MET 214 Heat exchanger module-1
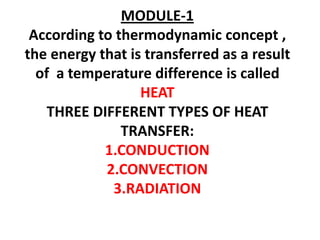
- 1. MODULE-1 According to thermodynamic concept , the energy that is transferred as a result of a temperature difference is called HEAT THREE DIFFERENT TYPES OF HEAT TRANSFER: 1.CONDUCTION 2.CONVECTION 3.RADIATION
- 2. Itmportances of heat transfer: 1.electrical engineerg:cooling system for motors,generators and transformor 2.chemical engineering: evaporation,condensation,heating and cooling of fluid 3. civil engineering: constructions dams,structures,building design. 4.mechanical engineering:heat transfer in internal combustion engine,steam generations,refrigeration and heating and ventillation.
- 3. Conduction:it is the process by which heat flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature within the substance. Conduction take place by two mechanism: a)by lattice vibration:molecules at higher temperature imparts energy to adjacent molecules at lower temperature. b)by free electrons: transfer of heat by free electrons, the free electrons concentration in non-metals is very low.Hence conduction is found in solids
- 4. Convection:it is possible only in the presence of fluids( liquid and gases).As fluid passes over hot objects,they pick up heat energy and carry it to colder area. Two types of convection: 1.free convection 2.forced convection
- 5. RADIATION:RADIATION HEAT TRANSFER BETWEEN TWO SUBSTANCES TAKE PLACE EVEN WITHOUT ANY MEDIUM THROUGH ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
- 6. Heat flux: it is the amount of heat flow per unit area through a body=Q/A W/m2 the materials having higher thermal conductivity are conductors, while material having lower thermal conductivity are called as insulators
- 7. Radiation is the only way that heat can move through a vaccum.Radiant heat can be felt by holding a hand near any hot object,higher the temperature of the object, more energy being released. The denser the solid, the faster heat will be transferred from the hottest regions to coldest.
- 8. Convection: Is the way heat flows through fluids, whether they are liquids or gases.
- 9. THE LAWS OF HEAT TRANSFER. 1.Fourier’s law of heat conduction. The rate of heat flow is proportional to the product of the area of flow A, and the temperature gradient (-dt/dx),the constant of proportionality being the thermal conductivity k, which is a property of material. Unit is j/s or W Qx=-kA(dt/dx)
- 10. 2.NEWTONS LAW OF HEAT CONVECTION Q=hA(t1-t2) heat transfer is occuring from a surface area A at temperature t1, to a fluid at a lower temperature t2. h is the convection co-efficient in w/m2K
- 11. STEFAN-BOLTZMANN LAW OF RADIATION: Q=EσAT4 T-absolute temperature, A-surface area, E-emissivity σ-stefan boltzmann constant,5.67*10-8w/m2k4 It states that the radiant energy emitted by a black body is proportional to the surface area and fourth power of its absolute temperature.
- 12. Thermal conductivity: thermal conductivity, k is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat PURE METALS HAVE HIGHER VALUES OF THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY WHILE GASES AND VAPORS HAVE LOWEST.
- 14. K for a pure metals decreases with temperature. K=ko(1+bф+cф2) where ф=T-Tref. K for a non homogeneous materials increases both with increasing temperature and increasing density.
- 21. Thermal conductivity: it is defined as the ability of a substance to conduct heat. It is expressed in w/m-k or w/moC. Heat transfer co-efficient(h): ability of the fluid carry away heat from the surfaces which in turn depends upon velocities and other thermal properties.unit w/m2 k or w/m2oC
