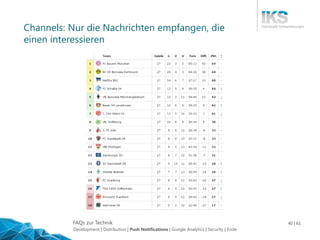
Das Dokument bietet einen umfassenden Überblick über die Entwicklung mobiler Apps, einschließlich der Unterschiede zwischen nativer und Cross-Plattform-Entwicklung. Es werden auch wichtige Aspekte wie Push-Benachrichtigungen, Google Analytics und Sicherheitsüberlegungen behandelt. Darüber hinaus werden die Vor- und Nachteile verschiedener Entwicklungsansätze sowie die Distribution von Apps im Apple App Store und Google Play Store erläutert.