Melden
Teilen
Downloaden Sie, um offline zu lesen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Andere mochten auch
Andere mochten auch (20)
More than just a pretty picture: improving the discoverability of illustrati...

More than just a pretty picture: improving the discoverability of illustrati...
How Soft Sensing Using Simulation Enhances Plant Process Management

How Soft Sensing Using Simulation Enhances Plant Process Management
Presentación "Golgi apparatus dynamics on cell division"

Presentación "Golgi apparatus dynamics on cell division"
MNPS: Mevis Neurosurgery Planning System. Overview.

MNPS: Mevis Neurosurgery Planning System. Overview.
Finite Element Simulation and Experiment of Chip Formation Process during Hig...

Finite Element Simulation and Experiment of Chip Formation Process during Hig...
One Solution for Simulation of Steam Turbine Power Upon 210MW 

One Solution for Simulation of Steam Turbine Power Upon 210MW
Ähnlich wie Osmosis
Ähnlich wie Osmosis (20)
10. Transport System in Organisms E-learning - Diffusion & Osmosis

10. Transport System in Organisms E-learning - Diffusion & Osmosis
Osmosis
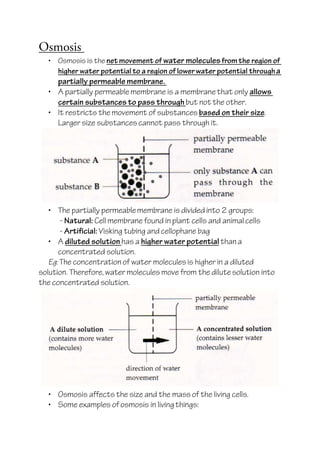
- 1. Osmosis • Osmosis is the net movement of water moleculesfrom the region of higher water potentialto a region of lower water potential througha partially permeable membrane. • A partially permeable membrane is a membrane that only allows certain substances to pass through but not the other. • It restricts the movement of substances based on their size. Larger size substancescannot pass through it. • The partially permeablemembrane is divided into 2 groups: - Natural: Cellmembrane found in plant cells and animal cells - Artificial: Visking tubing and cellophane bag • A diluted solution has a higher water potential thana concentrated solution. Eg: The concentrationof water molecules is higher in a diluted solution. Therefore, water molecules move from the dilute solution into the concentrated solution. • Osmosis affects the size and the mass of the living cells. • Some examples of osmosis in living things:
- 2. - Uptake of water molecules from the soil by the root hair cells - Absorption of water molecules in human large intestine Plant cells • The cell wall in plant cells is permeableto all substances. • When a plant cell is placed in distilledwater: 1. The concentrationof water molecules is higher in the surroundings than in the cytoplasm. 2. As a result, more water molecules enter the cell by osmosis and create a pressure on the cell wall known as turgor pressure. 3. The turgorpressure makes the plant cell become firm or turgid. • When a plant cell is placed in a concentratedsolution: 1. The concentrationof water molecules is lower in the surroundings than in the cytoplasm. 2. As a result, water molecules from the cell start to move out form the cytoplasm into the concentrated solution by osmosis. 3. The cytoplasmpeels away from the cell wall and the cell membrane becomes visible under the microscope. 4. The cell loses its turgidity. It is said to be plasmolysed.
- 3. Animal cell • Animal cells do not have cell walls. Therefore, the effect of osmosis will cause the cell to shrink or to burst. • When an animal cell is placed in distilledwater: 1. The concentrationof water molecules is higher in the surroundings than in the cytoplasm. 2. As a result,more water moleculesenter the cell by osmosis and cause the cell to swell. 3. Due to the lack of a cell wall, the animal cell will burst eventually. • When an animal cell is placed in a concentratedsolution: 1. The concentratedof water molecules is lower in the surroundings than in the cytoplasm. 2. As a result, water molecules from the cell start to move out form the cytoplasm into the concentrated solution by osmosis.
- 4. 3. The animal cell becomes soft and shrinks.