the Life Cycle of the Stars powerpoint presentation
Blue Brown Watercolour Style Water Cycle Presentation Title Slide: Title: "The Water Cycle: A Blue Brown Watercolour Journey" Subtitle: "Exploring the Earth's Natural Water Process" Background: Watercolor-style illustration blending blue and brown hues, depicting a stylized representation of the water cycle. Slide 1: Introduction Welcome message: "Welcome to our presentation on the water cycle!" Brief overview: "Today, we'll be diving into the fascinating world of the water cycle, exploring how water moves through the environment in a continuous process." Slide 2: What is the Water Cycle? Definition: "The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth." Visual: Diagram of the water cycle, with labels for evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection. Slide 3: Key Processes of the Water Cycle Evaporation: Explanation of how water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and rivers, driven by solar energy. Condensation: Description of how water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into clouds. Precipitation: Explanation of how condensed water droplets fall to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Collection: Overview of how water collects in bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, before repeating the cycle. Slide 4: Importance of the Water Cycle Environmental balance: Discussion on how the water cycle maintains ecological balance by distributing water across different ecosystems. Human impact: Explanation of how human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, can disrupt the water cycle and lead to water scarcity. Slide 5: Water Cycle in Action Real-world examples: Showcase of how the water cycle impacts different regions, such as arid deserts and tropical rainforests. Case study: Detailed analysis of a specific location or event where the water cycle plays a crucial role, such as a drought or flood. Slide 6: Conservation and Management Conservation practices: Overview of strategies for conserving water, such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation techniques. Management approaches: Discussion on how governments and organizations can manage water resources sustainably to ensure long-term availability. Slide 7: Conclusion Recap: Summary of key points discussed in the presentation. Call to action: Encouragement for viewers to learn more about the water cycle and take steps to protect water resources. Slide 8: Additional Resources Links to further reading: References to books, articles, or websites for more information on the water cycle and water conservation. Slide 9: Thank You Thank you message: "Thank you for joining us on this journey through the water cycle!" Contact information: Optional contact details for the presenter or organization hosting the presentation. Slide 10: Questions and Answers Q&A session: Invite viewers to ask questions or share their thoughts on the presentation. Feel free to add more de
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie the Life Cycle of the Stars powerpoint presentation
Ähnlich wie the Life Cycle of the Stars powerpoint presentation (20)
Mehr von ronnajanemanuel2
Mehr von ronnajanemanuel2 (7)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
the Life Cycle of the Stars powerpoint presentation
- 1. Star Life Cycle T. RONNA JANE DC. MANUEL
- 2. Objectives: Infers the characteristics of stars based on the characteristics of the sun
- 3. LET’S PICK-UP! T. RONNA JANE DC. MANUEL
- 4. The Constellations Origins Star patterns named by ancient peoples after gods, goddesses, animals, monsters, and mythic heroes. The constellations used by Western Culture today originated in Mesopotamia around 3,000 B.C.
- 5. The Constellations Only certain stars were part of the pattern and belonged to the constellation. Faint stars were not part of any constellations. Frequently constellations were named for their brightest star. Of the constellations defined by the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks, 48 are still used today.
- 6. The Constellations The ancient civilizations we got the 48 classical constellations from couldn’t see the entire southern sky. During the Age of Sail, European explorers added 40 modern constellations in the “uncharted” areas of the sky.
- 7. The Constellations The 48 classical and the 40 modern constellations make up the 88 official constellations used by astronomers today. The term constellation also now has a new meaning: No longer refers to the pattern of stars itself. Now refers to a well defined region of the sky that contains the traditional star pattern. Everything inside that region of the sky is now part of the constellation, like a “celestial state”.
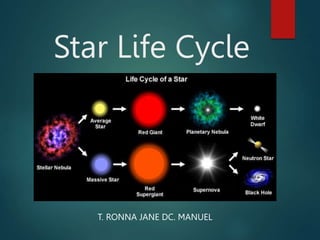
- 10. Stellar Evolution: Life of the Star The most massive stars have the shortest lives. Stars that are 25 to 50 times that of the sun live for only a few million years. Stars like our Sun live for about 10 billion years. Stars less massive than the Sun have even longer life spans Stars are like humans they are born, live and die
- 11. Stars are formed in 1. Nebulae, interstellar clouds of dust and gas (mostly hydrogen). 2. These stellar nurseries are abundant in the arms of spiral galaxies. 3. In these stellar nurseries, dense parts of these clouds undergo gravitational collapse and compress to form a rotating gas globule. The Birth of Stars It begins to spin as it shrinks
- 12. NEBULA PICTURES
- 13. Protostar stage: The nebula flattens and the center condenses: • Temps start to increase due to friction (more collision of molecules). • When temps reach 10 million K, NUCLEAR FUSION begins • Nuclear Fusion generates the energy for a star. • When fusion begins, it is officially considered a STAR. (yeah!) • Fusion – combining a lightweight nuclei into a heavier nuclei
- 16. Stars live out the majority of their lives in a phase termed as the Main Sequence. Longest stage of a star The protostar is now a stable main sequence star which will remain in this state for about 10 billion years. After that, the hydrogen fuel is depleted and the star begins to die. Main-Sequence Stage
- 18. When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming what is called a red giant. RED GIANT STAGE
- 19. Star has run out of Hydrogen atoms in the core to undergo fusion. Our sun has used only about 5% of its Hydrogen Star expands about 10x bigger and cools. Its luminosity increases, temp decreases. Helium fuses to form Carbon, and the core shrinks. It begins losing outer layers
- 20. BETELGEUSE –RED GIANT Only a few million years old, Betelgeuse is already dying. Astronomers predict that it's doomed to explode as a soon, within 1,000 years or so, an event that will be spectacular for Earth's future inhabitants. (Conceivably, it's already happened as Betelgeuse is 640 light-years away!)
- 22. Burnout and Death Fate of a Star depends on its mass All stars, regardless of size, run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity A star will become either a black dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, depending on how massive it was. .
- 23. Death of low-mass stars Never evolve into red giants Remain stable main-sequence stars until hydrogen is gone Collapse into white dwarfs
- 24. Death of medium-mass stars Sun-like Stars (Mass under 1.5 times the mass of the Sun) Red Giant --> Planetary Nebula -->White Dwarf --> Black Dwarf
- 25. Death of massive stars Huge Stars (Mass between 1.5 to 3 times the mass of the Sun) Red SuperGiant --> Supernova --> Neutron Star Giant Stars (Mass over 3 times the mass of the Sun) Red SuperGiant --> Supernova --> Black Hole
- 28. PLANETARY NEBULA This is left when a giant loses its outer layers of gas. Leaves only the core. The core will become a white dwarf
- 30. WHITE DWARF Only hot, dense core is left of this star. It will shine for billions of years before cooling. Stable star with no nuclear fuel,radiates left over fuel for billions of years Could become a black dwarf, but the universe is not old enough to form these
- 33. SUPER NOVA Super Giant eventually loses its outer layers in an explosion leaving only the core – this is the super nova.
- 34. Eventually this core collapses (in an instant). As the iron atoms are crushed together in this gravitational collapse, the core temperature rises to about 100 billion degrees. The repulsive electrical forces between the atoms' nuclei overcomes the gravitational forces, causing a massive, bright, short-lived explosion called a supernova. During the explosion, shock waves, blow away the star's outer layers.
- 35. NEUTRON STAR After a Super Nova explosion, the core may condense into a small core of neutrons. It is so dense – 1 spoonful of Earth would weigh 100 million tons. Rotates very rapidly. If the star's remaining mass is between 1 1/2 to 3 times the mass of the Sun, it will collapse into a small, dense neutron star (about ten miles in diameter, about 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, with an extraordinarily strong magnetic field, and rapid spin).
- 38. BLACK HOLE This is the 3rd predicted result to a star. This is the most dense core of a star that can be left. Gravity is so strong, light cannot escape. Makes it look like a dark hole in space. If the star's remaining mass is greater than three times the mass of the Sun, the star contracts tremendously and becomes a black hole
- 39. Black Hole Pictures Anatomy of a black hole
- 40. The density of a star is pre-determined based on its weight (the amount of dust and gas) it begins with. Smaller stars become white dwarfs. Very large stars become neutron stars or black holes. •Life Cycle of a Star Video
- 41. LET’S CREATE! Open your book on page 201 and answer Activity Zone