/85/SNMP-Applied-Sicheres-Anwendungs-Monitoring-mit-SNMP-29-320.jpg)
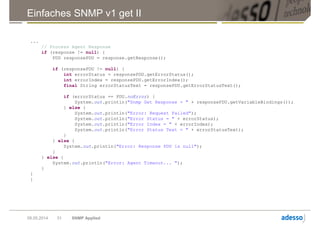
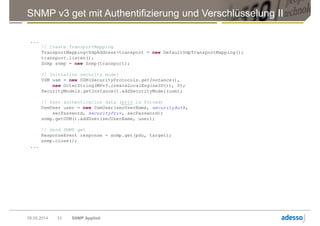
![SNMP v3 get mit Authentifizierung und Verschlüsselung I
09.05.2014 SNMP Applied32
public class V3Get {
private static String hostName = "snmp.dev";
private static String port = "161";
private static int snmpVersion = SnmpConstants.version3;
private static int securityLevel = SecurityLevel.AUTH_PRIV;
private static OID securityAuth = AuthMD5.ID;
private static OID securityPriv = PrivDES.ID;
private static String username = "gbeine";
private static String password = "strenggeheim";
// OID via snmptranslate -On -IR sysUpTime.0
private static String oid = ".1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
final OctetString secUserName = new OctetString(username);
final OctetString secPassword = new OctetString(password);
// Create Target Address object
UserTarget target = new UserTarget();
target.setAddress(new UdpAddress(hostName + "/" + port));
target.setVersion(snmpVersion);
target.setSecurityLevel(securityLevel);
target.setSecurityName(secUserName);
// Create the PDU object
ScopedPDU pdu = new ScopedPDU();
pdu.add(new VariableBinding(new OID(oid)));
pdu.setType(PDU.GET);
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snmpapplied-140702023240-phpapp01/85/SNMP-Applied-Sicheres-Anwendungs-Monitoring-mit-SNMP-31-320.jpg)