Buffer manager
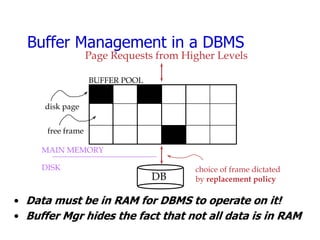
- 1. Buffer Management in a DBMS Page Requests from Higher Levels BUFFER POOL disk page free frame MAIN MEMORY DISK choice of frame dictated DB by replacement policy • Data must be in RAM for DBMS to operate on it! • Buffer Mgr hides the fact that not all data is in RAM
- 2. When a Page is Requested ... • Buffer pool information table contains: <frame#, pageid, pin_count, dirty> • If requested page is not in pool: – Choose a frame for replacement (only un-pinned pages are candidates) – If frame is “dirty”, write it to disk – Read requested page into chosen frame • Pin the page and return its address. If requests can be predicted (e.g., sequential scans) pages can be pre-fetched several pages at a time!
- 3. More on Buffer Management • Requestor of page must eventually unpin it, and indicate whether page has been modified: – dirty bit is used for this. • Page in pool may be requested many times, – a pin count is used. – To pin a page, pin_count++ – A page is a candidate for replacement iff pin_count == 0 (“unpinned”) • CC & recovery may entail additional I/O when a frame is chosen for replacement. (Write- Ahead Log protocol; more later.)
- 4. Buffer Replacement Policy • Frame is chosen for replacement by a replacement policy: – Least-recently-used (LRU), MRU, Clock, etc. • Policy can have big impact on # of I/O’s; depends on the access pattern.
- 5. LRU Replacement Policy • Least Recently Used (LRU) – for each page in buffer pool, keep track of time last unpinned – replace the frame that has the oldest (earliest) time – very common policy: intuitive and simple • Problems? • Problem: Sequential flooding – LRU + repeated sequential scans. – # buffer frames < # pages in file means each page request causes an I/O. MRU much better in this situation (but not in all situations, of course).
- 6. A(1) “Clock” Replacement Policy D(1) B(p) • An approximation of LRU • Arrange frames into a cycle, store one C(1) reference bit per frame – Can think of this as the 2nd chance bit • When pin count reduces to 0, turn on ref. bit • When replacement necessary do for each page in cycle { if (pincount == 0 && ref bit is on) turn off ref bit; else if (pincount == 0 && ref bit is off) choose this page for replacement; } until a page is chosen;
- 7. Code Navigation ctags – Allows you to use your favorite editor to find declarations – 1. cd to Hw1/MyStuff/MyCode – 2. Run ctags -R ../../postgresql-7.2.2/ – 3. Start vi filename.c – 4. ^] - Look up the location of the identifier under the cursor in the tags file, and move to that location. ^T - Return to the previous location in the tag stack, i.e., pop off one element. – Also Emacs support (ctags). Talk amongst yourselves
- 8. Code Debugging • ddd – Two ways to debug postgres • interactive mode • bare backend mode (described here) – Initialize postgres by typing • /local_tmp/$USER/postgresql-7.2.2- clock/bin/initdb –D <data directory> – Startup ddd with the newly complied and installed version of postgres • ddd /local_tmp/$USER/postgresql-7.2.2- clock/bin/postgres – You can now examine functions • Type in the search field the name of the function to be examined (e.g., GetFreeBuffer()). • Then click the Lookup button.
- 9. Code Debugging • ddd (cont‘d – Run postgres by hitting F2 or by using the menu option Program -> Run – A dialog box will appear where you enter -D <data dir> template1 – Click on Run and then the backend prompt should appears in the upper pane. – Place a breakpoint in GetFreeBuffer() on the first line of the code in the function (You can either right click your mouse and choose the set breakpoint menu or click on the line and then click on the Break button). – Type at the backend prompt Select * from pg_user; to run your query. – Now you can start debugging your code by either • Looking at the current state of your stack (Status -> Backtrace). • Display local variables (Data -> Display Local Variables) and function arguments (Data -> Display Arguments). • Display any expression you want to know about more (highlight the expression and click on the Display Button).
- 10. Stuff About Assignment 3 • Methods to know about – AddBufferToFreeList(BufferDesc) and InitFreeList(bool) can be ignored for implementing the Clock Algorithm. – BufferDescriptorGetBuffer(BufferDesc) – returns position of a page in buffer. – GetFreeBuffer() – method that needs to be re-implemented. • Data structures to know about – BufferDescriptors[] – Array representing the buffer pool of size NBuffers. – BufferDesc – represents a buffer page; stores among other things information like whether the page is currently pinned or unpinned (struct variable refcount).
- 11. Buffer 0 Buffer 1 Buffer 2.. Buffer N-2 Buffer N-1 0 1 2 … N-3 N-2 N-1 N freeNext freeNext … freeNext freeNext freeNext N=Nbuffers Data_Descriptors=N freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev Free_List_Descriptor=N BufferDescriptors Array after buf_init.c:212 in InitBufferPool() • InitBufferPool() creates BufferDescriptors Array of size N=Nbuffers+1 and creates a circular doubly linked list with first N items. • BufferDescriptors 0 to N-1 have pointers to buffer blocks in memory. • BufferDescriptors[N] serves as a dummy element and does not point to a valid buffer block.
- 12. Reference History Buffer 0 Buffer 1 Buffer 2.. Buffer N-2 Buffer N-1 1 2 … time N-3 N-2 0 1 2 … N-3 N-2 N-1 N N-1 0 freeNext freeNext … freeNext freeNext freeNext N=Nbuffers Data_Descriptors=N freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev Free_List_Descriptor=N SharedFreeList BufferDescriptors Array after freelist.c:243 in InitFreeList() •BufferDescriptors[N] is only used as a placeholder element in the linked list. InitFreeList() points SharedFreeList to BufferDescriptors[N] and inserts the latter between BufferDescriptors[0] and BufferDescriptors[1]. •SharedFreeList->FreeNext will serve as the handle to the first element in freelist. Freelist links the unpinned buffers, i.e. those that are eligible for eviction.
- 13. Buffer 0 Buffer 1 Buffer 2 Buffer 3.. Buffer N-1 N freeNext 0 1 2 3…N-2 N-1 N freePrev This buffer freeNext is deleted freeNext freeNext freeNext from … freelist. freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev SharedFreeList freelist.c:198, No free elements left condition check. SharedFreeList BufferDescriptors Array after freelist.c:233 in GetFreeBuffer() • GetFreeBuffer() returns the bufferDescriptor pointed by SharedFreeList->FreeNext. Since this buffer is no longer free, it is removed from freelist by rearranging the freeNext and freePrev pointers of the adjacent elements. • GetFreeBuffer() also checks that there are free elements available in the freelist.
- 14. Buffer 0 Buffer 1 Buffer 2 Buffer 3.. Buffer N-1 Buffer i 0 1 2 3…N-2 N-1 N i This buffer freeNext is deleted freeNext freeNext freeNext freeNext from … freelist. freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev SharedFreeList LRU policy insert (default), after freelist.c:81 in AddBufferToFreelist(), continued from GetFreeBuffer() slide. • AddBufferToFreelist() adds the input bufferDescriptor[i] to end of the freelist, i.e as SharedFreeList->freePrev. The freeNext and freePrev pointers of the adjacent elements are rearranged appropriately.
- 15. Buffer 0 Buffer 1 Buffer 2 Buffer 3.. Buffer N-1 Buffer i 0 1 2 3…N-2 N-1 N i This buffer freeNext is deleted freeNext freeNext freeNext freeNext from … freelist. freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev freePrev SharedFreeList MRU policy insert (freelist.c.mru), after freelist.c.mru:81 in AddBufferToFreelist(), continued from GetFreeBuffer() slide. • AddBufferToFreelist() adds the input BufferDescriptor[i] to start of the freelist, i.e as SharedFreeList->freeNext. Compare with LRU to understand the modifications in pointers. Note that this is the only change needed to switch from LRU to MRU.
- 16. Reference History 1 LRU MRU time … 2 N-3 N-2 N-1 0 0 1 1 0 freeNext freeNext freePrev freePrev SharedFreeList 0 1 SharedFreeList 1 0