Lecture 4 digestion and nutrition 2nd sem 2008-2009
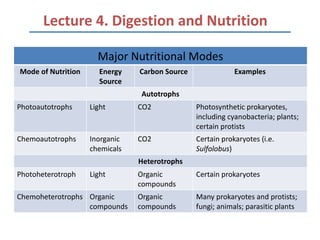
- 1. Lecture 4. Digestion and Nutrition Major Nutritional Modes Mode of Nutrition Energy Carbon Source Examples Source Autotrophs Photoautotrophs Light CO2 Photosynthetic prokaryotes, including cyanobacteria; plants; certain protists Chemoautotrophs Inorganic CO2 Certain prokaryotes (i.e. chemicals Sulfolobus) Heterotrophs Photoheterotroph Light Organic Certain prokaryotes compounds Chemoheterotrophs Organic Organic Many prokaryotes and protists; compounds compounds fungi; animals; parasitic plants
- 5. Dietary categories 4. Saprophagous deer fly (Chrysops callidus) Woodlice (Trachelipus ratzeburgii) hermit beetle (Osmoderma eremita) red ant (Formica pallidefulva )
- 6. Feeding Adaptations Suspension feeder – sifts through food particles in the water Baleen whale Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 7. • bivalve molluscs use their gills as feeding devices
- 8. • herring and other suspension-feeding fishes use gill rakers to strain plankton
- 9. krill • whalebone whales filter out plankton, mainly large crustaceans called krill, with whalebone or baleen
- 10. Feeding Adaptations Deposit feeder – eats its way through dirt or sediments and extract partially decayed organic material (detritus) consumed along with the soil or sediments Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Earthworm
- 11. Feeding Adaptations Substrate feeder – lives in or on its food source, eating its way through the food Leaf miners Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 12. Feeding Adaptations Fluid feeder – sucks nutrient-rich fluids from a living host and is considered a parasite Mosquito Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 13. Feeding Adaptations Bulk feeder – eats relatively large pieces of food Python Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 14. Cephalopod molluscs have beak-like jaws which serve as tearing devices
- 15. • chewing mouthparts adapted for seizing and crushing food • mandibles are strong, toothed plates whose edges can bite or tear • maxillae hold the food and pass it toward the mouth
- 16. • birds lack teeth • bills are often provided with serrated edges • In some, the upper bill is hooked for seizing and tearing prey
- 17. Four types of teeth found in mammals: • incisors, for biting, cutting, and stripping • canines, for seizing, piercing, and tearing • premolars, for grinding and crushing • molars, for grinding and crushing
- 18. • an elephant’s tusk is a modified upper incisor • used for defense, attack, and rooting • a male wild boar has modified canines that are used as weapons
- 20. Types of Digestive System • Incomplete – there is only one opening; no anus Paramecium Hydra
- 21. Types of Digestive System • Complete – there is a mouth opening and an anus
- 22. Four Main Stages of Food Processing • Ingestion – the act of eating • Digestion – breaking food down into molecules small enough for the body to absorb • Absorption – small molecules are taken in by the animal’s cells • Elimination – undigested material passes out of the digestive compartment
- 23. • digestion is entirely intracellular in protozoa and sponges
- 24. • radiates, turbellarian flatworms, and ribbon worms (nemerteans) practice both intracellular and extracellular digestion • in extracellular digestion, certain cells lining the lumen of alimentary canals form digestive secretions; other cells function in absorption • for arthropods and vertebrates digestion is almost entirely extracellular
- 25. Gut movement • alternate constriction of rings of smooth muscle of the intestine • constantly divide and squeeze contents back and forth • for mixing of food • waves of contraction of circular muscle behind the gut and relaxation in front of bolus • sweeps food down the gut
- 27. Human Digestive System Salivary glands
- 28. Human Esophagus Food is called bolus if it passes • through the esophagus
- 29. Human Stomach
- 30. Food is called • chyme after it passes through the stomach
- 31. • trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase are secreted in inactive form by the pancreas – the intestinal enzyme, enteropeptidase, converts inactive trypsinogen into active trypsin – active trypsin then activates the other two
- 32. Human Small Intestine • Made up of three regions: 1. duodenum - Nearest to the stomach; 26 cm in length - With Bruner’s glands - produce mucus-rich alkaline secretion with bicarbonates to - protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme; - provide alkaline condition for the intestinal enzymes to be active; and - lubricate the intestinal walls
- 33. Human Small Intestine • Made up of three regions: 2. jejunum - Next to duodenum; 2.5 m in length 3. ileum - Last segment of the small intestine; 3.5 m in length - Contains Peyer’s patches - Organized lymphoid tissues - Protects the intestinal lumen from pathogenic bacteria
- 35. • Food is called chyle once it is in the small intestine
- 36. Human Large Intestine • the colon recovers water that has entered the alimentary canal as the solvent to various digestive juices • the large intestine harbors a rich flora of mostly harmless bacteria • the terminal portion of the colon is called the rectum, where feces are stored until they can be eliminated
- 40. Regulation of Digestion CCK - cholecystokinin
- 41. • the length of the vertebrate digestive system is also correlated with diet
- 42. • ruminants (deer, cattle, and sheep) have the most elaborate adaptations for a herbivorous diet
- 43. Nutritional Requirements • A nutritionally adequate diet satisfies three needs: – fuel (chemical energy) for all the cellular work of the body – organic raw materials animals use in biosynthesis (carbon skeletons to make many of their own molecules) – essential nutrients
- 44. – If the diet of a person or other animal is chronically deficient in calories, undernourishment results – an animal whose diet is missing one or more essential nutrients is said to be malnourished – marasmus, general undernourishment from a diet low in both calories and protein – kwashiorkor, protein malnourishment from a diet adequate in calories but deficient in protein – overnourishment or obesity results from excessive food intake
- 45. • in mammals, a hormone called leptin, produced by adipose cells, is a key player in a complex feedback mechanism regulating fat storage and use
- 46. Appetite-regulating hormones • ghrelin (stomach wall) – triggers feelings of hunger as mealtimes approach • leptin (adipose tissue) – suppresses appetite • PYY or peptide-tyrosine-tyrosine (small intestine) – after meals – appetite suppressant; counters ghrelin • insulin (pancreas) – a rise in blood sugar level after a meal
- 47. • animals require 20 amino acids to make proteins • essential amino acids must be obtained from food in prefabricated form – eight amino acids are essential in the adult human (phenylalanine, lysine, isoleucine, leucine, valine, methionine, tryptophan, and threonine) with histidine and arginine essential for normal growth of children
- 48. • protein deficiency from a vegetarian diet can be avoided by eating a combination of plant foods that complement each other to supply all essential amino acids
- 49. • vitamins are organic molecules required in the diet in small quantities • 13 vitamins essential to humans have been identified • water-soluble vitamins generally function as co-enzymes
- 50. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 51. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
- 52. • Minerals are simple inorganic nutrients, usually required in small amounts – humans and other vertebrates require large quantities of calcium and phosphorus for the construction and maintenance of bone – iron is a component of the cytochromes and of hemoglobin – while sodium, potassium, and chloride have a major influence on the osmotic balance between cells and the interstitial fluids, excess consumption of salt (sodium chloride) is harmful
