IB Chemistry on Atomic Structure, Particle Physics and Relative Atomic Mass
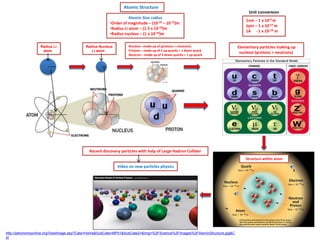
- 1. Atomic Structure Unit conversion Atomic Size radius •Order of magnitude – (10-10 – 10-12)m •Radius Li atom – (1.5 x 10-10)m •Radius nucleus – (1 x 10-14)m Radius Li atom Radius Nucleus Li atom Nucleon –made up of (protons + neutrons) Protons – made up of 2 up quarks + 1 down quark Neutron – made up of 2 down quarks + 1 up quark 1nm – 1 x 10-9 m 1pm – 1 x 10-12 m 1A - 1 x 10-10 m Elementary particles making up nucleon (protons + neutrons) Recent discovery particles with help of Large Hadron Collider Structure within atom Video on new particles physics http://astronomyonline.org/ViewImage.asp?Cate=Home&SubCate=MP01&SubCate2=&Img=%2FScience%2FImages%2FAtomicStructure.jpg&C pt
- 2. Discovery timeline Democritus to Quantum model Discovery of elementary particles Elementary particles Video on timeline discovery Structure within atom Recent discovery particles from Large Hadron Collider Discovery of Higgs boson and Higgs field Particles interact with Higgs field to produce mass Higgs boson leftover excitation of particles of Higgs field Video on new particles physics Higgs Boson Discovery Wins Nobel Prize for Physics Video on Higgs field part 1 Video on Higgs field part 2 Video on NOBEL PRIZE 2013 !!!!!!
- 3. Atomic Structure Unit conversion Atomic Size radius •Order of magnitude – (10-10 – 10-12)m •Radius Li atom – (1.5 x 10-10)m •Radius nucleus – (1 x 10-14)m Radius Li atom Radius Nucleus Li atom Nucleon –made up of (protons + neutrons) Protons – made up of 2 up quarks + 1 down quark Neutron – made up of 2 down quarks + 1 up quark 1nm – 1 x 10-9 m 1pm – 1 x 10-12 m 1A - 1 x 10-10 m Elementary particles making up nucleon (protons + neutrons) Scale/size of matter from smallest to largest Excellent Flash on scale of universe Excellent Flash on biological cells Video on scale of universe
- 4. Elementary particles Structure within atom Recent discovery particles from Large Hadron Collider Particles interact with Higgs field to produce mass Discovery of Higgs boson and Higgs field Mass (proton + neutron)- due to interaction between up quarks/down quarks with gluons (energy fluatutions) Proton -2 up quarks 1 down quark Video on Higgs field What is Higgs Boson ? What is Higgs Field ? Higgs boson leftover excitation of particles of Higgs field Neutron -1 up quark 2 down quarks Video (Veratasium) Excellent videos –Particles interact with Higgs field to create MASS Video (RI) Video (Ted Talk) Video (Minute physics)
- 5. Nuclear reaction vs Chemical reaction Chemical reaction Nuclear reaction • • • • • • • • Involve protons/neutrons in nucleus Decomposition of nucleus into smaller nuclei Energy released greater Conservation of charge / atomic mass number Involve outer most electrons Transfer/sharing/loss of electrons Energy released less Conservation of mass and charge Chemical equation – valence electrons Nuclear equation- decay of nucleus 2Na + CI2 2NaCI Transfer electrons Sharing electrons Type of radiation Type radiation Nature radiation Symbol Penetration (mass,m/charge,e ) Ionising power (removing electron) Alpha Helium nucleus α Low ratio (high m/e) High Beta High energy electron β Moderate Moderate Gamma High frequency electromagnetic radiation γ High ratio (small m/e) Low http://ths.talawanda.net/~BrambleN/classroom/Chemistry/Notes/Section%206A%20and%206B/RadioactiveDecay.htm http://www.classhelp.info/Biology/AUnit3Biochemistry.htm
- 6. Nuclear reaction Alpha Decay Unstable nucleus of atom Decay by emitting ionizing particles α β Alpha Decay •Losing an alpha particle – helium nucleus •Daughter nuclei lower in proton number •Mass of 4 (2 proton + 2 neutron) •+2 charged (only 2 protons) = +2 •Decay of uranium, thorium, actinium Beta Decay Beta Decay •Losing beta particle –Electron/positron •Daughter nuclei higher in proton number •Negative charge (-1) •Decay neutron proton + electron Gamma Decay Gamma decay •Losing a γ particle - electromagnetic radiation of high frequency •Daughter nuclei no change in atomic mass http://ths.talawanda.net/~BrambleN/classroom/Chemistry/Notes/Section%206A%20and%206B/RadioactiveDecay.htm http://molaire1.perso.sfr.fr/e_radioactiv.html +
- 7. Difference Between Alpha, Beta and Gamma Radiation Nucleus > 84 protons • Unstable, radioactive decay • Decay depends on ratio neutron/proton Mass number always Conserved/Same Alpha Decay •Lose alpha particle – helium nucleus •Mass He- 4 (2 proton + 2 neutron) •+2 charged (2 proton + 2 neutron + 0 e) •Daughter nuclei lower in proton number Decay depend on ratio neutron/proton Neutron/proton ratio LOW – Proton rich – Decay to reduce proton - Alpha decay, α (proton number ) Video on α decay Beta Decay •Lose beta particle –Electron/beta β •Negative charge (-1) •-1 charged (β or electron) •Daughter nuclei higher in proton number Decay depend on ratio neutron/proton Neutron/proton ratio HIGH – Neutron rich – Decay to reduce neutron -Beta decay β ( Neutron Proton + electron) -Ratio decrease Video on β decay Gamma decay •Lose a γ particle – electromagnetic radiation of high frequency •Daughter nuclei no change in atomic mass Decay depend on ratio neutron/proton Neutron/proton ratio HIGH /LOW -Gamma decay γ, is associated along with Alpha and Beta Video on γ decay
- 8. Isotopes Unstable Isotopes Stable Isotopes Simulation isotope 1H, 2H, 3H Simulation isotope 12C, 13C, 14C Emit radiation form unstable isotope Simulation half life C-14/uranuim Unstable Isotopes – emits radiation RADIOISOTOPES Half-life Radioisotopes •Half-life – time taken for conc/amt isotope to fall to half of its original value. •Half life decay – always constant Radioactive isotopes Uranium 238 4.5 x 109 Carbon-14 5.7 x 103 Radium-226 1.6 x 103 Strontium-90 28 years Iodine-131 8.1 days Bismuth-214 19.7 minutes Polonium-214 www.sciencelearn.org.nz Half-life 1.5 x 10-4 Long half-life More stable, decay slowly Video on Half life Shorter half-life More unstable, decay fast
- 9. Carbon – 3 Isotopes Carbon -12 Carbon -13 Abundance – 99% (Stable) Radiocarbon/carbon dating Carbon -14 Abundance – 1% (Stable) Abundance – trace amt (Unstable , radioactive) How it is form? • Half life C-14 = 5730 years • Beta (β/electron ) decay How is form? • C-14 produce in stratosphere when….. neutron hit a nitrogen atom to form C-14 •C-14 to N-14 by converting neutron proton (proton stay in nucleus), electron emit as β radiation • emit as β ray. (proton in nucleus – increase proton number) emit as β ray. •Ratio C14/C12- constant if alive – TAKE in C14 (C12 constant) •Ratio C14/C12- drop if dead - NOT taking C14. (C12 constant) Uses • Age dead organic material/fossil contain Carbon element • Max age limit is 60,000 years old. Conclusion Ratio C14/C12 is constant is organism alive Ratio C14/C12 drop organism die
- 10. How Radiocarbon dating works? Radiocarbon/carbon dating Carbon -14 Abundance – trace amt (Unstable , radioactive) • Half life C-14 = 5730 years • Beta (β/electron ) decay Simulation C-14 (Half life) At 100% (Starting) Simulation C-14 (Half life) At 50% (Starting) How is form? • C-14 produce in stratosphere when….. neutron hit a nitrogen atom to form C-14 •C-14 to N-14 by converting neutron proton (proton stay in nucleus), electron emit as β radiation • emit as β ray. (proton in nucleus – increase proton number) emit as β ray. Click to view simulation •Ratio C14/C12- constant if alive – TAKE in C14 (C12 constant) •Ratio C14/C12- drop if dead - NOT taking C14. (C12 constant) Video on Radiocarbon dating Video on C-14 Carbon Dating Video on C-14 Carbon Dating/Fossil Video on C-14 Half life Carbon Dating
- 11. Uses of radioactive isotopes Radiocarbon/carbon dating Carbon -14 Beta (β/electron) decay Carbon dating Age of fossil remains • Half life C-14 = 5730 years How Radiocarbon dating works? Radiotherapy/cancer/tumour Tracers/studying metabolic pathways Cobalt-60 Iodine-131 Gamma γ + β decay Gamma γ + β decay Sterilization – killing bacteria/germ Radiotherapy – kill tumor cells High energy electromagnetic ray • • • Radio tracer Trace the pathway in body Beta β (90%) and γ (10%) decay • Half life Co-60 = 5.27 years • Half life I-131 = 8 days How Gamma rays works? How Radio tracer works? Video on Radiocarbon dating Video on C-14 Carbon Dating Video on Radiotherapy Video on Radio tracer
- 12. Atomic /Mass number No isotopes are present Proton number = proton Mass number = proton + neutron Z A 6 protons 6 protons + 6 neutrons 8 protons 8 protons + 8 neutrons Atomic Weight With isotopes present Proton number = proton Z Mean relative mass (atomic weight) A Video on weighted average
- 13. Relative Atomic Mass No isotopes are present Relative Atomic Mass is used : • Impossible to weigh an atom in grams • Compare how heavy one atom is to carbon (standard) • One sulphur atom 32x heavier than 1/12 carbon -12 • Carbon -12 used as standard Proton number = proton Z A Mass number = proton + neutron Mass number ≠ Average atomic mass (atomic mass unit) Relative Atomic Mass, (Ar) of an element: • Number of times one atom of the element is heavier than one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 • Relative atomic mass = Mass of one atom of element 1/12 x mass of one carbon-12 • Relative atomic mass for sulphur = 32 (one sulphur atom is 32 x heavier than 1/12 of mass of one (C12) 6 Carbon-12 as standard 1/12 of C12 = 1 unit 6 protons + 6 neutrons 1/12 x 1 unit = 12 16 16 protons + 16 neutrons 32 unit 32 Sulphur – 32x heavier Assuming No isotopes present! http://www.tutorvista.com/content/science/science-i/atoms-molecules/atom.php
- 14. Relative Molecular Mass No isotopes are present Relative Molecular Mass is used : • Impossible to weigh an molecules in grams • Compare one molecule to carbon (standard) • One H2O is 18 x heavier than 1/12 carbon -12 • Carbon -12 is used as standard Mass number ≠ Average atomic weight (atomic mass unit) Proton number = proton Z A Mass number = proton + neutron Relative Molecular Mass, (Mr): • Number of times one molecule is heavier than one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 • Relative molecular mass = Mass of one molecule 1/12 x mass of one carbon-12 • Relative molecular mass for H2O= 18 (one H2O is 18 x heavier than 1/12 of mass of one (C12) Carbon-12 as standard 1/12 of C12 = 1 unit 6 protons + 6 neutrons 1/12 x 1 unit = 8 protons + 8 neutrons 16 unit 2 protons + 2 unit 18 unit H2O – 18x heavier Assuming No isotopes present! http://www.tutorvista.com/content/science/science-i/atoms-molecules/atom.php
- 15. Relative Isotopic Mass Proton number = proton Mass number = proton + neutron Presence of isotopes Z A Z = 29 protons A Z A= 29 protons + 35 neutrons = 64 Isotopes – Atoms of same element with • Different number of neutrons • Same number of protons and electrons Due to presence of isotopes, when calculating RAM, weighted average/mean of all isotopes present is used . Isotopes X - No isotopes Y - TWO isotopes 3 CI - TWO isotopes 11 Relative Abundance RAM/Ar X = 11 • Mass of 1 atom X Mass of 1/12 of 12C • Mass of 1 atom X relative to 1/12 mass of 1 atom 12C 17 17 35 37 Relative Abundance 75% 25% RAM /Ar, CI = 35.5 • Weighted average mass of 2 isotopes present = (mass 35CI x % Abundance) + (mass 37CI x % Abundance) = (35 x 75/100) + (37 x 25/100) = 35.5 3 10 3 11 50% 50% RAM/Ar Y = 10.5 • Average Mass of 1 atom Y Mass of 1/12 of 12C • Average mass of 1 atom Y relative to 1/12 mass of 1 atom 12C
- 16. Relative Atomic Mass Isotopes are present Why RAM is not a whole number? 12 Relative Abundance 98.9% 13 1.07% RAM = 12.01 Weighted average mass- due to presence of isotopes Relative Isotopic Mass, (Ar) of an element: •Relative isotopic mass = Average mass of one atom of element 1/12 x mass of one carbon-12 • Relative isotopic mass, carbon = 12.01 RAM, C : = (Mass 12C x % Abundance) + (Mass 13C x % Abundance) = (12 x 98.9/100) + (13 x 1.07/100) = 12.01 Video on Isotopes Video on weighted average Video on Isotopes http://www.tutorvista.com/content/science/science-i/atoms-molecules/atom.php RAM calculation Weighted average calculation
- 17. Relative Atomic Mass Mg - 3 Isotopes Relative Abundance % Abundance Convert relative abundance to % abundance 24 Mg – (100/127.2) x 100% - 78.6% Mg – (12.8/127.2) x 100% - 10.0% 26 Mg – (14.4/127.2) x 100% - 11.3% 25 RAM for Mg : = (Mass 24Mg x % Abundance) + (Mass 25Mg x % Abundance) + (Mass 26Mg x % Abundance) = (24 x 78.6/100) + (25 x 10.0/100) + (26 x 11.3/100) = 24.30 Pb - 4 Isotopes Relative Abundance % Abundance Convert relative abundance to % abundance 204Pb – (0.2/10) x 100% - 2% – (2.4/10) x 100% - 24% 207Pb – (2.2/10) x 100% - 22% 208Pb – (5.2/10) x 100% - 52% 206Pb RAM for Pb : = (Mass 204Pb x % Abundance) + (Mass 206Pb x % Abundance) + (Mass 207Pb x % Abundance) + (Mass 208Pb x % Abundance) = (204 x 2/100) + (206 x 24/100) + (207 x 22/100) + (208 x 52/100) = 207.20
- 18. Additional Resources Periodic Table from webelement Video on isotopes using mass spec Simulation C-14 dating (Half life) Excellent Video Higgs Field (Ted Talk) Video on Particle Physics (Higgs Field) Simulation U-238 dating (Half life) Excellent Video on scale of universe Video on new particles physics Simulation on atomic model Simulation isotope 1H, 2H, 3H and 12C, 13C, 14C
