6.3 - Magnetic Force and Field
- 1. 6.3 – Magnetic Force and Field
- 2. Magnetic Poles Every magnet has two poles (North & South) and is therefore called a Dipole Unlike Electric Fields it is impossible to have a Monopole. If you cut a magnet in half you end up with another dipole. N S N S N S Unlike poles attract, Like poles repel. N S N S N S S N These magnets will turn so that UNLIKE poles come together.
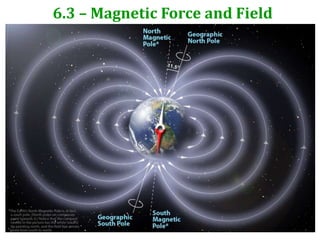
- 3. Earth’s Magnetic Field Because magnets will turn so that UNLIKE poles come together, the poles are really called ‘North seeking poles’ or ‘South seeking poles’ Compasses contain small magnets which turn towards the Earth’s poles. N S http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/magn ets-and-electromagnets
- 4. Magnetic Field Lines Magnetic Field This is a region of space where a test magnet experiences a turning force http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph14e/mfbar.htm Field Lines They point from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- 5. Magnetic Flux Density (B) The strength of the magnetic field seems linked to the density of the magnetic field lines. There is a stronger field at the poles where there are more field lines. Magnetic Flux Density (B) This is the equivalent of: g for Gravitational Fields (Nkg-1) E for Electric Fields (NC-1) The unit of Magnetic Flux Density (B) is the Tesla (T) and like the other field strengths it is a Vector. A good way to think about it is that it is just a measure of how many Field Lines there are in a certain area. A magnetic field is often called a ‘B Field’ Until we know more about Magnetism it isn’t possible to define The Magnetic Field Density (B) in the same way as we do for Gravitational Field Strength (g) and Electric Field Strength (E)
- 6. Fields Caused by Currents It turns out that if a small compass is placed near a wire carrying a current it experiences a weak turning force. This led scientists to realise that Magnetism is actually caused by moving charges. The field is strongest closest The fingers show the direction of to the wire. the field. The direction of the field can be found using the Right Hand Corkscrew Rule. http://www.walter- fendt.de/ph14e/mfwire.htm
- 7. Field inside a coil When a current flows All these circles add This makes a really around a circular loop together. strong field in the the magnetic field centre of the circular forms circles. loop.
- 8. Field inside a solenoid A solenoid is a coil of wire, carrying a current. The field that is created by a solenoid is just like that of a bar magnet but the field lines go through the centre.
- 9. Force on a current carrying conductor review
- 10. Changing the direction of the force review The direction of the force acting on a wire in an electromagnetic field can be reversed by: Reversing the Current Reversing the Magnetic Field The direction of the force is therefore relative to both the direction of the magnetic field and the current.
- 11. Fleming’s left-hand rule review It is possible to predict the direction of the force acting on a wire – its motion – if the direction of the current or the magnetic field are known. Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to do this. thuMb = Motion First finger = magnetic Field seCond finger = Current
- 12. Increasing the size of the force review
- 13. Force in a Magnetic Field equation As you have just seen the size of the force depends on: B – Magnetic Flux Density I – current in the wire l – length of wire If the field is not at Right Angles to the wire then the perpendicular component of the field is used and the equation is:
- 14. Force in a Magnetic Field alternative equation B – Magnetic Flux Density I – current in the wire l – length of wire 1. 2. 3. 4.
- 15. Charges in Magnetic Fields . = B Field coming out of page 1. Electrons moving in a wire ⨯ B Field going away into page = Imagine an arrow coming towards you or going away from you. In the picture above, the electron is moving to the right, so Conventional Current (I) is moving to the left. From Fleming’s Left Hand Rule the electron experiences a force downwards at right angles to it’s motion. It’s the sum of all the forces on all the electrons that gives the total force on the wire. 2. Electrons moving freely through a magnetic field The force is always perpendicular to it’s motion, so it ends up moving in a circle. The Magnetic Field provides the Centripetal Force.
- 16. What forces are there between two current carrying wires? Step 1 – What does I2 do to I1 ? Use the Right Hand Corkscrew rule to see what the field lines do. Step 2 – Which way does I1 move? Use Fleming’s Left Hand Rule to see what the force is on I1 F
- 17. Now repeat for the other wire: Force caused by I2 on I1 Force caused by I1 on I2 F F The two wires move together!
- 18. If the currents are flowing in opposite directions: I I If the currents are flowing in opposite directions:
- 19. What would happen to a coil? What happens to the shape of the coils?
- 20. What would happen to a coil? http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/8/8.02T/f04/visualizations/magnetostatics/15 -MagneticForceAttract/MagForceAtt_640.mpg
- 21. Aurora Borealis Knut Birkeland (1867–1917) is on the 200 Norwegian kroner note. He was a Physicist best known for his studies on the aurora borealis. Timelapse of the Aurora http://vimeo.com/16917950
- 22. Aurora Borealis – the Physics The Earth has a magnetic field caused by currents in its core, which channels charged particles from solar flares and from our upper atmosphere towards the poles
- 23. Aurora Borealis – the Physics Charged particles from space experience a force on them from the earth’s magnetic field which makes them spiral around the magnetic field lines and head towards the poles. As they meet air molecules they excite the molecules causing them to give out light. Without the protection of the earth’s magnetic field we would be constantly bombarded with high energy particles. This is one of the reasons that Space flight is so difficult. Astronauts report white flashes in their vision as Cosmic rays pass straight through their heads. Without shielding missions to Mars will be impossible.