Chemistry Fundamentals
•
0 gefällt mir•13 views
The Fundamentals of Chemistry is an introduction to the Periodic Table, stoichiometry, chemical states, chemical equilibria, acid & base, oxidation & reduction reactions, chemical kinetics, inorganic nomenclature, and chemical bonding.
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Downloaden Sie, um offline zu lesen
Empfohlen
Electrons in Atoms

The document discusses the development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr and beyond. It describes Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and Bohr's model of electrons in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Later, the quantum mechanical model was developed, restricting electrons to specific energy levels rather than exact orbits. This modern model determines the probability of finding electrons in different locations around the nucleus.
MODULE 1 ELETCRONIC STRUCTURE OF MATTER.pptx

- The document discusses the history and development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr. It describes key discoveries and experiments.
- Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space, with a small, dense nucleus at the center containing positive charge. This led him to propose the nuclear model of the atom.
- Bohr incorporated Rutherford's nuclear model into his planetary model of the atom. He proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in defined energy levels. This model had limitations when describing multi-electron atoms.
- The quantum mechanical model was developed based on discoveries that electrons can be described as waves using quantum physics principles like wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle. This model uses atomic orbit
Bell301

The document discusses the Bohr model of the atomic structure, which proposes that electrons orbit the nucleus in defined shells corresponding to specific energy levels. It notes several limitations of the Bohr model, including that it violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and cannot explain phenomena like the Zeeman effect. More modern quantum mechanical models of the atom use probabilistic electron orbitals and sublevels within energy shells to better describe atomic structure and spectra.
atomic_structure.pdf

An electron moving with a speed of some value has a de Broglie wavelength that can be calculated using de Broglie's wave equation. De Broglie proposed that particles like electrons can behave as waves, with a wavelength inversely proportional to its momentum. The document provides background on atomic structure and quantum theory concepts like quantized energy levels and wave-particle duality.
Models

The document discusses the evolution of atomic models over time from Dalton's model to the current quantum mechanical model. It summarizes key developments including the plum pudding model, Bohr's model of electrons in orbits, and how the Schrodinger equation led to the quantum mechanical model where electrons occupy distinct energy levels and orbitals. The modern model describes electron probability clouds rather than set orbits and accounts for properties like electron spin and the Pauli exclusion principle.
Structure of atom

This document discusses the historical development of atomic models from Thomson's plum pudding model to Bohr's model of electron shells. It describes key experiments and findings, including:
1) Rutherford's gold foil experiment which showed that the positive charge of atoms is concentrated in a small, dense nucleus.
2) Bohr's model which explained atomic stability by proposing discrete electron orbits where electrons do not radiate energy.
3) The discovery of the neutron by Chadwick in 1932, completing understanding of atomic structure with protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in shells surrounding it.
Atomic Structure Powerpoint Presentation by Computer Careers

Powerpoint Presentation on Atomic Structure by Computer Careers.What is an Atom?ATOMIC STRUCTURE,There are two ways to represent the atomic structure of n element or compound,DOT & CROSS DIAGRAMS and many more ....
Atomicstructureppt 140315053706-phpapp02

This document provides information about atomic structure. It discusses the basic parts of an atom including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Early atomic models proposed by Rutherford and Bohr are described, noting their limitations in explaining experimental observations. The modern quantum mechanical model represents electrons using quantum numbers and wave functions or "fuzzy clouds" to describe atomic orbitals. Electrons occupy different energy levels and sublevels based on their quantum numbers.
Empfohlen
Electrons in Atoms

The document discusses the development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr and beyond. It describes Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and Bohr's model of electrons in fixed orbits around the nucleus. Later, the quantum mechanical model was developed, restricting electrons to specific energy levels rather than exact orbits. This modern model determines the probability of finding electrons in different locations around the nucleus.
MODULE 1 ELETCRONIC STRUCTURE OF MATTER.pptx

- The document discusses the history and development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr. It describes key discoveries and experiments.
- Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space, with a small, dense nucleus at the center containing positive charge. This led him to propose the nuclear model of the atom.
- Bohr incorporated Rutherford's nuclear model into his planetary model of the atom. He proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in defined energy levels. This model had limitations when describing multi-electron atoms.
- The quantum mechanical model was developed based on discoveries that electrons can be described as waves using quantum physics principles like wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle. This model uses atomic orbit
Bell301

The document discusses the Bohr model of the atomic structure, which proposes that electrons orbit the nucleus in defined shells corresponding to specific energy levels. It notes several limitations of the Bohr model, including that it violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and cannot explain phenomena like the Zeeman effect. More modern quantum mechanical models of the atom use probabilistic electron orbitals and sublevels within energy shells to better describe atomic structure and spectra.
atomic_structure.pdf

An electron moving with a speed of some value has a de Broglie wavelength that can be calculated using de Broglie's wave equation. De Broglie proposed that particles like electrons can behave as waves, with a wavelength inversely proportional to its momentum. The document provides background on atomic structure and quantum theory concepts like quantized energy levels and wave-particle duality.
Models

The document discusses the evolution of atomic models over time from Dalton's model to the current quantum mechanical model. It summarizes key developments including the plum pudding model, Bohr's model of electrons in orbits, and how the Schrodinger equation led to the quantum mechanical model where electrons occupy distinct energy levels and orbitals. The modern model describes electron probability clouds rather than set orbits and accounts for properties like electron spin and the Pauli exclusion principle.
Structure of atom

This document discusses the historical development of atomic models from Thomson's plum pudding model to Bohr's model of electron shells. It describes key experiments and findings, including:
1) Rutherford's gold foil experiment which showed that the positive charge of atoms is concentrated in a small, dense nucleus.
2) Bohr's model which explained atomic stability by proposing discrete electron orbits where electrons do not radiate energy.
3) The discovery of the neutron by Chadwick in 1932, completing understanding of atomic structure with protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in shells surrounding it.
Atomic Structure Powerpoint Presentation by Computer Careers

Powerpoint Presentation on Atomic Structure by Computer Careers.What is an Atom?ATOMIC STRUCTURE,There are two ways to represent the atomic structure of n element or compound,DOT & CROSS DIAGRAMS and many more ....
Atomicstructureppt 140315053706-phpapp02

This document provides information about atomic structure. It discusses the basic parts of an atom including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Early atomic models proposed by Rutherford and Bohr are described, noting their limitations in explaining experimental observations. The modern quantum mechanical model represents electrons using quantum numbers and wave functions or "fuzzy clouds" to describe atomic orbitals. Electrons occupy different energy levels and sublevels based on their quantum numbers.
Structure Of The Atom.pdf notes important

The document provides information on the structure of atoms, including key experiments and models that helped reveal the internal structure of atoms. It discusses J.J. Thomson's cathode ray experiment that discovered electrons, Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment that showed atoms have a small, dense nucleus, and Bohr's model of electron orbits around the nucleus. It also covers topics like isotopes, mass number, atomic number, electron configuration, and valency.
Electrons in atoms

The document discusses the historical development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr and beyond. It introduces John Dalton's early model of atoms as indivisible particles with no internal structure in 1863. Later models incorporated the discoveries of the electron by J.J. Thomson in 1897 and the nuclear structure of atoms by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. Niels Bohr's 1913 model proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed, quantized energy levels. This laid the foundations for understanding atomic emission spectra and the quantum mechanical model that later replaced Bohr's model.
atomicstructurevinay-161206190926.pdf

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 where electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra. However, it did not explain more complex atomic structures.
Basic Atomic structure

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 in which electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra.
Atomic structure

1. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the nucleus surrounded by electrons that reside in orbitals classified by quantum numbers.
2. Electrons fill orbitals systematically according to rules like the Aufbau principle. The configuration of electrons plays a vital role in chemistry as chemical interactions occur between valence electrons.
3. Atoms with similar electron configurations display similar chemical properties, explaining periodic trends in the periodic table. Properties like atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity follow periodic trends related to electron configuration.
Qrt-2-Week-1-Module-1-Lesson-1.pptx

This document provides an overview of the quantum mechanical model of the atom. It discusses key concepts like the development of atomic models, electron configuration, quantum numbers, electron orbitals, and energy levels. Some key points:
- The quantum mechanical model describes the probable locations of electrons in an atom and how they can have discrete energy levels. It improved upon earlier planetary and Bohr models.
- Electrons occupy specific orbitals and energy levels denoted by quantum numbers like principal and azimuthal quantum numbers.
- Electron configuration notation specifies the distribution of electrons across orbitals based on Aufbau's principle and other rules.
- Transitions between energy levels explain the emission or absorption of photons and thus the colors
408283346-Structure-of-Atom.pdf

This pdf is written to describe structure of atom for school students of grades 9 to 10. In this the basics of atomic structure has been described. Starting from Dalton's atomic model to Rutherford's scatering of alpha particles, JJ Thomson and Bohr's models with photos.
Students can download and use it for studying atomic structure.
Atoms and molecules best presentation

The document discusses the structure of atoms and various atomic models proposed over time. It begins by defining an atom as the smallest particle of an element consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. J.J. Thomson's cathode ray experiments discovered electrons. Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiments showed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus. Bohr proposed discrete energy levels to explain the stability of atoms. Later, the neutron was discovered, completing the standard atomic model with protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in shells or orbits around the nucleus.
atomicstructurevinay-161206190926 (1).pptx

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 where electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra. However, it did not explain more complex atomic structures.
Chapter 4 electrons in atoms

This chapter discusses the evolution of atomic models and the arrangement of electrons in atoms. It covers difficult concepts such as electrons occupying specific energy levels and orbitals. Students are advised to do all assigned homework and bring their textbook to class to fully understand these abstract ideas. Key models discussed include the Rutherford model, the planetary model, Bohr's model linking electrons and photon emission, and the modern quantum mechanical model based on probability.
Structure of the Atom.pptx.pdf

The document discusses the structure of atoms. It describes how early scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr contributed to developing models of the atom through experiments. Thomson's "plum pudding" model depicted electrons distributed uniformly in a positively charged sphere, but it could not explain atomic stability. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the positive charge and mass of atoms are concentrated in a tiny nucleus, leading to his nuclear model. Bohr's model incorporated discrete electron orbits to explain atomic stability. The document also discusses subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, isotopes, isobars, and how electrons are arranged in shells according to their quantum numbers.
Atomic structure & chemical bond

1) The presentation summarizes atomic structure and chemical bonding models including fundamental particles, Rutherford and Bohr atomic models, quantum numbers, and types of chemical bonds.
2) It discusses limitations of earlier atomic models and introduces concepts like electron energy levels, photon energy, and spectral lines.
3) Various types of chemical bonds are defined including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Molecular orbital theory of covalent bonding is also introduced.
Structure of atom ppt by shiva prasad class 9th a

Structure of atom ppt by shiva prasad class 9th a
it is very useful to read
and it is also useful for making projects in this chapter
ATOMIC PHYSICS

This document provides an overview of atomic physics, including:
1. Models of the atom including Rutherford and Bohr models, and explanations of atomic energy levels and quantum numbers.
2. Quantum physics concepts including Planck's quantum theory, Einstein's theories of light and the photoelectric effect, and de Broglie's hypothesis of matter waves.
3. Lasers including production of laser light, properties, types, and applications.
4. Nuclear physics including structure of the nucleus, radioactive decay, nuclear stability, fission and fusion processes, and applications of nuclear technology.
ch4 structure of an atom.pdf

The document provides information about the structure of atoms. It discusses that atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus at the center, while the electrons move around the nucleus. It explains different atomic models proposed by scientists like Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr. It also discusses the distribution of electrons in shells, valency, atomic number and mass number. Isotopes and isobars are defined. In summary, the document outlines the key particles that make up an atom and the various atomic structure models developed over time.
the building block ATOMS

this ppt is all about basic working of most basic unit atom. and could enrich your knowledge about atom. and follow me at my instagram
https://www.instagram.com/shantanu_stark/?hl=en
2650471_ATOMICSTRUCTUREINTERATOMICBONDING.pptx

This document provides an overview of atomic structure and interatomic bonding. It begins by discussing the fundamental particles that make up atoms, including protons, electrons, and neutrons. It then reviews several major historical atomic models including Dalton's model, Thomson's plum pudding model, and Rutherford's nuclear model. Next, it describes the Bohr model of electron orbitals and its limitations. Finally, it introduces quantum mechanics and quantum numbers that characterize the behavior of electrons in atoms, and how these principles govern the filling of electron orbitals in the aufbau principle.
Chapter 5 electrons in atoms

This document provides an overview of atomic structure and quantum mechanics. It discusses early atomic models proposed by Rutherford and Bohr and limitations they faced. It then introduces the quantum mechanical model, which describes electrons as existing in distinct energy levels and orbitals. The document explains how electron configurations are written based on Aufbau principle, Hund's rule and Pauli exclusion principle. It also discusses atomic spectra and how light emitted during electron energy level transitions can be used to identify elements.
Slides on atoms and atomic structure

Atoms are composed of subatomic particles including electrons, protons, and neutrons. John Dalton developed atomic theory, proposing that all matter is composed of indivisible atoms that combine in simple whole number ratios. Atoms consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons in energy levels. Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed the small, dense nucleus at the atom's center. Niels Bohr incorporated quantum theory into atomic structure, proposing electrons orbit in discrete energy levels. The modern atomic model consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in quantized energy shells or orbitals.
Chapter 1 - Lesson (1)

Secondary Education
Chemistry
Chapter 1
Lesson 1
if you have any question don't hesitate to contact me
join the facebook group
http://www.facebook.com/#!/group.php?gid=17663120872&v=info
Best of luck
Mr.Ehab Mohamed
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM

A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of programs that enables users to create and maintain databases and control all access to them. The primary goal of a DBMS is to provide an environment that is both convenient and efficient for users to retrieve and store information.
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION

Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is an electronic process in which a continuously variable, or analog, the signal is changed into a multilevel digital signal without altering its essential content.
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie Chemistry Fundamentals
Structure Of The Atom.pdf notes important

The document provides information on the structure of atoms, including key experiments and models that helped reveal the internal structure of atoms. It discusses J.J. Thomson's cathode ray experiment that discovered electrons, Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment that showed atoms have a small, dense nucleus, and Bohr's model of electron orbits around the nucleus. It also covers topics like isotopes, mass number, atomic number, electron configuration, and valency.
Electrons in atoms

The document discusses the historical development of atomic models from Dalton to Bohr and beyond. It introduces John Dalton's early model of atoms as indivisible particles with no internal structure in 1863. Later models incorporated the discoveries of the electron by J.J. Thomson in 1897 and the nuclear structure of atoms by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. Niels Bohr's 1913 model proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed, quantized energy levels. This laid the foundations for understanding atomic emission spectra and the quantum mechanical model that later replaced Bohr's model.
atomicstructurevinay-161206190926.pdf

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 where electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra. However, it did not explain more complex atomic structures.
Basic Atomic structure

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 in which electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra.
Atomic structure

1. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the nucleus surrounded by electrons that reside in orbitals classified by quantum numbers.
2. Electrons fill orbitals systematically according to rules like the Aufbau principle. The configuration of electrons plays a vital role in chemistry as chemical interactions occur between valence electrons.
3. Atoms with similar electron configurations display similar chemical properties, explaining periodic trends in the periodic table. Properties like atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity follow periodic trends related to electron configuration.
Qrt-2-Week-1-Module-1-Lesson-1.pptx

This document provides an overview of the quantum mechanical model of the atom. It discusses key concepts like the development of atomic models, electron configuration, quantum numbers, electron orbitals, and energy levels. Some key points:
- The quantum mechanical model describes the probable locations of electrons in an atom and how they can have discrete energy levels. It improved upon earlier planetary and Bohr models.
- Electrons occupy specific orbitals and energy levels denoted by quantum numbers like principal and azimuthal quantum numbers.
- Electron configuration notation specifies the distribution of electrons across orbitals based on Aufbau's principle and other rules.
- Transitions between energy levels explain the emission or absorption of photons and thus the colors
408283346-Structure-of-Atom.pdf

This pdf is written to describe structure of atom for school students of grades 9 to 10. In this the basics of atomic structure has been described. Starting from Dalton's atomic model to Rutherford's scatering of alpha particles, JJ Thomson and Bohr's models with photos.
Students can download and use it for studying atomic structure.
Atoms and molecules best presentation

The document discusses the structure of atoms and various atomic models proposed over time. It begins by defining an atom as the smallest particle of an element consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. J.J. Thomson's cathode ray experiments discovered electrons. Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiments showed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus. Bohr proposed discrete energy levels to explain the stability of atoms. Later, the neutron was discovered, completing the standard atomic model with protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in shells or orbits around the nucleus.
atomicstructurevinay-161206190926 (1).pptx

1. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
2. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 showed that the atom has a small, dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons.
3. Niels Bohr proposed his model of the atom in 1913 where electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells at specific energy levels, explaining atomic spectra. However, it did not explain more complex atomic structures.
Chapter 4 electrons in atoms

This chapter discusses the evolution of atomic models and the arrangement of electrons in atoms. It covers difficult concepts such as electrons occupying specific energy levels and orbitals. Students are advised to do all assigned homework and bring their textbook to class to fully understand these abstract ideas. Key models discussed include the Rutherford model, the planetary model, Bohr's model linking electrons and photon emission, and the modern quantum mechanical model based on probability.
Structure of the Atom.pptx.pdf

The document discusses the structure of atoms. It describes how early scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr contributed to developing models of the atom through experiments. Thomson's "plum pudding" model depicted electrons distributed uniformly in a positively charged sphere, but it could not explain atomic stability. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the positive charge and mass of atoms are concentrated in a tiny nucleus, leading to his nuclear model. Bohr's model incorporated discrete electron orbits to explain atomic stability. The document also discusses subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, isotopes, isobars, and how electrons are arranged in shells according to their quantum numbers.
Atomic structure & chemical bond

1) The presentation summarizes atomic structure and chemical bonding models including fundamental particles, Rutherford and Bohr atomic models, quantum numbers, and types of chemical bonds.
2) It discusses limitations of earlier atomic models and introduces concepts like electron energy levels, photon energy, and spectral lines.
3) Various types of chemical bonds are defined including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Molecular orbital theory of covalent bonding is also introduced.
Structure of atom ppt by shiva prasad class 9th a

Structure of atom ppt by shiva prasad class 9th a
it is very useful to read
and it is also useful for making projects in this chapter
ATOMIC PHYSICS

This document provides an overview of atomic physics, including:
1. Models of the atom including Rutherford and Bohr models, and explanations of atomic energy levels and quantum numbers.
2. Quantum physics concepts including Planck's quantum theory, Einstein's theories of light and the photoelectric effect, and de Broglie's hypothesis of matter waves.
3. Lasers including production of laser light, properties, types, and applications.
4. Nuclear physics including structure of the nucleus, radioactive decay, nuclear stability, fission and fusion processes, and applications of nuclear technology.
ch4 structure of an atom.pdf

The document provides information about the structure of atoms. It discusses that atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus at the center, while the electrons move around the nucleus. It explains different atomic models proposed by scientists like Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr. It also discusses the distribution of electrons in shells, valency, atomic number and mass number. Isotopes and isobars are defined. In summary, the document outlines the key particles that make up an atom and the various atomic structure models developed over time.
the building block ATOMS

this ppt is all about basic working of most basic unit atom. and could enrich your knowledge about atom. and follow me at my instagram
https://www.instagram.com/shantanu_stark/?hl=en
2650471_ATOMICSTRUCTUREINTERATOMICBONDING.pptx

This document provides an overview of atomic structure and interatomic bonding. It begins by discussing the fundamental particles that make up atoms, including protons, electrons, and neutrons. It then reviews several major historical atomic models including Dalton's model, Thomson's plum pudding model, and Rutherford's nuclear model. Next, it describes the Bohr model of electron orbitals and its limitations. Finally, it introduces quantum mechanics and quantum numbers that characterize the behavior of electrons in atoms, and how these principles govern the filling of electron orbitals in the aufbau principle.
Chapter 5 electrons in atoms

This document provides an overview of atomic structure and quantum mechanics. It discusses early atomic models proposed by Rutherford and Bohr and limitations they faced. It then introduces the quantum mechanical model, which describes electrons as existing in distinct energy levels and orbitals. The document explains how electron configurations are written based on Aufbau principle, Hund's rule and Pauli exclusion principle. It also discusses atomic spectra and how light emitted during electron energy level transitions can be used to identify elements.
Slides on atoms and atomic structure

Atoms are composed of subatomic particles including electrons, protons, and neutrons. John Dalton developed atomic theory, proposing that all matter is composed of indivisible atoms that combine in simple whole number ratios. Atoms consist of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons in energy levels. Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed the small, dense nucleus at the atom's center. Niels Bohr incorporated quantum theory into atomic structure, proposing electrons orbit in discrete energy levels. The modern atomic model consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in quantized energy shells or orbitals.
Chapter 1 - Lesson (1)

Secondary Education
Chemistry
Chapter 1
Lesson 1
if you have any question don't hesitate to contact me
join the facebook group
http://www.facebook.com/#!/group.php?gid=17663120872&v=info
Best of luck
Mr.Ehab Mohamed
Ähnlich wie Chemistry Fundamentals (20)
Mehr von Mahmud Hasan Tanvir
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM

A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of programs that enables users to create and maintain databases and control all access to them. The primary goal of a DBMS is to provide an environment that is both convenient and efficient for users to retrieve and store information.
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION

Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is an electronic process in which a continuously variable, or analog, the signal is changed into a multilevel digital signal without altering its essential content.
Cybercrime

Cybercrime is defined as a crime in which a computer is the object of the crime or is used as a
tool to commit an offense.
COMPUTER VIRUSES AND WORMS.pdf

Computer viruses and worms are malicious software programs that spread from computer to computer and interfere with operations. Viruses spread through email attachments and downloads, while worms replicate by exploiting security vulnerabilities to copy themselves to other systems on a network. Common types are executable viruses, boot sector viruses, and macro viruses like the damaging Melissa virus of 1999. Prevention methods include installing antivirus software, keeping systems updated, and using firewalls. Trojan viruses differ in that they do not self-replicate but perform unauthorized actions like deleting or blocking access to data when activated. The first major computer worm was the Morris worm of 1988, which disrupted many systems and led to the conviction of its creator.
Computer Fundamental

It is derived from the Latin word "computare" which means to calculate. Our Computer fundamentals tutorial includes all topics of Computer fundamentals such as input devices, output devices, memory, CPU, motherboard, computer network, viruses, software, hardware, etc.
C++ QNA

C++ provides several mechanisms for dynamically allocating memory at runtime. Function overloading allows functions to have the same name but different signatures defined by their parameters. Default arguments allow functions to have default values specified if arguments are not provided during a call. Dynamic memory allocation provides flexibility for programs to allocate variable amounts of memory as needed at runtime, such as for linked lists and trees. The new operator requests memory allocation from the heap and returns a pointer to the initialized memory. The delete operator is used to deallocate dynamically allocated memory as it is the programmer's responsibility to free up memory. Enumerated types define a data type where every possible value is a symbolic constant.
Attributes in Entity-Relationship Model

This document discusses attributes in entity-relationship modeling. It defines attributes as properties that define entity types, and notes that attributes always have values. It describes five types of attributes: atomic/simple, composite, single-valued, multi-valued, and derived. Simple attributes are indivisible values like a phone number. Composite attributes combine simple attributes, like a name from first and last parts. Derived attributes provide values not stored in the database, like age from date of birth. Entities can have single or multiple attribute values. The document also outlines symbols used in entity relationship diagrams.
Applications of Radioisotopes.pdf

Radioisotopes are unstable isotopes that decay and emit radiation. There are approximately 5,000 known natural and artificial radioisotopes. They are used in two main ways: for their radiation alone or in combination with their chemical properties and radiation. Radioisotopes have many applications including use as tracers in biology to track processes like photosynthesis, use in nuclear medicine for diagnosis and cancer treatment, and use in food preservation to kill parasites and control ripening. They are also used in industry for tasks like detecting leaks in pipes and monitoring mineral content.
Arithmetic Expression

An arithmetic expression contains operators and operands, along with constants and operations. It can take three forms: prefix, infix, or postfix. In prefix form, the operator comes before the operands. In infix form, the operator is between the operands. And in postfix form, the operator follows the operands. The main advantages of arithmetic expressions are that they are easier to evaluate, require fewer brackets, and are fast to calculate. However, they are sensitive to extreme values and not suitable for time series data.
FOUR DIFFERENT TYPES OF WRITING STYLES

This document contains 6 sections discussing various topics:
1. The origins and importance of writing, with early cave drawings considered some of the earliest forms of writing.
2. Different styles of writing including expository, descriptive, persuasive, and narrative styles and their key characteristics.
3. Arguments for allowing euthanasia/physician-assisted suicide for terminally ill patients experiencing unbearable suffering.
4. How "half-truths" and omitting important context can mislead people even when just stating true facts.
5. Views that genuine satisfaction and what is obtained from life is often greater in humble homes of the poor than palaces of the rich.
6.
Fable.docx

A fable is a short story that uses animals to represent human qualities and teach moral lessons. The document provides two examples of fables. The first is about a fox and wolf who conspire to kill other animals but are outsmarted by a rabbit. The second tells the story of rabbits who are blamed by wolves for natural disasters and imprisoned, though the wolves later eat them and claim the rabbits tried to escape. Both fables use animals to represent humans and convey messages about greed, power, and oppression.
Basic C Programming Lab Practice

The document contains the answers to 12 tasks/problems involving C programming concepts like arrays, matrices, strings, functions, recursion, structures, files etc. Each answer provides the full code to solve the problem. The tasks include programs to sort arrays, add matrices, count characters in strings, check palindromes, find prime numbers using functions, calculate factorials and Fibonacci terms recursively, define nested structures, and read/write numbers to files.
Rape in Rural Bangladesh.pdf

This study examined the pattern of alleged rape victims in a rural district of Bangladesh. It found that the majority (70%) of victims were under 20 years old. Over two-thirds of assailants were known to the victims, and most incidents (64.2%) occurred in the victim's home or nearby. Only a minority (14.2%) of victims reported for medical examination within 24 hours. Nearly one-fourth of cases involved gang rape, and three-fourths showed no evidence of sexual intercourse. The study concludes public awareness about rape is needed to encourage timely reporting and preserving evidence, which could help detect assailants through techniques like DNA analysis.
First Law Of Thermodynamics.pdf

1. Internal energy is the sum of translational, rotational, vibrational, and bond energies of a system. A gas molecule only has translational energy.
2. Work done by a gas during expansion can be calculated by integrating pressure with respect to change in volume from the initial to final volumes.
3. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat absorbed by the system minus the work done by the system.
Difference between a variable and a constant.pdf

A variable's value can change throughout a program, while a constant's value remains locked for the entire duration of the program. There are two types of variables - numeric and character - that can take on different values, but constants like PI represent a fixed value that cannot be altered. Variables and constants differ in that a variable's content is mutable while a constant's content remains immutable.
Defects In Image Formation By Lenses.pdf

This document discusses two defects that can occur in image formation by lenses: spherical aberration, which is caused by rays from the outer edges of a lens deviating more than central rays, preventing all rays from meeting at a single point. The second defect is chromatic aberration, which is a lens's inability to focus all colors of light to the same point due to differences in refraction of different wavelengths of light.
Mehr von Mahmud Hasan Tanvir (16)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Solutons Maths Escape Room Spatial .pptx

Solutions of Puzzles of Mathematics Escape Room Game in Spatial.io
Main Java[All of the Base Concepts}.docx

This is part 1 of my Java Learning Journey. This Contains Custom methods, classes, constructors, packages, multithreading , try- catch block, finally block and more.
clinical examination of hip joint (1).pdf

described clinical examination all orthopeadic conditions .
Wound healing PPT

This document provides an overview of wound healing, its functions, stages, mechanisms, factors affecting it, and complications.
A wound is a break in the integrity of the skin or tissues, which may be associated with disruption of the structure and function.
Healing is the body’s response to injury in an attempt to restore normal structure and functions.
Healing can occur in two ways: Regeneration and Repair
There are 4 phases of wound healing: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. This document also describes the mechanism of wound healing. Factors that affect healing include infection, uncontrolled diabetes, poor nutrition, age, anemia, the presence of foreign bodies, etc.
Complications of wound healing like infection, hyperpigmentation of scar, contractures, and keloid formation.
ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...

Denis is a dynamic and results-driven Chief Information Officer (CIO) with a distinguished career spanning information systems analysis and technical project management. With a proven track record of spearheading the design and delivery of cutting-edge Information Management solutions, he has consistently elevated business operations, streamlined reporting functions, and maximized process efficiency.
Certified as an ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) Lead Implementer, Data Protection Officer, and Cyber Risks Analyst, Denis brings a heightened focus on data security, privacy, and cyber resilience to every endeavor.
His expertise extends across a diverse spectrum of reporting, database, and web development applications, underpinned by an exceptional grasp of data storage and virtualization technologies. His proficiency in application testing, database administration, and data cleansing ensures seamless execution of complex projects.
What sets Denis apart is his comprehensive understanding of Business and Systems Analysis technologies, honed through involvement in all phases of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). From meticulous requirements gathering to precise analysis, innovative design, rigorous development, thorough testing, and successful implementation, he has consistently delivered exceptional results.
Throughout his career, he has taken on multifaceted roles, from leading technical project management teams to owning solutions that drive operational excellence. His conscientious and proactive approach is unwavering, whether he is working independently or collaboratively within a team. His ability to connect with colleagues on a personal level underscores his commitment to fostering a harmonious and productive workplace environment.
Date: May 29, 2024
Tags: Information Security, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, Artificial Intelligence, GDPR
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Find out more about ISO training and certification services
Training: ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management System - EN | PECB
ISO/IEC 42001 Artificial Intelligence Management System - EN | PECB
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - Training Courses - EN | PECB
Webinars: https://pecb.com/webinars
Article: https://pecb.com/article
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more information about PECB:
Website: https://pecb.com/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/pecb/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PECBInternational/
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/PECBCERTIFICATION
Leveraging Generative AI to Drive Nonprofit Innovation

In this webinar, participants learned how to utilize Generative AI to streamline operations and elevate member engagement. Amazon Web Service experts provided a customer specific use cases and dived into low/no-code tools that are quick and easy to deploy through Amazon Web Service (AWS.)
Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Traditional Musical Instruments of Arunachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh - RAYH...

Traditional Musical Instruments of Arunachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
ANATOMY AND BIOMECHANICS OF HIP JOINT.pdf

it describes the bony anatomy including the femoral head , acetabulum, labrum . also discusses the capsule , ligaments . muscle that act on the hip joint and the range of motion are outlined. factors affecting hip joint stability and weight transmission through the joint are summarized.
How to Make a Field Mandatory in Odoo 17

In Odoo, making a field required can be done through both Python code and XML views. When you set the required attribute to True in Python code, it makes the field required across all views where it's used. Conversely, when you set the required attribute in XML views, it makes the field required only in the context of that particular view.
Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
This is part 2 of my Java Learning Journey. This contains Hashing, ArrayList, LinkedList, Date and Time Classes, Calendar Class and more.
Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum

(𝐓𝐋𝐄 𝟏𝟎𝟎) (𝐋𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐨𝐧 𝟏)-𝐏𝐫𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐦𝐬
𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐜𝐮𝐬𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐄𝐏𝐏 𝐂𝐮𝐫𝐫𝐢𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐮𝐦 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐏𝐡𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐩𝐩𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬:
- Understand the goals and objectives of the Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) curriculum, recognizing its importance in fostering practical life skills and values among students. Students will also be able to identify the key components and subjects covered, such as agriculture, home economics, industrial arts, and information and communication technology.
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐍𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐒𝐜𝐨𝐩𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐚𝐧 𝐄𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐮𝐫:
-Define entrepreneurship, distinguishing it from general business activities by emphasizing its focus on innovation, risk-taking, and value creation. Students will describe the characteristics and traits of successful entrepreneurs, including their roles and responsibilities, and discuss the broader economic and social impacts of entrepreneurial activities on both local and global scales.
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf

Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf
Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie

Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie
ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...

ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...
Leveraging Generative AI to Drive Nonprofit Innovation

Leveraging Generative AI to Drive Nonprofit Innovation
Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...

Gender and Mental Health - Counselling and Family Therapy Applications and In...
Traditional Musical Instruments of Arunachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh - RAYH...

Traditional Musical Instruments of Arunachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh - RAYH...
Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum

Philippine Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (EPP) Curriculum
NEWSPAPERS - QUESTION 1 - REVISION POWERPOINT.pptx

NEWSPAPERS - QUESTION 1 - REVISION POWERPOINT.pptx
Chemistry Fundamentals
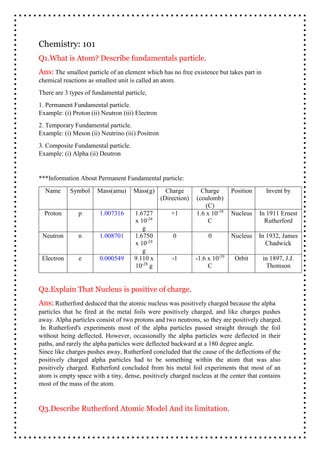
- 1. chemical reactions as smallest unit is called an atom. There are 3 types of fundamental particle, 1. Permanent Fundamental particle. Example: (i) Proton (ii) Neutron (iii) Electron 2. Temporary Fundamental particle. Example: (i) Meson (ii) Neutrino (iii) Positron 3. Composite Fundamental particle. Example: (i) Alpha (ii) Deutron ***Information About Permanent Fundamental particle: Name Symbol Mass(amu) Mass(g) Charge (Direction) Charge (coulomb) (C) Position Invent by Proton p 1.007316 1.6727 x 10-24 g +1 1.6 x 10-19 C Nucleus In 1911 Ernest Rutherford Neutron n 1.008701 1.6750 x 10-24 g 0 0 Nucleus In 1932, James Chadwick Electron e 0.000549 9.110 x 10-28 g -1 -1.6 x 10-19 C Orbit in 1897, J.J. Thomson Q3.Describe Rutherford Atomic Model And its limitation. Q1.What is Atom? Describe fundamentals particle. Ans: The smallest particle of an element which has no free existence but takes part in Chemistry: 101 Q2.Explain That Nucleus is positive of charge. Ans: Rutherford deduced that the atomic nucleus was positively charged because the alpha particles that he fired at the metal foils were positively charged, and like charges pushes away. Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons, so they are positively charged. In Rutherford's experiments most of the alpha particles passed straight through the foil without being deflected. However, occasionally the alpha particles were deflected in their paths, and rarely the alpha particles were deflected backward at a 180 degree angle. Since like charges pushes away, Rutherford concluded that the cause of the deflections of the positively charged alpha particles had to be something within the atom that was also positively charged. Rutherford concluded from his metal foil experiments that most of an atom is empty space with a tiny, dense, positively charged nucleus at the center that contains most of the mass of the atom.
- 2. Q4.Describe Bohr’s Atomic Model And its limitation. Ans: Rutherford’s atom model: This is as follows- 1. In the center of the atom there is a positively charged massive substance. This massive substance is called the centre of nucleus of the atom. Compared to the whole volume of the atom the volume of nucleus is negligible. It possesses almost the whole mass and all positive charges. 2. Atoms are electrically neutral. So nucleus is surrounded by a number of negative charge electrons, equal to the number of positive charge proton of the nucleus. 3. Electrons always move round the nucleus as the planets revolve round the sun in the solar system. The centripetal force due to the electrostatic force between the positive nucleus and the negative electrons is equal to the centrifugal force of the moving electrons. The limitations are: 1. Planets in the solar system are electrically neutral, but the electrons are negatively charged. 2. According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory of radiation any charged particle, if moves in a circular way, always emits radiation and it radius of movement will become smaller gradually and ultimately reach the centre. Therefore, electrons gradually emit energy and ultimately reach the nucleus. Thus, according to Rutherford’s atom model, atoms will get an unstable state. But atoms do not emit energy, or electrons never enter into the nucleus. 3. This model can not give satisfactory explanation of the formation of the spectrum of atom. 4. Rutherford’s atom model did not give any idea about the shape and size of the orbit where the electron moves. 5. There is no explanation regarding how the electron will move round the nucleus in case of atoms having more than one electrons.
- 3. Ans: Bohr’s atom model: This is as follows- 1. Electrons move round the nucleus of atom in some circular paths. 2. Around the nucleus there are some circular stable axes on which electron moves Limitations of Bohr’s atom model: As the Bohr’s atom model has many advantages it also has some limitations. Such as- 1. Although Bohr’s atom model can explain the spectrum of hydrogen and atoms or ions like hydrogen containing one electron, but it can not explain the spectrum on ions or atoms containing more then one electrons. 2. When electrons are transferred from one energy level to another energy level according to Bohr’s atom model there would be a single line in spectrum. But observing the spectrum of hydrogen or other ions with a sensitive apparatus it is seen that every line splits into several fine lines. Q5.Define-Atomic number, Isotope, Isobar, Isotone, and Quantum number. Ans: Atomic number: The number of proton is called the atomic number. Isotope: Atoms of the same elements with different mass numbers are called isotope of each other. Isobar: Atoms of the different elements with same mass numbers but different atomic number are called isotope of each other. Isotone: Atoms of the different elements with same numbers of nuetrons but different atomic number are called isotone of each other. around. These are called energy level or orbit. The energy levels are designated as capital letters K, L, M, N in terms of the value of the hypothetical number ‘n’. The first energy level is denoted as n = 1 (K energy level), the second energy level as n = 2 (L energy level) and, in this way, the value of n keeps increasing in full numbers such as 3, 4, 5 while the energy levels are marked by capital letters M, N, O respectively. While remaining in a certain orbit electrons neither emit nor absorb energy. 3. When any electron gets transferred from a lower orbit or energy level such as n = 1 to a higher orbit or energy level such as n = 2, it absorbs a certain amount of energy. Again when any electron is transferred from a higher orbit or energy level such as n = 2 to a lower orbit or energy level such as n = 1, it emits a fixed amount of energy.
- 4. Quantum number: The Number which express The Size, shape, orientation in space of the orbit in the Nuecleus and the direction of spin of the electrons in their own axis are called quantum number. Q6.Why 19th electron of K(Potassium) enters into $s orbital instead of 3d? Ans: According to this rule we can show the electronic configurations of K (19), K (19) =1s2 2s2 3s2 3p6 3d0 4s1 The Aufbau principle states that electron's occupy orbitals in order of increasing energy. The order of occupation is as follows: 1s<2s<2p<3s<3p<4s<3d<4p<5s<4d<5p<6s<4f<5d<6p<7s<5f<6d<7p So As the energy of 4s orbital is lower then the energy of 3d orbital, so the last electron of potassium (K) entered into 4s orbital not entering 3d orbital. Q7.Describe Laws of electron configuration. Ans: Aufbau Principle: The Aufbau principle, also called the building-up principle, states that electron's occupy orbitals in order of increasing energy. The order of occupation is as follows: 1s<2s<2p<3s<3p<4s<3d<4p<5s<4d<5p<6s<4f<5d<6p<7s<5f<6d<7p Hund's Rule: Hund's Rule states that when electrons occupy degenerate orbitals (i.e. same n and l quantum numbers), they must first occupy the empty orbitals before double occupying them. Pauli-Exclusion Principle: Wolfgang Pauli postulated that each electron can be described with a unique set of four quantum numbers.
