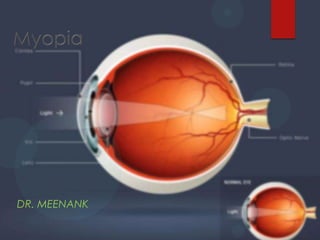
Myopia refractive error-M.B
- 1. DR. MEENANK
- 2. 1. Definition 2. Etiology 3. Optics 4. Classification 5. Clinical varieties in detail 6. Treatment
- 3. Definetion Myopia ( short sight ) condition where parallel rays come to focus in front of the sentient layer of retina when accommodation is at rest Muopia (Greek) = To close the eye
- 4. History Kepler (1611), Plempius (1632) - lengthening of posterior part. Donders (1866) est.. Pathological basis, and detail clinical manifestation's
- 5. Etiology Axial : most commonest 1mm = 3D Curvatural : cornea thickness causes astigmatism 1mm = 6D eg : ectasies conical cornea
- 6. lenticular curvature eg : ant/post lenticonus – marked Positional : dislocation of lens Myopia due to excessive accommodation - spasm of accommodation, suspensory lig. Rupture
- 7. Index myopia : change in the R.I of the crystalline lens eg : Nuclear Sclerosis, Incipient Cataract, Diabetes.
- 8. Buphthalmos : cong/ infantile glaucoma. Defective development – A.P diameter myopia not in ratio enlarged and
- 9. Optics Optical system – eye too powerful for axial length Image of distant object on retina are circles of diffusion form by divergent beam Far point is finite pt in front of eye – object at far pt focused without acc. Angle of alpha –ve resulting in convergent squint
- 10. Accommodation- uncorrected- not developed , as not needed for Nv. Thus may develop exophoria, convergence insufficiency and presbyopia Enlarged image is cause of nodal pt being far away from retina
- 11. Classification
- 12. myopia Congenital myopia Simple (or) Developmental myopia Pathological (or) Degenerative myopia Acquired myopia
- 13. Congenital myopia Since birth Diagnosed – 2 -3 yrs. Associated – prematurity, birth defects, congenital squint, and axial length Unilateral or bilateral Unilateral – manifest as anisometropia diagnosed - after squint- amblyopia
- 14. Associated – cataract, microphthalmas, cong. Retinal separation, megalo-cornea Prognosis – early detection no 6/6 uni-ocular
- 15. Simple Myopia Physiological / developmental / school Biological variation in development Limited progression no disease Factors associated : Axial – A.P diameter (or) neurological Curvatural – underdevelopment of eye ball Diet – poor nutriention Genetic influence – one (or) both parents
- 16. Physiological – A/S normal along with normal fundus Simple Myopia Intermittent – early signs of globe enlargement temporally Sever category of intermittent – crescent with super-traction of disc
- 17. course Born hyper metropic Emmetropic • overshoot Stabilized at teens Myopic • 7-10 yrs • -5D to -8D symptom's : Poor distance vision – beyond far point impaired Asthenopic sympt – eye strain due to difference b/w convergence and accommodation Nv -No accommodation – convergence weakness – exophoria – suppression of one eye Nv –convergence – excessive accommodation – ciliary spasm Physiological out-look – myopic child behavior
- 18. Signs A.C. – deep Pupil – large and sluggish Fundus – normal Eye – large and prominent Error - -5.00 D to -8.00D Diagnosis –visual acuity subjective testing retinoscopy
- 19. Pathological Myopia Degenerative / progressive 2-3 % More marked, high degree Hereditary Postnatal Inc. progressive
- 20. Prevalence – earlier and higher in females higher – Asians, Arabs, Jews lower – Africans, Caucasians more in urban populations
- 21. Etiology Results from rapid growth of eye out side its biological variation 2 theories - Hereditary - General growth Genetic factors Retinal growth Scleral stretching Increase in axial length Pathological myopia • Degeneration – choroid, retinae, vitreous
- 22. Symptoms Muscae volitantes – deg. lig. Vitreous Diminished Vn – progressive due to degeneration Night blindness – high myopes with choroidi-retinal changes Signs Prominent, elongated(post), unilateral, stimulating exophthalmos Cornea – large; A.C – deep; pupil – large, sluggish Refractive error – by -4D/yr up to 20-30yrs
- 23. Fundus – Generalized atrophy of choroid and retinae Loss of RPE- fundus tugroid- prominent choroidal vessels Choroid disappears – visible sclera – atrophic patch - post. Pole – macula (common) Foster – Fuchs's spots – rare, sudden, dark pig. sub-retinal neovascularization and choroidal hx. Cystoid degeneration at periphery
- 24. Advance cases – total retinal atrophy, central Lattice degeneration/ snail track lesion
- 25. Optic disc Myopic crescent – from elongation of disc separation of retina and choroid from temp may be annular Super traction crescent – nasal retina extending over the disc – blur margin Posterior staphyloma – higher degree, herniation of post. Pole – sudden kinking of vessels at margin as in glaucoma
- 26. Vitreous – degeneration, PVD-Wiess reflex, liquefaction, opacities Visual field – ring scotoma Electo-retinograph – chorioretinol atrophy Complications retinal tears, detachment, Hx (high myopia) vitreous detachment, degeneration complicated cataract –↓ lenticular metabolism Nuclear sclerosis – common, effects refraction Choroidal Hx – sever Vn loss if in fovea POAG – not common but seen
- 27. acquired index – nuclear sclerosis, incipient cataract, diabetic myopia Curvatural – true inc. in corneal curvature (or) lenticular Positional – subluxation(ant) of lens Consecutive – surgical overcorrection(cataract/ hypermetropia) Pseudo-myopia – due to excessive accommodation and spasm of accommodation Space myopia – no stimulus for Nv, its variable, trouble in flying and in fog Night/twilight – shift from photic to scotopic vn is associated with inc. sensitivity to shorter wavelength viz myopic Cholinergic – pilocarpine, echothiosulphate Drug induced - Steroid – show changes in crystalline lens Sulplanamides – changes the refractive indices in media
- 28. Diagnosis presentation Simple – blurred Dv, constant/ transient, Nv may be normal, co-existing condt. Nocturnal – blurred Dv in dim illumination, difficulty in driving Pseudo myopia – transient Dv blur, inc after near work Degenerative - considerable Dv blur, flashes/ floaters, Vn loss Induced – transient Dv blur until drug effect, pupils constricted – cholinergic antagonist
- 29. Ocular examination Visual acuity – both unaided Nv and Dv should be measured-mean gives reduced V.A Refraction – retinoscopy or and A.R. , but A.R not qualitative retinoscopy – diagnosis for nocturnal myopia with cyclopegics Ocular motility, binocular Vn, accommodation – heterophoria, versions, accommodative facility test systemic and ocular health – IOP, SLB, postsegment
- 30. Special test Fundus Photography A and B scan Visual field Fasting blood sugars
- 31. Treatment Optical Correction Proper correction with concave lens for image to fall on retina Myopia up to -6.00D Children – full correction Young adults – prevent over correction Adults - ↓ 30 yrs. – full correction ↑ 30 yrs. – under corrected – ciliary muscles fail to accommodate
- 32. Spectacle's Contact lens Economical, safe Larger retinal image Allow incorporation Better Vn in Sr. myopia Better correction of astigmatism Better visual field Less acco- near pt. blur in presbyopia Dec. prismatic effect Rigid lens dec. progressive myopia
- 33. Surgical Treatment Incisional – Radial Keratotomy Lamellar corneal refractive Sx Non-freeze keratomileusis Keratomileusis insitu Freeze keratomileusis of Barraque for myopia Automated lamellar keratoplasty Laser-based corneal refractive Sx Laser insitu keratomileusis (LASIK) Custom Laser insitu keratomileusis (C-LASIK) Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) Epithelial Laser insitu keratomileusis (E-LASIK) Miscellaneous corneal refractive Sx Intracorneal contact lens Orthokeratology Intra stromal corneal ring segment Intra ocular refractive procedure's Phakic refractive lens Refractive lens exchange obsolete
- 34. Radial keratotomy Photorefractive keratectomy Intraocular refractive procedure's LASIK
- 35. Radial keratotomy Deep radial incisions (90% thickness) sparing central 4mm – cornea flatter's on healing Disadvantages – globe rupture, irregular astigmatism, glare, bullous keratopathy
- 36. Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) First refractive procedure to use the excimer laser Max success in myopia Good for -2.00D to -6.00D Photoabalation of central optical zone of ant. Corneal stroma De-epithelialzation – photo ablative Ablation – 6mm for myopia 0.5.1.0mm more Laser should be coaxial with pupil Prevent extreme drying or wetting of cornea and residual islands Hand held ring for centration Toric photoabalation corneal curvature shifts as ant stroma collapse and thins Intrastromal PPk – double NdYAG Plasmamediated photodistribution shock wave Complications – decentation Corneal haze, infiltrates, ulcers Night glare , halos Delayed epi healing Islands, Hx, IOP↑
- 37. Combination – Incisional & Ablative Procedure LASIK - Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Microkeratome to make a corneal flap – excimer to ablate the refractive error adv – bilateral, PRK healing risks avoided, stable results Dis-adv – flap related, striae, diffuse lamellar keratitis, under (or) over correction
- 38. LASEK – LASER Epithelial Keratomileusis Similar to PRK – epithelium is removed and replace post Sx Alcohol to store the epithelium For large pupils and thin corneas For > -8.00 D Adv – no risk of flap dislocation (LASIK) Thin flap Less chance of ectasia Dis- adv – visual recovery slower than LASIK
- 39. Epi LASIK Cleaves epi from bowmen's – structural integrity maintained Newer version of LASEK- advantage on LASIK More thin flap, less haze, faster recovery Custom LASIK Customized for each eye Less halos and glare, More chance of 6/6 Wave front aberrometer - corneal topography Ablation – flexible laser system
- 40. Intra ocular refractive Sx Refractive lens exchange Existing cataract and cornea unfit for refractive Sx For -16.00D to -30.00D PCO reduced Accommodation retained thrgh ‘hinges’
- 41. Phakic IOLs Patients not qualified for refractive Sx Ant / Post chamber lens with out removing crystalline lens Made of plastic (or) silicone
- 42. Patient history and examination Supplement al testing Management flow chart Simple myopia Correction Infants and toddlers – no correction < 3D Pre-school/earlyschool – correct if >1-2D Adolescent's/adult s – correct significantly Control plus lens for Nv Rigid contact lens Visual hygiene Assessment and diagnosis Patient counseling and education Treatment and management Nocturnal myopia Reduction Corneal modification – refractive Sx Pseudomyopia Myopia correction for night time seeing only Reduction of accommodative response – vision therapy, plus lens for Nv, cycloplegic agents, visual hygiene Degenerative myopia Induced myopia Identificatio n and treatment of causative agent Correction and manageme nt of retinal changes
- 43. If a man is called to be a street sweeper, he should sweep street so well that all the host of heaven and earth will pause to say, here lived a great street sweeper who did his job well. - Martin Luther King, Jr.
