career monograph
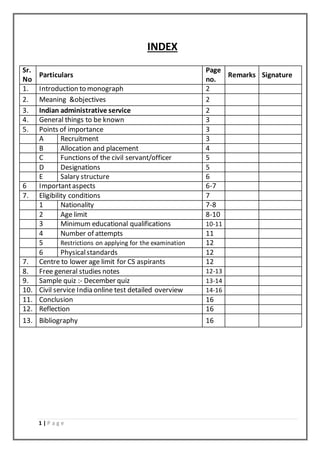
- 1. 1 | P a g e INDEX Sr. No Particulars Page no. Remarks Signature 1. Introduction to monograph 2 2. Meaning &objectives 2 3. Indian administrative service 2 4. General things to be known 3 5. Points of importance 3 A Recruitment 3 B Allocation and placement 4 C Functions of the civil servant/officer 5 D Designations 5 E Salary structure 6 6 Importantaspects 6-7 7. Eligibility conditions 7 1 Nationality 7-8 2 Age limit 8-10 3 Minimum educational qualifications 10-11 4 Number of attempts 11 5 Restrictions on applying for the examination 12 6 Physicalstandards 12 7. Centre to lower age limit for CS aspirants 12 8. Free general studies notes 12-13 9. Sample quiz :- December quiz 13-14 10. Civil service India online test detailed overview 14-16 11. Conclusion 16 12. Reflection 16 13. Bibliography 16
- 2. 2 | P a g e INTRODUCTION:- The term "monographia" is derived from the Greek mono (single) and grapho (to write), meaning "writing on a single subject". Unlike a textbook, which surveys the state of knowledge in a field, the main purpose of a monograph is to present primary research and original scholarship. This research is presented at length, distinguishing a monograph from an article. For these reasons, publication of a monograph is commonly regarded as vital for career progression in many academic disciplines. Book publishers use the term "artist monograph" to indicate books consisting of reproductions of works of art by a single artist, as opposed to surveys of art from multiple artists. Here to study the career monograph relates to understanding the overall aspect of the particular single career been selected. Meaning :- A monograph is a specialist work of writing on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, usually by a single author. A career monograph is a work of writing on a single career by a single author. Thus considering INDIAN ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICE as the topic for my career monograph, the format is given below. Objective:- To understand the overall view of a particular career {here IAS is concerned } INDIAN ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICE The Indian Administrative Service (abbreviated as IAS) (Hindi: भारतीय प्रशासनिक सेवा) is the premier administrative civil service of the Government of India. IAS officers hold key and strategic positions in the Union Government, States and public-sector undertakings. Like in various countries (example UK) following Parliamentary system, IAS as the permanent bureaucracy in India forms an inseparable part of the executive branch of the Government of India thus providing continuity and neutrality to the administration. Unlike Candidates selected to other civil services, a person once appointed to Indian Administrative Service or Indian Foreign Service(IFS) becomes ineligible to reappear in Civil Services Examination conducted by Union Public Service Commission because there are no higher civil services other than aforementioned two services under Government of India. Along with the Indian police and forest services, the IAS is one of the three All India Services—its cadre can be employed by both - the Union Government and the States. Apart from this IAS officials along with their counterparts from Indian Foreign Service are posted in various International Organisations like in the UN and it's agencies, World Bank and IMF etc.
- 3. 3 | P a g e either representing India or working under them on deputations. They can also be deputed to relevant divisions of Indian Embassies and consulates along with Indian Foreign Service officers if and when required. Along with Indian diplomats they represent India or forms part of the delegations in Intergovernmental conferences and International summits. General things to be known:- Abbreviation : I.A.S. Formed : 1946 Country : India Training Ground : Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration, Mussoorie, (Uttarakhand) Controlling Authority : Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pension, Department of Personnel and Training Legal personality : Governmental: Government service General nature : i. Policy Formulation ii. Policy Implementation iii. Civil administration iv. Advisors to Ministers v. Managing bureaucracy (Centre and State) Preceding service : Imperial Civil Service (1893–1946) Cadre Size : 4737 members (direct recruitment – 3398, promotion – 1339) (2013) Association : IAS officers Association Head of the All India Civil Services :Cabinet Secretary Current: Ajit Seth, IAS Points of Importance :- IAS officers at various levels of administration plays a vital role in conducting free, fair and smooth elections in India under the direction of Election Commission of India and states. 1 Recruitment 2 Allocation and placement 3 Functions of the civil servant/Officer 4 Designations 5 Salary structure RECRUITMENT Recruitment to the Indian Administrative Service is done through an extremely competitive examination called the "Civil Services Examination", organized by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). In 2012, over 500,000 candidates applied for this examfrom which 170
- 4. 4 | P a g e were finally recruited into the Indian Administrative Service. The IAS is usually overwhelmingly the top choice of Civil Service Exam aspirants because of the high diversity and prestige of career it offers.Due to very few number of vacancies in IAS and first preference by most of the candidates, entry into the IAS becomes furthermore difficult. Almost all of the applicants rank IAS as their first preference because of the high prestige and diversity of career it offers. For example, in the 2011 batch, of the 425 selected candidates, 370 indicated IAS as their first preference, 25 chose IFS and 15 IRS, and 15 chose IPS. But when it came to second preference, 246 candidates marked IRS as their choice, while only 120 marked IPS as their second choice and 49 as IFS. The Civil Services Examination is a three-stage process spanning nearly twelve months. Candidates have to first write a preliminary examination consisting of two papers, where they are tested on areas such as economics, politics, history, geography, environment, awareness of current affairs, reading comprehension, logical reasoning and basic numeracy skills. Only those that qualify at the preliminary level are eligible to proceed to the second stage, referred to as the "Mains" exams. Candidates have to write nine papers in the Mains exams, where they are tested on Indian and world history, constitutional law, international relations and multilateral bodies, world geography and administrative ethics. Those who successfully clear the Mains exams are then interviewed by the Union Public Service Commission, and a final list of recommended candidates is forwarded to the Government of India. ALLOCATION AND PLACEMENT After being selected, candidates are not allocated to "cadres." There is one cadre in each Indian state, except for three joint cadres: Assam–Meghalaya, Manipur–Tripura, and Arunachal Pradesh–Goa–Mizoram–Union Territories (AGMUT). The "insider-outsider ratio" (ratio of officers who are posted in their home states) is maintained as 1:2. as 'insiders'. The rest are posted outsiders according to the 'roster' in states other than their home states. Till 2008 there was no choice for any state cadre and the candidates, if not placed in the insider vacancy of their home states, were allotted to different states in alphabetic order of the roster, beginning with the letters A,H,M,T for that particular year. For example if in a particular year the roster begins from 'A', which means the first candidate in the roster will go to the Andhra Pradesh state cadre of IAS, the next one to Bihar, and subsequently to Chhattisgarh, Gujarat and so on in alphabetical order. The next year the roster starts from 'H', for either Haryana or Himachal Pradesh.( if it has started from Haryana in the previous occasion when it all started from 'H', then this time it would start from Himachal Pradesh). This highly intricate system has on one hand ensured that officers from different states are placed all over India, it has also resulted in wide disparities in the kind of professional exposure for officers, when we compare officers in small and big and also
- 5. 5 | P a g e developed and backward state, since the system ensures that the officers are permanently placed to one state cadre. The only way the allotted state cadre can be changed is by marriage to an officer of another state cadre of IAS/IPS/IFS. One can even go to his home state cadre on deputation for a limited period, after which one has to invariably return to the cadre allotted to him or her. The centralising effect of these measures was considered extremely important by the system's framers, but has received increasing criticism over the years. In his keynote address at the 50th anniversary of the Service in Mussoorie, former Cabinet Secretary NirmalMukarji argued that separate central, state and local bureaucracies should eventually replace the IAS as an aid to efficiency. There are also concerns that without such reform, the IAS will be unable to "move from a command and control strategy to a more interactive, interdependent system". FUNCTIONS OF THE CIVIL SERVANT/OFFICER A civil servant is responsible for the law and order and general administration in the area under his work. Typically the functions of an IAS officer are as follows: i. To handle the daily affairs of the government, including framing and implementation of policy in consultation with the minister-in-charge of the concerned ministry. ii. Implementation of policy requires supervision. iii. Implementation requires travelling to places where the policies are being implemented. iv. Implementation also includes expenditure of public funds which again requires personal supervision as the officers are answerable to the Parliament and State Legislature for any irregularities that may occur. v. In the process of policy formulation and decision making, officers at various levels like joint secretary, deputy secretary make their contributions and the final shape to the policy is given or a final decision is taken with the concurrence of the minister concerned or the cabinet depending upon the gravity of the issue. SardarVallabhbhai Patel is remembered as the "Patron Saint" of India's civil servants for establishing modern all-India services. In an unprecedented and unrepeated gesture, on the day after his death more than 1,500 officers of India's civil and police services congregated to mourn at Patel's residence in Delhi and pledged "complete loyalty and unremitting zeal" in India's service. DESIGNATIONS Progression of career of IAS officers in State and Centre Government Most IAS officers start their careers in the state administration at the sub-divisional level as a sub divisional magistrate. They are entrusted with the law and order situation of the city along with general administration and development work of the areas under their charge. Since early
- 6. 6 | P a g e 20th-century, Indian civil servants are colloquially called "babus", while Indian bureaucracy is called "babudom", as in the "rule of babus", especially in India media. SALARY STRUCTURE Grade Position in the State Government(s) or Central government Pay Scale Cabinet Secretary Grade Cabinet Secretary of India 90,000 Apex Scale Chief Secretary of States, Union Secretaries in charge of various ministries of Government of India 80,000 (fixed) Above Super Time Scale Principal Secretaries/Financial Commissioners in states, Additional Secretaries to the Government of India 67,000-79,000 Super Time Scale Divisional Commissioner in a division or Secretary in state government or position of Joint Secretary to Government of India 37,400- 67,000 plus grade pay of 10000 Selection Grade District collector in a district or Special Secretary in the state government or a Director in the central government 37,400- 67,000 plus grade Pay of 8700 Junior Administrative Grade Joint Secretary in the state government or a Deputy Secretary in the central government 15,600- 39,100 plus grade pay of 7600 Senior Time Scale Chief Development Officer or Municipal Commissioner in a district or Under Secretary in State or O.S.D in Central government 15,600- 39,100 plus grade pay of 6600 Junior Time Scale Sub-Divisional Magistrate in a sub-division of a district (Entry) 15,600- 39,100 plus grade pay of 5400 IMPORTANT ASPECTS :- 1. Procedure of the Civil Services Examination 2. Eligibility - Academic, Age limit and Nationality 3. Number of Attempts 4. Preliminary Examination
- 7. 7 | P a g e 5. Mains Examination Syllabus 6. Interview 7. Application Procedure 8. Selection of Persons with Disabilities (New) 9. Job Prospects and Remuneration 10.Candidates Appeared and Recommended 11.Cut-Off Marks 12.UPSC Exams Centers 13.Upsc Application form Part I 14.Upsc Application form Part II 15.UPSC not to relax upper age limit 16.Steep fall in non-English exams 17.How to choose a Subject 18.How To Prepare For Prelims 19.Strategy for General Studies Preliminary Examination 2014 20.Civil Services Intake for 2014/15 is fixed at 1,291 ELIGIBILITY :- CANDIDATES SHOULD ENSURE THAT THEY SATISFY ALL THE ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA FOR THE EXAMINATION. The Candidates applying for the examination should ensure that they fulfill all the eligibility conditions for admission into the examination. Their admission to all the stages of the examination will be purely provisional subject to satisfying the prescribed eligibility conditions. Mere issue of admission certificate to the candidate will not imply that his / her candidature has been finally cleared by the Commission. The Commission generally takes up verification of eligibility conditions with reference to the original documents only after the candidate has qualified for the Interview / Personality Test. ELIGIBILITY CONDITIONS: 1. Nationality 2. Age Limit 3. Minimum Educational Qualifications 4. Number of Attempts 5. Restrictions on applying for the Examination 6. Physical Standards 1. Nationality i. For the Indian Administrative Service and the Indian Police Service, a candidate must be a citizen of India.
- 8. 8 | P a g e ii. For other services, a candidate must be either :— a. a citizen of India, or b. a subject of Nepal, or c. a subject of Bhutan, or d. a Tibetan refugee who came over to India before 1st January, 1962 with the intention of permanently settling in India, or e. a person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, East African countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi, Zaire, Ethiopia and Vietnam with the intention of permanently settling in India. iii. Provided that a candidate belonging to categories (b), (c), (d) and (e) shall be a person in whose favour a certificate of eligibility has been issued by the Government of India. iv. Provided further that candidates belonging to categories (b), (c) and (d) above will not be eligible for appointment to the Indian Foreign Service. v. A candidate in whose case a certificate of eligibility is necessary, may be admitted to the examination but the offer of appointment may be given only after the necessary eligibility certificate has been issued to him/her by the Government of India. 2. Age Limit i. A candidate must have attained the age of 21 years and must not have attained the age of 32 years as on 1st August of the year of examination. ii. The upper age limit prescribed above will be relaxable under the following conditions. iii. upto a maximum of five years if a candidate belongs to a Scheduled Caste (SC) or a Scheduled Tribe (ST). iv. upto a maximum of three years in the case of candidates belonging to Other Backward Classes (OBC) who are eligible to avail of reservation applicable to such candidates. v. upto a maximum of five years if a candidate had ordinarily been domiciled in the State of Jammu & Kashmir during the period from the 1st January, 1980 to the 31st day of December, 1989. vi. upto a maximum of three years in the case of Defence Services personnel disabled in operations during hostilities with any foreign country or in a disturbed area and released as a consequence thereof. vii. upto a maximum of five years in the case of ex-servicemen including Commissioned Officers and ECOs / SSCOs who have rendered at least five years Military Service as on 1st August of the year of Examination and have been released a. on completion of assignment (including those whose assignment is due to be completed within one year from 1st August of the year of examination)
- 9. 9 | P a g e otherwise than by way of dismissal or discharge on account of misconduct or inefficiency, or b. on account of physical disability attributable to Military Service, or c. oninvalidment. viii. upto a maximum of five years in the case of ECOs / SSCOs who have completed an initial period of assignment of five years Military Service as on 1st August of the year of examination and whose assignment has been extended beyond five years and in whose case the Ministry of Defence issues a certificate that they can apply for civil employment and that they will be released on three months notice on selection from the date of receipt of offer of appointment. ix. upto a maximum of 10 years in the case of blind, deaf-mute and orthopaedically handicapped persons. NOTE: Candidates belonging to the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes and the Other Backward Classes who are also covered under any of the clauses (a) to (g) mentioned above, viz. those coming under the category of Ex-servicemen, persons domiciled in the State of J & K, blind, deaf-mute and orthopaedically handicapped etc. will be eligible for grant of cumulative age-relaxation under both the categories. The term ex-servicemen will apply to the persons who are defined as ex-servicemen in the Ex-servicemen (Re-employment in Civil Services and Posts) Rules, 1979, as amended from time to time. The age concession under clause (e) and (f) will not be admissible to Ex-Servicemen and Commissioned Officers including ECOs / SSCOs who are released on own request. Notwithstanding the provision of age-relaxation under clause (g) above, a physically disabled candidate will be considered to be eligible for appointment only if he/she (after such physical examination as the Government or appointing authority, as the case may be, may prescribe) is found to satisfy the requirements of physical and medical standards for the concerned Services/posts to be allocated to the physically disabled candidates by the Government. Proof of Date of Birth The date of birth accepted by the Commission is that entered in the Matriculation or Secondary School Leaving Certificate or in a certificate recognised by an Indian University as equivalent to Matriculation or in an extract from a Register of Matriculates maintained by a University, which extract must be certified by the proper authority of the University or in the Higher Secondary or an equivalent examination certificate. These certificates are required to be submitted only at the time of applying for the Civil Services (Main) Examination.
- 10. 10 | P a g e i. The expression Matriculation / Secondary Examination Certificate in this part of the instruction includes the alternative certificates mentioned above. ii. No other document relating to age like horoscopes, affidavits, birth extracts from Municipal Corporation, service records and the like will be accepted. iii. Candidates should note that only the Date of Birth as recorded in the Matriculation / Secondary Examination Certificate or an equivalent certificate as on the date of submission of applications will be accepted by the Commission and no subsequent request for its change will be considered or granted. iv. Candidates should also note that once a Date of Birth has been claimed by them and entered in the records of the Commission for the purpose of admission to an examination, no change will be allowed subsequently (or at any other examination of the Commission) on any grounds whatsoever. v. The candidate should exercise due care while entering their date of birth in column 3 of the Application Form for the Preliminary Examination. If on verification at any subsequent stage, any variation is found in their date of birth from the one entered in their matriculation or equivalent Examination certificate, disciplinary action will be taken against them by the Commission under the Rules. 3. Minimum Educational Qualifications The candidate must hold a degree of any of Universities incorporated by an Act of the Central or State Legislature in India or other educational institutions established by an Act of Parliament or declared to be deemed as a University Under Section-3 of the University Grants Commission Act, 1956, or possess an equivalent qualification. i. Candidates who have appeared at an examination the passing of which would render them educationally qualified for the Commission's examination but have not been informed of the results as also the candidates who intend to appear at such a qualifying examination will also be eligible for admission to the Preliminary Examination. ii. All candidates who are declared qualified by the Commission for taking the Civil Services (Main) Examination will be required to produce proof of passing the requisite examination with their application for the Main Examination failing which such candidates will not be admitted to the Main Examination. The applications for the Main Examination will be called sometime in the month of September / October. iii. In exceptional cases, the Union Public Service Commission may treat a candidate who has not any of the foregoing qualifications as a qualified candidate provided that he / she has passed examination conducted by the other Institutions, the standard of which in the opinion of the Commission justifies his / her admission to the examination.
- 11. 11 | P a g e iv. Candidates possessing professional and technical qualifications which are recognised by Government as equivalent to professional and technical degree would also be eligible for admission to the examination. v. Candidates who have passed the final professional M.B.B.S. or any other Medical Examination but have not completed their internship by the time of submission of their applications for the Civil Services (Main) Examination, will be provisionally admitted to the Examination provided they submit along with their application a copy of certificate from the concerned authority of the University / Institution that they had passed the requisite final professional medical examination. In such cases, the candidates will be required to produce at the time of their interview original Degree or a certificate from the concerned competent authority of the University / Institution that they had completed all requirements (including completion of internship) for the award of the Degree. 4. Number of Attempts i. Every candidate appearing at the examination who is otherwise eligible, shall be permitted Six attempts at the examination. ii. This restriction on the number of attempts will not apply in the case of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes candidates who are otherwise eligible. iii. The number of attempts permissible to candidates belonging to Other Backward Classes, who are otherwise eligible shall be nine. iv. The relaxation will be available to the candidates who are eligible to avail of reservation applicable to such candidates. v. A physically handicapped will get as many attempts as are available to other non- physically handicapped candidates of his or her community, subject to the condition that a physically handicapped candidate belonging to the General Category shall be eligible for nine attempts. vi. The relaxation will be available to the physically handicapped candidates who are eligible to avail of reservation applicable to such candidates. NOTE: An attempt at a Preliminary Examination shall be deemed to be an attempt at the Examination. If a candidate actually appears in any one paper in the Preliminary Examination, he/she shall be deemed to have made an attempt at the Examination. Notwithstanding the disqualification / cancellation of candidature, the fact of appearance of the candidate at the examination will count as an attempt.
- 12. 12 | P a g e 5. Restrictions on applying for the Examination i. A candidate who is appointed to the Indian Administrative Service or the Indian Foreign Service on the results of an earlier examination and continues to be a member of that service will not be eligible to compete at this examination. ii. In case a candidate is appointed to the IAS / IFS after the Preliminary Examination of Civil Services Examination of that year is over, and he/she continues to be a member of that service, he/she shall not be eligible to appear in the Civil Services (Main) Examination of that year notwithstanding his/her having qualified in the Preliminary Examination of that year. iii. If a candidate is appointed to IAS/IFS after the commencement of the Civil Services (Main) Examination of that year, but before the result thereof and continues to be a member of that service, he/she shall not be considered for appointment to any service/post on the basis of the result of the Civil Services Examination of that year. 6. Physical Standards Candidates must be physically fit according to physical standards for admission to Civil Services Examination of a particular year as per guidelines given in Rules for Examination published in the Gazette of India Extraordinary during the year of examination. CENTRE TO LOWER AGE LIMIT FOR CS ASPIRANTS i. The Union government intends to reduce the upper age limit and number of attempts of applicants of the UPSC Civil Service Examination with effect from 2015. ii. According to information published on the website of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, the upper age limit will be 29 years for SC/ST candidates, 28 years for OBC and 26 for the unreserved category. There will be an additional two years for physically challenged candidates in each category. iii. At present, the upper age limit for SC/ST, OBC and unreserved candidates is 35, 33 and 30 years respectively. iv. Similarly the number of attempts allowed for candidates appearing for the Civil Services Examination would also be reduced to six for SC/ST candidates, five for OBC and three for unreserved candidates. v. The measures, recommended by the Second Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) and almost entirely accepted by the government, were put up on the website. vi. The Centre has decided to retain August 1 in the examination year as the cut-off date for eligibility and not to review the structure of the examination (both preliminary and main) since this was only recently changed.
- 13. 13 | P a g e Free General Studies Notes :-Civil Service India strives to provide with as much free materials as possible to help you prepare for the IAS exam, they try to source as much original and authentic study materials as we can and place it on the website. Do use these notes on General Studies to supplement your preparations. We are hoping that our free General Studies notes for upsc are useful in the UPSC mains exam. Also they say, please do remember to go to the listed reference books and make your own notes as many topics may not have been covered in these General Studies notes that we have uploaded. Effects of globalisation on Indian society Major Threats Faced By Amazon Rainforest And Consequences Of Reduced Forest Cover In Amazon Rainforest Region. Impact Of Climatic Change On Arctic Ecosystem Influence of Himalayas in Indian Continent Nomenclature Of Tropical Cyclones Current Affairs December Quiz Giving updated Current Affairs Quizzes that will include 2014 General Knowledge, Current Affairs Gk Questions and more. The Current Affairs Quiz will help you refresh your memory on current affairs of India and the world targetted at getting you ready for the UPSC exam. This 2014 General Knowledge Quiz will updated on monthly basis. Sample Quiz :- December Quiz 1.Where was 18th Saarc Summit held a. Colombo b. Islamabad c. Kathmandu d. New Delhi 2.SAARC is headquartered in---- a. Colombo b. Islamabad c. Kathmandu d. New Delhi 3.Which declaration was signed at 18th saarc summit a. Energy pact b. Road pact c. Rail pact d. Sea pact 4.Which of the following is not a member of SAARC? a. The Maldives b. Afghanistan
- 14. 14 | P a g e c. Mauritius d. Nepal 5.In which year SAARC was Established a. 1975 b. 1985 c. 1995 d. 2005 6.How many countries are founding members of SAARC a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7 7.How many countries are members of SAARC a. 8 b. 7 c. 6 d. 5 8.Which is the last country Latest to join Saarc a. Maldives b. Afghanistan c. Myanmar d. Bhutan 9.SAARC Secretariat was established in which year a. 1987 b. 1988 c. 1999 d. 2000 10.SAARC Secretariat was inaugurated by? a. Prime Minster of India b. King of Nepal c. Military ruler of Pakistan d. King of Bhutan Score = (whatever achieved by the student) CIVIL SERVICE INDIA ONLINE TEST DETAILED OVERVIEW Dear Aspirants, Please login if you are registered and your account has been activated! Login ID
- 15. 15 | P a g e Password Subject New Member Sign UP The best online IAS Coaching with questions collected from previous papers as well as from other sources to give you a real taste of the IAS exams. Register imeediately if haven't as yet and know for yourself. We update the question bank pretty often so that you may get as much practice as you need. Please sedn us your experiences and feedback to make it even better for you. For all those Civil Service Aspirants who are new and would like to register yourself for our online test please click here Test modules are all up to date and based on the 2013 Prelims model. Registering with it is a very simple procedure and may go a long way in helping you crack the Prelims. Please sign up for each subject (GS & GAT) separately ie a separate User ID for each subject you register for. The cost per subject is Rs 960/- for two years ( Revised on 13-10-2014 onwards). How to Register Step 1: Payment of Rs 960/- for two years through given payment mode Step 2: Send us your details with the DD or Email to info@civilserviceindia.com if online payments, Name User ID Subject Email id Mobile / telephone no. Step 3: Once your payment is received, we will activate your account. Upon activation we will intimate you through an e-mail and you can test your preparation by undertaking our online tests as many times as you wish. You will get a new question paper randomly generated, every time you come online to give a test. Payment Mode Payments to be made by DD Favoring "Concern InfotechPvt. Ltd." and Courier the DD to the Address : Concern InfotechPvt. Ltd. 1/45-1A, 1st floor, Butt Road, St. Thomas Mount, Chennai-600 016. Payment can be done through online transfer too. Bank: HDFC A/c: 04922020000296 Concern InfotechPvt.Ltd. Kilpauk - PH road branch. Chennai
- 16. 16 | P a g e IFSC code is HDFC 0000492 (Use IFSC Code Only if it is required in payment process) - use for online transfer Pay Through PAYPAL Once payment is made, send the transaction details to email id – info@civilserviceindia.com. For More Information Contact 044-43504824 Special Features of Online Test i. A 2 hour question paper as per the UPSC prelims exam. ii. Now based on the new pattern of 2013 Exam(With Negative Marking). iii. The format of questions and the topics are same as the UPSC. iv. A new question paper every time you log in. v. Answers given at the end and also your score. vi. Once registered give as many tests as you want. vii. Cost of Registration:Rs.960 per Subject for two years ( Revised on 13-10-2014 onwards). CONCLUSION:- Preparing of career monograph requires indepth study of the particular career as in detail knowledge is been displayed & potrayed to be referred. REFLECTION:- It was a heartful assignment as the career here is one of my dream career & the aspirants possessing are a dream come true hardworkers & person who turm oil at night.I have brought the overall criteria required for the career monongraph. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Narendra Kumar Singhi (1974). Bureaucracy, Positions and Persons: Role Structures, Interactions, and Value-orientations of Bureaucrats in Rajasthan. Abhinav Publications. ISBN 978-0-88386-294-0. 2. Bankey Bihari Misra (1977). The bureaucracy in India: an historical analysis of development up to 1947. Oxford University Press. 3. Indian bureaucracy at the crossroads, by Syamal Kumar Ray. Published by Sterling, 1979. 4. Corruption in Indian politics and bureaucracy, by Satyavan Bhatnagar, S. K. Sharma, Punjab University. Published by EssEss Publications, 1991. ISBN 81-7000-123-4. 5. T. S. R. Subramanian (2004). Journeys through babudom and netaland: governance in India. Rupa & Co. 6. Sudhansu Mohanty (2004). Babudom : Catacombs Of India Bureaucracy. Rupa& Company. ISBN 978-81-291-0383-3.
