Time Line Ch17
•Als PPTX, PDF herunterladen•
2 gefällt mir•753 views
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Andere mochten auch
Andere mochten auch (20)
Engineering controls in safety, health environment management 

Engineering controls in safety, health environment management
Ähnlich wie Time Line Ch17
Ähnlich wie Time Line Ch17 (20)
Prehistory 1: Geologic Timeline- Notes on the geologic & life history of Ear...

Prehistory 1: Geologic Timeline- Notes on the geologic & life history of Ear...
GTS paleozoic-Geomorphology Chapter-Geomorhology Chapter

GTS paleozoic-Geomorphology Chapter-Geomorhology Chapter
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges

ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges
Modular Monolith - a Practical Alternative to Microservices @ Devoxx UK 2024

Modular Monolith - a Practical Alternative to Microservices @ Devoxx UK 2024
Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME

Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME
Vector Search -An Introduction in Oracle Database 23ai.pptx

Vector Search -An Introduction in Oracle Database 23ai.pptx
Introduction to Multilingual Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)

Introduction to Multilingual Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
WSO2's API Vision: Unifying Control, Empowering Developers

WSO2's API Vision: Unifying Control, Empowering Developers
Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff

Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff
Mcleodganj Call Girls 🥰 8617370543 Service Offer VIP Hot Model

Mcleodganj Call Girls 🥰 8617370543 Service Offer VIP Hot Model
AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform

AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform
DEV meet-up UiPath Document Understanding May 7 2024 Amsterdam

DEV meet-up UiPath Document Understanding May 7 2024 Amsterdam
TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery

TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery
Web Form Automation for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions Apri...

Web Form Automation for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions Apri...
Navigating the Deluge_ Dubai Floods and the Resilience of Dubai International...

Navigating the Deluge_ Dubai Floods and the Resilience of Dubai International...
Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME

Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME
Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood

Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood
CNIC Information System with Pakdata Cf In Pakistan

CNIC Information System with Pakdata Cf In Pakistan
Time Line Ch17
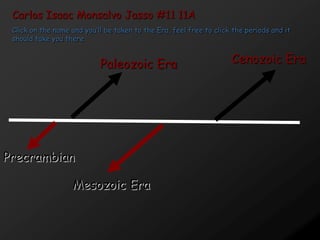
- 1. Carlos Isaac Monsalvo Jasso #11 11A Click on the name and you’ll be taken to the Era, feel free to click the periods and it should take you there. Paleozoic Era Cenozoic Era Precrambian Mesozoic Era
- 2. Precrambian Time * It takes over 650 – 544 millions of years ago. During this time, 90% of Earth’s history occurred here. * Anaerobic structures appeared with photosynthetic methods, adding oxygen to the atmosphere and allowing evolution. *There are few fossils since animals were soft bodied, and during this time life only existed in the sea. Back
- 3. Paleozoic Era * This period was from 544 to 290 millions years ago. * Early in the Paleozoic Era, fossil record became rich with evidence of many types of marine life. * This fossil evidence shows that life was highly diverse by the first part of the Paleozoic Era. * This era is divided into 4 periods: Cambrian Period, Ordovician & Silurian Periods, Devonian Period and Carboniferous & Permian Periods. Back
- 4. Cambrian Period * According to Paleontologists, this is the period in which diversification of life existed, “Cambrian Explosion”. * In this period, organisms finally had hard structures (shells and exoskeletons). * In this period there were invertebrates like jellyfishes which drifted through the water, crawled in the surface or attached themselves to ocean floors; trilobites were common as well. Back
- 5. Ordovician & Silurian Periods * Fist vertebrates to appear were jawless fishes. During these periods, the ancestors of modern octopi and squid appeared. * Some animals in this time grew to the length of 13M. * During these periods, insects appeared, plants evolved and grew low to the ground in damp areas. Back
- 6. Devonian Period * Several plants during this period adapted to drier areas, which enabled them to invade more habitats. * In this period many groups of fishes were present in the ocean; and sharks appeared in the later times. * During the Devonian period, animals began to invade the land. Some fish developed the ability to crawl on leg like fins and eventually evolved into amphibians. Back
- 7. Carboniferous & Permian Periods * During this period, life expanded over Earth’s continents. * Several animals evolved from amphibians (i.e. reptiles). * Remains of ancient plants formed deposits of sediment that became coal. * At the end of the Paleozoic era, many organisms died due to a mass extinction: 95% of the complex life in oceans disappeared. Back
- 8. Mesozoic Era * It lasted about 180 million years ago. * During this period there was an increasing dominance of dinosaurs. The Mesozoic Era is marked by the appearance of flowering plants. * This Era was divided into three periods: Triassic Period, Jurassic Period and Cretaceous Period. Back
- 9. Triassic Period * Organisms that survived the mass extinction became the main forms of life early in this period. * Important organisms that survived: fishes, insects, reptiles and cone bearing plants. This era is commonly called “Age of the Reptiles”. * About 225 million years ago, the first dinosaurs appeared, and the first Mammals appeared at late Triassic period, which resembled mouse or shrew. Back
- 10. Jurassic Period * Dinosaurs became the dominant animals on land in this period. * Dinosaurs “ruled” for about 150 million years but there were different types in different times. * One of the first birds appeared during this time, which made paleontologists think that birds are relatives of dinosaurs. Back
- 11. Cretaceous Period * Reptiles still were the dominant vertebrates throughout this period. * Meat eating dinosaurs dominated land ecosystems, while flying reptiles and birds soared the sky. * The Cretaceous period brought new forms of life: leafy threes, shrubs, and small flowering plants which produced seeds. * There was another mass extinction, which wiped half of all plant and animals groups, including dinosaurs. Back
- 12. Cenozoic Era * This era lasts from 65 million years ago to present days. * During this era, early mammals competed with dinosaurs for food and places to live. * During the Cenozoic era, mammals evolved adaptations that allowed them to live in various environments. * This era is often called the “Age of Mammals”. * This era is divided into two periods: Quaternary Period & Tertiary Period. Back
- 13. Tertiary Period * Earth’s climate was warm and mild. * In oceans, marine mammals like whales and dolphins evolved; on land, flowering plants and insects flourished, providing food source for grazing mammals. * Some mammals became very large during this period. Back
- 14. Quaternary Period * Mammals that had evolved in the Tertiary Period had to face a changing environment during this period. * In this period, Earth’s climate went into a series of ice ages. * About 20.000 years ago Earth’s climate began to warm up, melting glaciers over time. * During this time, the Homo Sapiens might have evolved as early as 100.000 years ago in Africa. Back