Behaviour of randomly distributed fiber reinforced soil
•
1 gefällt mir•162 views
This document summarizes a study on the engineering behavior of fiber-reinforced soil. Specifically, it investigates how adding polypropylene fibers to locally available soil affects the soil's California Bearing Ratio (CBR), shear strength parameters from direct shear tests, and unconfined compressive strength. The tests found that including fibers up to an optimum content of 0.4-0.6% increased the CBR, shear strength, and unconfined compressive strength of the soil. The maximum increases were 1.45 times higher CBR, 2.5 times higher unconfined compressive strength, and higher shear strength parameters compared to unreinforced soil. In conclusion, adding a small amount of fibers can
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Downloaden Sie, um offline zu lesen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (17)
A Study on Concrete Using Bottom Ash, Manufacturing Sand and Hybrid Steel and...

A Study on Concrete Using Bottom Ash, Manufacturing Sand and Hybrid Steel and...
LABORATORY MODEL TESTS TO EFFECT OF DENSITY TO FILL MATERIAL ON THE PERFORMAN...

LABORATORY MODEL TESTS TO EFFECT OF DENSITY TO FILL MATERIAL ON THE PERFORMAN...
A Research Paper on the Performance of Synthetic Fibre Reinforced Concrete

A Research Paper on the Performance of Synthetic Fibre Reinforced Concrete
Mechanical Behavior of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials Reinforced With Cer...

Mechanical Behavior of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials Reinforced With Cer...
A Study on Effect of Sizes of aggregates on Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete

A Study on Effect of Sizes of aggregates on Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete
Comprehensive study of high strength fiber rienforced concrete under pull out...

Comprehensive study of high strength fiber rienforced concrete under pull out...
Taguchi Analysis of Erosion Wear Maize Husk Based Polymer Composite

Taguchi Analysis of Erosion Wear Maize Husk Based Polymer Composite
Study on properties of sisal fiber reinforced concrete with different mix pro...

Study on properties of sisal fiber reinforced concrete with different mix pro...
IRJET-Experimental behavior of Concrete under Compression Load with Steel Fib...

IRJET-Experimental behavior of Concrete under Compression Load with Steel Fib...
IRJET- Mechanical Characterization of Cissus Quadrangularis Stem/Glass Fiber ...

IRJET- Mechanical Characterization of Cissus Quadrangularis Stem/Glass Fiber ...
IRJET- Utilization & Effects of Crown Caps on Strength Properties of Conc...

IRJET- Utilization & Effects of Crown Caps on Strength Properties of Conc...
A Study on Effect of Carbon and Ash Fillers on Flexural Properties in GFRP Co...

A Study on Effect of Carbon and Ash Fillers on Flexural Properties in GFRP Co...
BEHAVIOR OF HIGH STRENGTH FIBER REINFORCED CONCRETE UNDER SHEAR 

BEHAVIOR OF HIGH STRENGTH FIBER REINFORCED CONCRETE UNDER SHEAR
Modal analysis of hybrid sisaljute natural fiber polymer composite beam

Modal analysis of hybrid sisaljute natural fiber polymer composite beam
Ähnlich wie Behaviour of randomly distributed fiber reinforced soil
Ähnlich wie Behaviour of randomly distributed fiber reinforced soil (20)
IRJET - Study on the Engineering Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Low Plast...

IRJET - Study on the Engineering Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Low Plast...
Polypropylene fiber reinforced cohesive soil - constro facilitator

Polypropylene fiber reinforced cohesive soil - constro facilitator
Soil Stabilization using Plain and Treated Coir Fibres

Soil Stabilization using Plain and Treated Coir Fibres
An Experimental Study of Soil Stabilization with Cement and Polymer

An Experimental Study of Soil Stabilization with Cement and Polymer
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development

International Journal of Engineering Research and Development
Efficacy of overlying coarse aggregate and geosynthetic separator on cbr valu...

Efficacy of overlying coarse aggregate and geosynthetic separator on cbr valu...
IRJET- Experimental Study on Improvement of Soil Subgrade Reinforced with Ban...

IRJET- Experimental Study on Improvement of Soil Subgrade Reinforced with Ban...
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON EFFECT OF REINFORCEMENT IN POLYMER AND FIBER FORMS O...

AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON EFFECT OF REINFORCEMENT IN POLYMER AND FIBER FORMS O...
Stabilization of pavement subgrade by using fly ash reinforced with geotextile

Stabilization of pavement subgrade by using fly ash reinforced with geotextile
Mehr von eSAT Journals
Mehr von eSAT Journals (20)
Mechanical properties of hybrid fiber reinforced concrete for pavements

Mechanical properties of hybrid fiber reinforced concrete for pavements
Material management in construction – a case study

Material management in construction – a case study
Managing drought short term strategies in semi arid regions a case study

Managing drought short term strategies in semi arid regions a case study
Life cycle cost analysis of overlay for an urban road in bangalore

Life cycle cost analysis of overlay for an urban road in bangalore
Laboratory studies of dense bituminous mixes ii with reclaimed asphalt materials

Laboratory studies of dense bituminous mixes ii with reclaimed asphalt materials
Laboratory investigation of expansive soil stabilized with natural inorganic ...

Laboratory investigation of expansive soil stabilized with natural inorganic ...
Influence of reinforcement on the behavior of hollow concrete block masonry p...

Influence of reinforcement on the behavior of hollow concrete block masonry p...
Influence of compaction energy on soil stabilized with chemical stabilizer

Influence of compaction energy on soil stabilized with chemical stabilizer
Geographical information system (gis) for water resources management

Geographical information system (gis) for water resources management
Forest type mapping of bidar forest division, karnataka using geoinformatics ...

Forest type mapping of bidar forest division, karnataka using geoinformatics ...
Factors influencing compressive strength of geopolymer concrete

Factors influencing compressive strength of geopolymer concrete
Experimental investigation on circular hollow steel columns in filled with li...

Experimental investigation on circular hollow steel columns in filled with li...
Experimental behavior of circular hsscfrc filled steel tubular columns under ...

Experimental behavior of circular hsscfrc filled steel tubular columns under ...
Evaluation of performance of intake tower dam for recent earthquake in india

Evaluation of performance of intake tower dam for recent earthquake in india
Evaluation of operational efficiency of urban road network using travel time ...

Evaluation of operational efficiency of urban road network using travel time ...
Estimation of surface runoff in nallur amanikere watershed using scs cn method

Estimation of surface runoff in nallur amanikere watershed using scs cn method
Estimation of morphometric parameters and runoff using rs & gis techniques

Estimation of morphometric parameters and runoff using rs & gis techniques
Effect of variation of plastic hinge length on the results of non linear anal...

Effect of variation of plastic hinge length on the results of non linear anal...
Effect of use of recycled materials on indirect tensile strength of asphalt c...

Effect of use of recycled materials on indirect tensile strength of asphalt c...
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Our CPM guide includes everything you need to get started in the Critical Path Method - with step-by-step examples, solutions, as well as schedules to help get your next project done faster and easier. The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a simple but powerful technique for analyzing, planning, and scheduling large, complex projects. It is used to determine a project’s critical path—the longest sequence of tasks that must be finished for the entire project to be complete.
CPM, also known as Critical Path Analysis (CPA), identifies dependencies between tasks, and shows which tasks are critical to a project. The Critical Path Method (CPM) is one of the most important concepts in project management, and certainly among the most enduring. But what is the Critical Path Method, exactly? This beginner-friendly guide will help you understand the Critical Path Method and apply it in your projects.
Early iterations of the Critical Path Method can be traced all the way back to the Manhattan Project in the early 1940s. Given the ambition, scale, and importance of this world-altering project, scientists - and the managers behind them - developed a number of techniques to make sure that the project delivered results on time. For a project management technique, the Critical Path Method has quite an illustrious history. One of these techniques was to map out the most important tasks in any project and use that to estimate the project completion date.
The Critical Path Method in project management is a cornerstone of project planning even to this day. How long a project takes often depends on the most important tasks that constitute it.Activity Planning: Objectives, Project Schedule, Network Planning Model. Time...

Activity Planning: Objectives, Project Schedule, Network Planning Model. Time...Lovely Professional University
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Research Methodolgy & Intellectual Property Rights Series 1

Research Methodolgy & Intellectual Property Rights Series 1
NO1 Pandit Black Magic Removal in Uk kala jadu Specialist kala jadu for Love ...

NO1 Pandit Black Magic Removal in Uk kala jadu Specialist kala jadu for Love ...
Teachers record management system project report..pdf

Teachers record management system project report..pdf
Online resume builder management system project report.pdf

Online resume builder management system project report.pdf
KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-5.pdf Frame Works and Visualization

KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-5.pdf Frame Works and Visualization
Low rpm Generator for efficient energy harnessing from a two stage wind turbine

Low rpm Generator for efficient energy harnessing from a two stage wind turbine
RESORT MANAGEMENT AND RESERVATION SYSTEM PROJECT REPORT.pdf

RESORT MANAGEMENT AND RESERVATION SYSTEM PROJECT REPORT.pdf
Activity Planning: Objectives, Project Schedule, Network Planning Model. Time...

Activity Planning: Objectives, Project Schedule, Network Planning Model. Time...
Construction method of steel structure space frame .pptx

Construction method of steel structure space frame .pptx
Behaviour of randomly distributed fiber reinforced soil
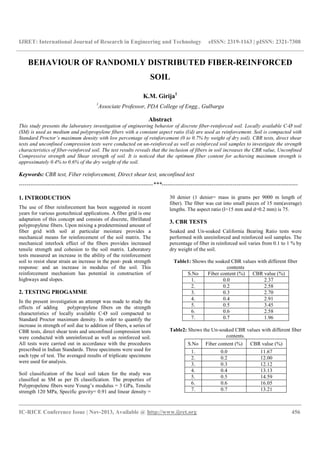
- 1. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308 __________________________________________________________________________________________ IC-RICE Conference Issue | Nov-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 456 BEHAVIOUR OF RANDOMLY DISTRIBUTED FIBER-REINFORCED SOIL K.M. Girija1 1 Associate Professor, PDA College of Engg., Gulbarga Abstract This study presents the laboratory investigation of engineering behavior of discrete fiber-reinforced soil. Locally available C-Ø soil (SM) is used as medium and polypropylene fibers with a constant aspect ratio (l/d) are used as reinforcement. Soil is compacted with Standard Proctor’s maximum density with low percentage of reinforcement (0 to 0.7% by weight of dry soil). CBR tests, direct shear tests and unconfined compression tests were conducted on un-reinforced as well as reinforced soil samples to investigate the strength characteristics of fiber-reinforced soil. The test results reveals that the inclusion of fibers in soil increases the CBR value, Unconfined Compressive strength and Shear strength of soil. It is noticed that the optimum fiber content for achieving maximum strength is approximately 0.4% to 0.6% of the dry weight of the soil. Keywords: CBR test, Fiber reinforcement, Direct shear test, unconfined test ----------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. INTRODUCTION The use of fiber reinforcement has been suggested in recent years for various geotechnical applications. A fiber grid is one adaptation of this concept and consists of discrete, fibrillated polypropylene fibers. Upon mixing a predetermined amount of fiber grid with soil at particular moisture provides a mechanical means for reinforcement of the soil matrix. The mechanical interlock effect of the fibers provides increased tensile strength and cohesion to the soil matrix. Laboratory tests measured an increase in the ability of the reinforcement soil to resist shear strain an increase in the post- peak strength response: and an increase in modulus of the soil. This reinforcement mechanism has potential in construction of highways and slopes. 2. TESTING PROGAMME In the present investigation an attempt was made to study the effects of adding polypropylene fibers on the strength characteristics of locally available C-Ø soil compacted to Standard Proctor maximum density. In order to quantify the increase in strength of soil due to addition of fibers, a series of CBR tests, direct shear tests and unconfined compression tests were conducted with unreinforced as well as reinforced soil. All tests were carried out in accordance with the procedures prescribed in Indian Standards. Three specimens were used for each type of test. The averaged results of triplicate specimens were used for analysis. Soil classification of the local soil taken for the study was classified as SM as per IS classification. The properties of Polypropelene fibers were Young’s modulus = 3 GPa, Tensile strength 120 MPa, Specific gravity= 0.91 and linear density = 30 denier (1 denier= mass in grams per 9000 m length of fiber). The fiber was cut into small pieces of 15 mm(average) lengths. The aspect ratio (l=15 mm and d=0.2 mm) is 75. 3. CBR TESTS Soaked and Un-soaked California Bearing Ratio tests were performed with unreinforced and reinforced soil samples. The percentage of fiber in reinforced soil varies from 0.1 to 1 % by dry weight of the soil. Table1: Shows the soaked CBR values with different fiber contents S.No Fiber content (%) CBR value (%) 1. 0.0 2.37 2. 0.2 2.58 3. 0.3 2.70 4. 0.4 2.91 5. 0.5 3.45 6. 0.6 2.58 7. 0.7 1.96 Table2: Shows the Un-soaked CBR values with different fiber contents. S.No Fiber content (%) CBR value (%) 1. 0.0 11.67 2. 0.2 12.00 3. 0.3 12.12 4. 0.4 13.13 5. 0.5 14.59 6. 0.6 16.05 7. 0.7 13.21
- 2. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308 __________________________________________________________________________________________ IC-RICE Conference Issue | Nov-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 457 The optimum fiber content in soaked and un-soaked samples is observed to be 0.5% and 0.6% respectively. At optimum fiber content the maximum increase in CBR value are 1.45 times and 1.37 times compared to the unreinforced soil for soaked and un-soaked conditions respectively. 4. DIRECT SHEAR TEST In direct shear tests, both unreinforced and reinforced specimens were tested at the shearing rate of 1.25mm per minute in direct shear box. The fiber content in reinforced specimens varied from 0.1% to 0.7% by dry weight of the soil. Table 3: Shows the variation of shear parameters for different percentage of fiber content. S No Percentage of Fiber Value of cohesion Intercept= C kg/cm2 Angle of Internal Friction = Ø0 1. 0 0.45 32.5 2. 0.2 1.57 37.6 3. 0.3 1.76 46.8 4. 0.4 2.16 50.8 5. 0.5 1.72 52.4 6. 0.6 1.42 51.4 7. 0.7 1.21 50.1 Figure 1: Normal stress and shear stress relationship. Observation of the Table 3 and Figure1 indicates that with increase in normal stress, strength of reinforced soil increases. Also, these strengths increase with increase in fiber content up to 0.4% beyond which they decrease. The optimum fiber content is found to be 0.4%. 5. UNCONFINED COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF SOIL Unconfined compressive tests were performed on unreinforced and reinforced specimens for fiber content varying from 0 to 0.7%. Strain Figure 2: Stress and strain relationship. Table 4: Shows the unconfined compressive strength of soil for different fiber contents S.No Fiber content (%) Unconfined compressive Strength (kg/cm2 ) .1. 0.0 0.75 2. 0.2 1.35 3. 0.3 1.42 4. 0.4 1.53 5. 0.5 1.67 6. 0.6 1.90 7. 0.7 1.55 8. 0.8 1.09 The results show that the reinforcement increases the strength. The maximum increase in stress, approximately 2.5 times higher than that for unreinforced soil, occurred for fiber content of 0.6 %. Also it can be seen from figure 2, that both failure stress and strain increase with increase in fiber content up to 0.6% beyond which both decrease. Thus, the optimum fiber content is to be 0.6%.
- 3. IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308 __________________________________________________________________________________________ IC-RICE Conference Issue | Nov-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 458 CONCLUSIONS On the basis of experimental investigations the following conclusions are drawn 1. The optimum fiber content for achieving maximum CBR values of reinforced soil in un-soaked and soaked condition are 0.6% and 0.5% respectively. 2. The shear strength of soil increases with inclusion of fiber up to 0.4%, beyond which it decreases. 3. Both cohesion and angle of friction increases with increase in fiber content up to 0.4%, beyond which it remains almost constant. 4. The shear strength of fiber-reinforced soil occurs at higher strain compared to un- reinforced soil. 5. The rate of increase of peak shear strength increases with increases in fiber content commensurate with increase in normal stress. 6. The maximum increase in unconfined compressive strength is found to be 2.5 times higher than that for unreinforced soil at the optimum fiber content of 0.6%. The corresponding failure strain is higher than that for un-reinforced soil. REFERENCES [1] Al WAhab ,R M and Al-Qurna, H.H,1995, “Fiber Reinforced Cohesive Soils for Application in Compacted Eart Structures”, Proceedings of Geosynthetics 95, IFAI,Vol. 2, Nashville, Tennesse, USA, February 1995, pp. 433-446 [2] ASTM D 698, Standard test methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil using Standard effort (600kN/m/m3) , West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, USA. [3] Fletcher, C.S and Humphries, W.K, 1991, “California Bearing Ratio improvement of Remoulded soils by the addition of Polypropylene Fiber Reinforcement”, Proceedings of Seventieth Annual Meeting, Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 80-86. [4] Fretaig, D.R, 1986, “Soil Randomly Reinforced with Fibers”, Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, vol.112, No. 8, pp. 823-826. [5] H. Jiang, Y.Cai and Liu, “Engineering Properties of soils reinforced by short discrete polypropylene fiber”, Journal of Materials in civil Engineering, Vol. 22, 2010, pp. 1315-1322.
