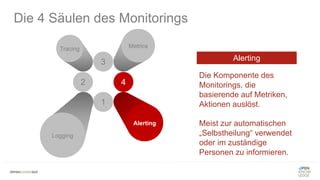
Das Dokument behandelt das Konzept von Serverless Computing, bei dem Entwickler sich auf die Implementierung von Business-Logik konzentrieren und die Cloud-Anbieter die Infrastruktur verwalten. Es werden verschiedene Anwendungsfälle und Szenarien vorgestellt, wie beispielsweise Datei-/Datenbearbeitung, Streaming-Datenverarbeitung und Webanwendungen, sowie Best Practices für das Testen und Überwachen von serverlosen Anwendungen. Zudem werden zentrale Monitoring-Strategien und Kennzahlen für eine effektive Überwachung der Anwendung vorgestellt.









































































































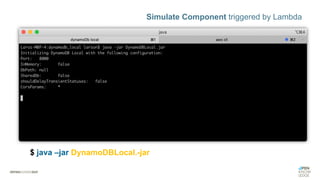
![$ sam local generate-event [SERVICE] [OPTION]
Simulate Component Event to trigger Lambda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverlessmissingmanual-200206092045/85/Serverless-The-Missing-Manual-107-320.jpg)
![$ sam local generate-event [SERVICE] [OPTION]
Simulate Component Event to trigger Lambda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverlessmissingmanual-200206092045/85/Serverless-The-Missing-Manual-108-320.jpg)