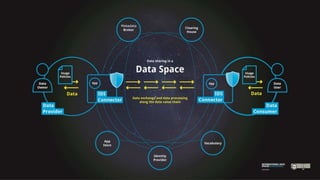
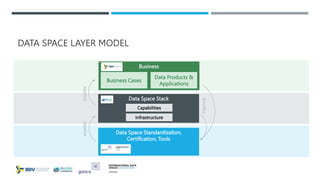
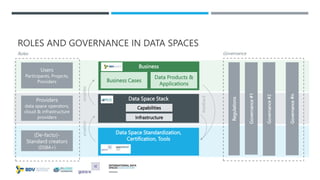
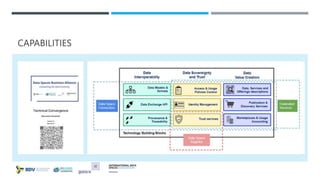
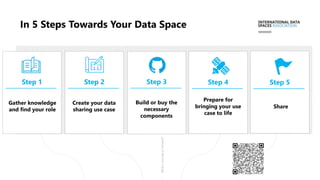
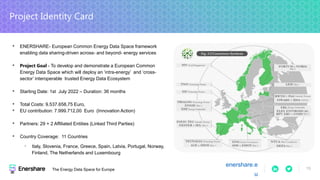
Das Dokument beschreibt die Entwicklung und Standardisierung von Datenspeichern innerhalb von dezentralen und dynamischen Datenökosystemen, um eine effektive Datenfreigabe und Nutzung zu ermöglichen. Es werden fünf Schritte skizziert, um Datenräume zu schaffen, und verschiedene Forschungsprojekte sowie Förderungen werden vorgestellt, darunter das MERLOT-Projekt zur nachhaltigen Gestaltung des Bildungsdatenraums. Zudem wird auf die Bedeutung von Datenhoheit, Interoperabilität und innovative datengestützte Dienste eingegangen.