IB Chemistry on Redox, Reactivity Series and Displacement reaction
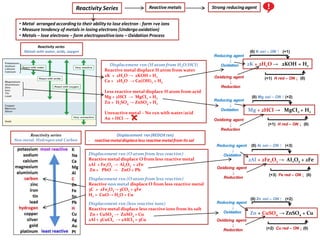
- 1. Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metals – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactivity series Metals with water, acids, oxygen Reactivity series Non metal, Hydrogen and Carbon Displacement rxn (H atom from H2O/HCI) Reactive metal displace H atom from water 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2 Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2 Less reactive metal displace H atom from acid Mg + 2HCI → MgCI2 + H2 Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 Unreactive metal – No rxn with water/acid Au + HCI → Displacement rxn (REDOX rxn) - reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2 (0) K oxi – ON ↑ (+1) (+1) H red – ON ↓ (0) Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) Mg oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+1) H red – ON ↓ (0) Reactivity series Non metal, Hydrogen and Carbon Mg + 2HCI → MgCI2 + H2 Displacement rxn (O atom from less reactive) Reactive metal displace O from less reactive metal 2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe Zn + PbO → ZnO + Pb Displacement rxn (O atom from less reactive) Reactive non metal displace O from less reactive metal 3C + 2Fe2O3→ 3CO2 + 4Fe H2 + CuO→ H2O + Cu Displacement rxn (less reactive ions) Reactive metal displace less reactive ions from its salt Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu 2Al + 3CuCI2 → 2AlCI3 + 3Cu Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation (0) Ai oxi – ON ↑ (+3) 2Al + 2Fe2O3 → AI2O3 + 2Fe (+3) Fe red – ON ↓ (0) Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) Zn oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+2) Cu red – ON ↓ (0)
- 2. Reactivity Series Reactivity series Metals with water, acids, oxygen Reactivity series Non metal, Hydrogen and Carbon Displacement rxn (H atom from H2O/HCI) Reactive metal displace H atom from water 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2 Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2 Less reactive metal displace H atom from acid Mg + 2HCI → MgCI2 + H2 Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 Unreactive metal – No rxn with water /acid Au + HCI → Displacement rxn (REDOX reaction) - reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol Reactivity series Non metal, Hydrogen and Carbon Displacement rxn (O atom from less reactive) Reactive metal displace O from less reactive metal 2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe Zn + PbO → ZnO + Pb Displacement rxn (O atom from less reactive) Reactive non metal displace O from less reactive metal C + 2Fe2O3→ 3CO2 + 4Fe H2 + CuO→ H2O + Cu Displacement rxn (less reactive ions) Reactive metal displace less reactive ions from its salt Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu 2Al + 3CuCI2 → 2AlCI3 + 3Cu Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Click here AI/CuCI3 displacement Click here to view Flinn Scientific Click here Iron extraction (Thermite) • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metals – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Click here microscale Fe reduction
- 3. Reactivity Series • Metals arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metals – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactivity series Non metal, Hydrogen and Carbon Reactive metals Strong reducingagent reactivity increase Strong reducing agent Oxidation rxn favour strongreducingagent strongreducingagent Reactivity series Non metal, Halogen (Gp 7) Metal → lose elec (Oxidation) M → M+ + Non Metal + gain elec → (Reduction) F + → F- strongoxidizingagent reactivity increase Strong oxidizing agent Reduction rxn favour Mg AI Zn Fe Pb Cu Ag Strongest reducing agent. Oxidized easily (lose e) Weakest reducing agent. Least readily oxidized F CI Br I Metals Non Metals Halogens Strongest oxidizing agent. Reduced easily (gain e) Weakest oxidizing agent. Least readily reduced
- 4. Reactivity Series • Metals arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metals – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent K ↔ K+ + e Na ↔ Na+ + e Ca ↔ Ca2+ + 2e Mg ↔ Mg2+ + 2e Al ↔ Al3+ + 3e Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e Sn ↔ Sn2+ + 2e Pb ↔ Pb2+ + 2e Cu ↔ Cu2+ + 2e Ag ↔ Ag+ + e Au ↔ Au+ + e Potassium metal, K • Strong ReducingAgent • High ↑ Tendencylose e Gold metal Au • Weak Reducing Agent • Low ↓ Tendencyto lose e Potassium ion K+ • Weak Oxidising Agent • Low ↓ Tendencygain e Gold ion Au+ • Strong Oxidising Agent • High ↑ Tendency gain e Strong Reducing Agent Strong Oxidising Agent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol • Add Zn, Mg, Cu, Pb into spotting tile • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it solution • Arrange metal in order of reactivity Mg Zn Pb Cu Magnesium nitrate Zinc nitrate Lead nitrate Copper nitrate Click here displacement expt Solution/ Metal Mg Zn Pb Cu Magnesium nitrate Zinc nitrate Lead nitrate Copper nitrate Result Zn → Zn 2+ + 2e (oxidized) Cu2+ + 2e → Cu (reduced) Zn displaces Cu from its sol Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu Click here redox practical filter paper Oxidation ability – Losing electron - +ve ions
- 5. K Na Ca Mg AI C Zn H Fe Sn Pb Cu Ag Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metal – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol • Add Zn, Mg, Cu, Pb into spotting tile • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it solution • Arrange metal in order of reactivity Mg Zn Pb Cu Magnesium nitrate Zinc nitrate Lead nitrate Copper nitrate Click here displacement expt Solution/ Metal Mg Zn Pb Cu Magnesium nitrate Zinc nitrate Lead nitrate Copper nitrate Result Zn → Zn 2+ + 2e (oxidized) Cu2+ + 2e → Cu (reduced) Zn displaces Cu from its sol Zn + Cu(NO3)2 → Zn(NO3)2 + Cu Most reactive Least reactive Zn more reactive О О Cu less reactive Add Zn into copper nitrate Displacement rxn – Brown Cu ppt deposited Blue sol fades away (Cu2+ conc decrease) Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) Zn oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+2) Cu red – ON ↓ (0) Observation Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu Mg > Zn > Pb > Cu
- 6. K Na Ca Mg AI C Zn H Fe Sn Pb Cu Ag Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metal – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol • Add Mg, Zn, Pb, Cu to spotting tile with AgNO3 • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it solution • Arrange metal in order of reactivity Silver nitrate Click here displacement expt Metal/ Solution Mg Zn Pb Cu Silver nitrate Result Cu → Cu2+ + 2e (oxidized) Ag+ + e → Ag (reduced) Cu displaces Ag+ from its sol Cu + AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag Less reactive О О Cu more reactive Add Cu into silver nitrate Displacement rxn – Grey Ag ppt deposited Blue sol forms (Cu2+ conc increases) Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) Cu oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+1) Ag red – ON ↓ (0) Observation Cu + AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag Mg > Zn > Pb > Cu > Ag Mg Zn Pb Cu Click here Cu/AgNO3 displacement
- 7. Metal/ Solution Mg Zn Fe Cu Hydrochloric acid (HCI) K Na Ca Mg AI C Zn H Fe Sn Pb Cu Ag Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metal – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its sol • Add Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu to spotting tile with HCI • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it solution • Arrange metal in order of reactivity HCI Click here displacement expt Result Zn → Zn2+ + 2e (oxidized) 2H+ + 2e → H2 (reduced) Zn displaces H+ from its sol Zn + 2HCI → ZnCI2 + H2 Less reactive О О Zn more reactive Add Zn into Hydrochloric acid Displacement rxn – Effervescence H2 gas seen Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) Zn oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+1) H red – ON ↓ (0) Observation Zn + HCI → ZnCI2 + H2 Mg > Zn > H > Fe > Cu Mg Zn Fe Cu H2 production Metal above Zn able to displace H from acid – H2 gas О
- 8. K Na Ca Mg AI C Zn H Fe Sn Sn Pb Cu Ag О Metal oside MgO ZnO Fe2O3 CuO Carbon Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metal – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its oxide/ores • Add Metal oxide into crucible with Carbon • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it ores • Arrange metal in order of reactivity C Click here displacement expt Result C → C2+ + 2e (oxidized) Fe3+ + 3e → Fe (reduced) C displace Fe3+ from its oxide 3C + Fe2O3 → 3CO + 2Fe Less reactive О C more reactive Add Carbon into iron oxide, Fe2O3 Displacement rxn – Effervescence CO gas seen Brown iron produced Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) C oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+3) Fe red – ON ↓ (0) Observation Mg > C > Zn > Fe > Cu MgO ZnO Fe2O3 CuO Iron extraction 3C + Fe2O3 → 3CO + 2Fe Metal above Pb able to displace Fe from its oxide О
- 9. Metal oxide C AI Fe2O3 K Na Ca Mg AI C Zn H Fe Sn Pb Cu Ag Reactivity Series • Metal arranged accordingto their ability to lose electron - form +ve ions • Measure tendency of metals in losing electrons (Undergooxidation) • Metal – lose electrons – form electropositiveions – Oxidation Process Reactive metals Strong reducingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive metaldisplace less reactive metalfrom its oxide/ores • Add carbon and aluminium to crucible with Fe2O3 • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive metal displace less reactive metal from it ores • Arrange metal in order of reactivity Result C → C2+ + 2e (oxidized) Fe3+ + 3e → Fe (reduced) C displace Fe3+ from its oxide 3C + Fe2O3 → 3CO + 2Fe Less reactive О О AI/C more reactive Add Carbon/Aluminium to iron oxide, Fe2O3 Displacement rxn – Effervescence seen CO gas produced Brown iron produced Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (0) C oxi – ON ↑ (+2) (+3) Fe red – ON ↓ (0) Observation AI > C > Fe Iron extraction 3C + Fe2O3 → 3CO + 2Fe Metal above Pb able to displace Fe from its oxide 2AI + Fe2O3 → AI2O3 + 2Fe Thermite welding AI → AI3+ + 3e (oxidized) Fe3+ + 3e → Fe (reduced) Al displace Fe3+ from its oxide О (0) AI oxi – ON ↑ (+3) (+3) Fe red – ON ↓ (0) Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction 2AI + Fe2O3 → AI2O3 + 2Fe
- 10. F CI Br I Reactivity Series • Non metal arranged accordingto their ability to gain electron - form -ve ion • Measure tendency of non metal in gaining electron(Undergo reduction) • Non Metal – gain electron – form electronegativeion – Reduction Process Reactive non metals (Halogens, Gp 7) Strong oxidizingagent Displacement rxn (REDOXrxn) - Reactive halogen displace less reactive halide from its solution • Add CI2, Br2, I2 into tubes . • Make observation if rxn happen • Reactive halogen displace less reactive halogen from its solution • Arrange halogen in order of reactivity Result 2Br- → Br2 + 2e (oxidized) CI + e → CI- (reduced) CI displace Br- from its solution CI2 + 2NaBr → 2NaCI + Br2 Br less reactive О О CI more reactive Add CI2 into NaBr Displacement rxn – reddish brown solution Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (-1) Br oxi – ON ↑ (0) (0) CI red – ON ↓ (-1) Observation F > CI > Br > I О Halogen/ Halide CI2 Br2 I2 Sodium chloride Sodium bromide Sodium iodide Click here video displacement rxn CI2 + 2NaBr -> 2NaCI + Br2 ✓ CI2 + 2NaI -> 2NaCI + I2 ✓ Br2 + NaCI -> ✗ Br2 + 2NaI -> 2NaBr + I2 ✓ I2 + NaCI -> ✗ I2 + NaBr -> ✗ Reactive halogen displace less reactive halogen from its halide solution CI2 + 2NaBr → 2NaCI + Br2 Redox rxn gallium beating heart Result
- 11. F2 + 2KCI -> 2KF + CI2 CI2 + 2KBr -> 2KCI + Br2 Br2 + 2KI -> 2KBr + I2 Ag+ + CI- -> AgCI Ag+ + Br- -> AgBr Ag+ + I- -> AgI Chemical PropertiesGroup 17 Size increase Reactionwith water Click here video fluorine chemistry shell 2.7 2.8.7 2.8.8.7 2.8.18.18.7 CI F Br I Ability attract electron decrease/ENlower Reactivitydecrease Group 17 (Halogen) Chemicalreaction CI2 + H2O -> HCI + HOCI Br2 + H2O -> HBr + HOBr I2 + H2O -> HI + HOI Reactionwith AgNO3 Adding AgNO3 AgCI – white ppt AgBr - yellow cream ppt AgI – yellow ppt Kept in seal, reactive Fluorine – yellow gas Chlorine – greenish gas Bromine – brown liquid Iodine – violet solid Click here video on chlorine chemistry Similar chemical property - decrease reactivity Chlorine – dissolve quickly – yellowish HOCI Bromine – dissolve slowly – brown HOBr Iodine – slightly soluble - brown HOI DisplacementReaction Reactive halogen displace less reactive halogen from its halide solution Click here video displacement reaction Strong oxidizingagent
- 12. Add NaBrAdd NaCIAdd NaIAdd NaCIAdd NaIAdd NaBr violet solid brown liquid yellow gas Click here video displacement rxn Click here video displacement rxn CI2 + 2NaBr -> 2NaCI + Br2 ✓ CI2 + 2NaI -> 2NaCI + I2 ✓ Br2 + NaCI -> ✗ Br2 + 2NaI -> 2NaBr + I2 ✓ I2 + NaCI -> ✗ I2 + NaBr -> ✗ Chemical PropertiesGroup 17 Group 17 (Halogen) greenish gas Displacement Reaction Reactive halogen displace less reactive halogen from its halide solution CI2 in hexane Br2 in hexane I2 in hexane Br2 in hexane I2 in hexane I2 in hexane CI2 + 2NaBr -> 2NaCI + Br2 CI2 + 2NaI -> 2NaCI + I2 ✗ Br2 + 2NaI -> 2NaBr + I2 ✗ ✗ Strong oxidizingagent
- 13. 2Li + CI2 -> 2LiCI 2Na + CI2 -> 2NaCI 2K + CI2 -> 2KCI Chemical PropertiesGroup 1 Size increase Reactionwith water 4Li + O2 -> 2Li2O 4Na + O2 -> 2Na2O 4K + O2 -> 2K2O Click here video potassium in water shell 2.1 2.8.1 2.8.8.1 2.8.8.18.1 Na Li K Rb lose electron easily electropositive Reactivity increase Group 1 (Alkali Metal) Chemicalreaction 2Li + 2H2O -> 2LiOH + H2 2Na + 2H2O -> 2NaOH + H2 2K + 2H2O -> 2KOH + H2 Reaction with oxygen Reactionwith halogen Lithium – move slowly surface water – red flame Sodium – move fast, hissing sound – yellow flame Potassium – move fast, ignite - lilac flame Turn red litmus blue- produce hydrogen gas Solution of metal hydroxide/alkaline produced Click here video sodium in water Similar chemical property but diff reactivity Lithium –burn slowly , red flame Sodium – burn brightly, yellow flame Potassium –burn very brightly, lilac flame Kept in paraffin oil Strong reducing agent Reduce H+ ion to H2 gas (losing e to H+) Strong reducingagent Oxidizing agent using potassium chlorate
- 14. Redox (Oxidation and Reduction) Oxidation – Gain of oxygen ↑ Oxidation – Loss of hydrogen ↓ Reduction – Gain of hydrogen ↑ Reduction – Loss of oxygen ↓ Oxidation Reduction Gain oxygen ↑ Loss oxygen ↓ Gain oxidation Number ↑ Loss oxidation Number ↓ Loss hydrogen↓ Gain hydrogen ↑ Loss electron ↓ Gain electron ↑ Ca + O2 → CaO CH4 + 2O2 → CO2+ 2H2O gain oxygen gain oxygen Zn + CuO → ZnO + Cu PbO + CO → Pb + CO2 loss oxygen loss oxygen H2S + CI2 → S +2HCI loss hydrogen H2S + CI2 → S + 2HCI Redox- Oxidation state change - Electron transfer CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O gain hydrogen Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu Zn + CI2 → ZnCI2 No gain/loss oxygen/hydrogen Redox gain oxygen gain hydrogen Reduction Oxidation Are these redox rxns? Most rxn does not involve H2 and O2
- 15. carbon oxidized Oxidation Reduction Gain oxygen ↑ Loss oxygen ↓ Loss hydrogen ↓ Gain hydrogen ↑ Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) Rxn involve gain/loss of oxygen/hydrogen CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O Gain hydrogen oxygen reduced gain oxygen carbon oxidized Rxn involve gain/loss of electron Oxidation Reduction Gain ON ↑ Loss ON ↓ Loss electron ↓ Gain electron ↑- broader definition - cover more rxn types lead reduced gain oxygen carbon oxidized (-4) (+4) (0) (-2) ON ↑ ON ↓ oxygen reduced carbon oxidized (+2) (0) lead reduced (+2) (+4) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O ON ↑ ON ↓ loss oxygen PbO + CO → Pb + CO2PbO + CO → Pb + CO2 Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent Causes Oxidation Cause Reduction Undergo reduction Undergo oxidation Gain electron ↑ Loss electron ↓ Decrease oxidation number ↓ Increase oxidation number ↑ Oxidation Reduction Gain oxygen ↑ Loss oxygen ↓ Gain oxidation Number ↑ Loss oxidation Number ↓ Loss hydrogen ↓ Gain hydrogen ↑ Loss electron ↓ Gain electron ↑ Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent MnO4 - Fe2+ Cr2O7 2- SO2 HNO3 I- H2O2 H2S CI2 SO3 2-
- 16. CI2 + 2KBr-→ 2KCI + Br2 3CuO + 2NH3→ 3H2O+ 3Cu + N2 Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) (+7) (+2)Mn red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe oxi – ON ↑ (+3) MnO4 - + Fe2+ + 8H+ → Mn2+ + Fe3+ 4H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent MnO4 - Fe2+ Reduction Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent CI2 Br- Reduction Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation (0) CI red – ON ↓ (-1) (-1) Br - oxi – ON ↑ (0) Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent CuO NH3 Reduction Oxidation Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation (-3) NH3 oxi – ON ↑ (0) Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (+2) Cu red – ON ↓ (0) 2HCI + Zn → H2 + ZnCI2 (0) Zn oxi – ON ↑ (+2)Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (+1) H red – ON ↓ (0) Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent HCI Zn Reduction Oxidation
- 17. CI2 + 2KBr-→ 2KCI + Br2 3CuO + 2NH3→ 3H2O+ 3Cu +N2 Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) (+7) (+2)Mn red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe oxi – ON ↑ (+3) MnO4 - + 8H+ + Fe2+ → Mn2+ + Fe3+ 4H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction MnO4 - + 5e → Mn2+ Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation (0) CI red – ON ↓ (-1) (-1) Br - oxi – ON ↑ (0) Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation (-3) NH3 oxi – ON ↑ (0) Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (+2) Cu red – ON ↓ (0) 2HCI + Zn → H2 + ZnCI2 (0) Zn oxi – ON ↑ (+2)Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction (+1) H red – ON ↓ (0) Reducing Agent Oxidation Fe 2+ → Fe2+ + e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Reducing Agent Oxidation 2Br - → Br2 + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Oxidizing Agent Reduction CI2 + 2e → 2CI- Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Reducing Agent Oxidation (NH3) -N3- → N + 3e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Oxidizing Agent Reduction (CuO) Cu2+ + 2e → Cu Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Reducing Agent Oxidation Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Oxidizing Agent Reduction 2H+ + 2e → H2 Gain electron Decrease ON ↓
- 18. Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) Half equations Oxidation rxn Oxidation half eqn Reduction half eqn Loss electron ↓ Reduction rxn Loss hydrogen ↓ Gain oxygen ↑ Gain ON ↑ Gain electron ↑ Gain hydrogen ↑ Loss oxygen ↓ Loss ON ↓ OxidizingAgentReducing Agent Oxidation rxn Reduction rxn lose electron Zn + 2H+ → H2 + Zn2+ Zn → Zn2+ + 2e 2H+ + 2e → H2 (0) ON increase ↑ (+2) Zn → Zn2+ + 2e 2H+ + 2e → H2 2H+ + Zn → Zn2+ + H2 lose electron gain electron (+1) ON decrease ↓ (0) Completefull eqn Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + CuOxidation half eqn Zn → Zn2+ + 2e lose electron (0) ON increase ↑ (+2) Reduction half eqn Cu2+ + 2e → Cu (+2) ON decrease ↓ (0) gain electron Zn → Zn2+ + 2e Cu2+ + 2e → Cu Cu2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Cu Half equations
- 19. Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) Half equations Oxidation half eqn Reduction half eqn Zn → Zn2+ + 2e 2H+ + 2e → H2 (0) ON increase ↑ (+2) Zn → Zn2+ + 2e 2H+ + 2e → H2 2H+ + Zn → Zn2+ + H2 lose electron gain electron (+1) ON decrease ↓ (0) Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqn Zn → Zn2+ + 2e lose electron (0) ON increase ↑ (+2) Reduction half eqn Cu2+ + 2e → Cu (+2) ON decrease ↓ (0) gain electron Zn → Zn2+ + 2e Cu2+ + 2e → Cu Cu2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Cu Half equations Zn + 2HCI → H2 + ZnCI2 Zn + 2H+ + 2CI- → H2 + Zn2+ + 2CI - Completeionic/redox eqn Zn + 2H+ → H2 + Zn2+ spectator ionsspectator ions Zn + 2H+ → H2 + Zn2+ Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu Zn + Cu2++ SO4 2- → Zn2+ + SO4 2- + Cu Completefull eqn Completeionic/redox eqn spectator ions Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu Half equations Half equations Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
- 20. Redox (Oxidationand Reduction) Half equations Oxidation half eqn Reduction half eqn Mg → Mg2+ + 2e Pb2+ + 2e → Pb (0) ON increase ↑ (+2) Mg → Mg2+ + 2e Pb2+ + 2e → Pb Pb2+ + Mg → Mg2+ + Pb lose electron gain electron (+2) ON decrease ↓ (0) Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqn 2Br- → Br2 + 2e lose electron (-1) ON increase ↑ (0) Reduction half eqn CI2 + 2e → 2CI- (0) ON decrease ↓ (-1) gain electron 2Br- → Br2 + 2e CI2 + 2e → 2CI- CI2 + 2Br- → 2CI- + Br2 Half equations Mg + PbO → Pb + MgO Mg + Pb2+ + O2- → Pb + Mg2+ + O 2- Completeionic/redox eqn spectator ionsspectator ions Mg + Pb2+ → Pb + Mg2+ 2KBr + CI2 → Br2 + 2KCI 2K+ + 2Br- + CI2 → Br2 + 2K+ + 2CI - Completefull eqn Completeionic/redox eqn spectator ions 2Br- + CI2 → Br2 + 2CI- Half equations Half equations Mg + Pb2+ → Pb + Mg2+ 2Br- + CI2 → Br2 + 2CI- lose electron
- 21. MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O ConstructingHalf and complete redox equation (+7) (+2)Mn red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe oxi – ON ↑ (+3) MnO4 - + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction MnO4 - + 5e → Mn2+ Reducing Agent Oxidation Fe 2+ → Fe2+ + e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O -add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges -add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer MnO4 - → Mn2+ MnO4 - → Mn2+ + 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ → Mn2++ 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O Fe2+ → Fe3+ Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- 5Fe2+ → 5Fe3+ + 5e-MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O x 5x 1 MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O 5Fe2+ → 5Fe3+ + 5e- + MnO4 - - In acidic medium - Strong oxidizing agent MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ 4H2O
- 22. 2MnO4 - + 5SO2+ 2H2O → 2Mn2+ + 5SO4 2- + 4H+ ConstructingHalf and complete redox equation (+7) (+2)Mn red - ON ↓ (+4) SO2 oxi – ON ↑ (+6) 2MnO4 - + 5SO2 + 2H2O→ 2Mn2+ + 5SO4 2- + 4H+ Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction MnO4 - + 5e → Mn2+ Reducing Agent Oxidation SO2 → SO4 2- + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer MnO4 - → Mn2+ MnO4 - → Mn2+ + 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ → Mn2++ 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O SO2 → SO4 2- 2MnO4 - + 16H+ + 10e- → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O x 5x 2 2MnO4 - + 16H+ + 10e- → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O 5SO2 + 10H2O → 5SO4 2- + 20H+ + 10e- + 2MnO4 - + 5SO2 + 2H2O→ 2Mn2+ + 5SO4 2- 4H+ SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- 5SO2 + 10H2O → 5SO4 2- + 20H+ + 10e-
- 23. 2MnO4 - + 5H2O2 + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5O2 + 8H2O ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+7) (+2)Mn red - ON ↓ (-1) H2O2 oxi – ON ↑ (0) 2MnO4 - + 5H2O2 + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5O2 + 8H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction MnO4 - + 5e → Mn2+ Reducing Agent Oxidation H2O2 → O2 + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer MnO4 - → Mn2+ MnO4 - → Mn2+ + 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ → Mn2++ 4H2O MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O 2MnO4 - + 16H+ + 10e- → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O x 5x 2 2MnO4 - + 16H+ + 10e- → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O 5H2O2 → 5O2 + 10H+ + 10e- + 2MnO4 - + 5H2O2 + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5O2 + 8H2O H2O2 → O2 H2O2 → O2 + 2H+ H2O2 → O2 + 2H+ + 2e- 5H2O2 → 5O2 + 10H+ + 10e-
- 24. Cr2O7 2- + 3NO2 - + 8H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3NO3 - + 4H2O Cr2O7 2-→ 2Cr3+ ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+6) (+3)Cr red - ON ↓ (+3) NO2 - oxi – ON ↑ (+5) Cr2O7 2- + 3NO2 - + 8H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3NO3 - + 4H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction Cr2O7 2- + 6e- → 2Cr3+ Reducing Agent Oxidation NO2 - → NO3 - + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 3x 1 Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O 3NO2 -+ 3H2O → 3NO3 - + 6H+ + 6e- + Cr2O7 2- + 3NO2 - + 8H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3NO3 - + 4H2O Cr2O7 2- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O NO2 - → NO3 - NO2 - + H2O → NO3 - NO2 - + H2O → NO3 - + 2H+ NO2 - + H2O → NO3 - + 2H+ + 2e- 3NO2 - + 3H2O → 3NO3 - + 6H+ + 6e-
- 25. Cr2O7 2- + 6Fe2+ + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2-→ 2Cr3+ ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+6) (+3)Cr red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe2+ oxi – ON ↑ (+3) Cr2O7 2- + 6Fe2+ + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction Cr2O7 2- + 6e- → 2Cr3+ Reducing Agent Oxidation Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 6x 1 Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O 6Fe2+ → 6Fe3+ + 6e- + Cr2O7 2- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O Cr2O7 2- + 6Fe2+ + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ 7H2O Fe2+ → Fe3+ Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e 6Fe2+ → 6Fe3+ + 6e
- 26. ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+5) (-1)CIO3 - red - ON ↓ (-1) I- oxi – ON ↑ (0) CIO3 - + 6I- + 6H+ → 3I2 + CI- + 3H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction CIO3 - + 6e- → CI- Reducing Agent Oxidation 2I- → I2 + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 3x 1 CIO3 - + 6H+ + 6e- → CI- + 3H2O 6I- → 3I2 + 6e- + CIO3 - + 6I- + 6H+ → 3I2 + CI- + 3H2O CIO3 - → CI- CIO3 - → CI- + 3H2O CIO3 - + 6H+ → CI- + 3H2O CIO3 - + 6H+ + 6e- → CI- + 3H2O CIO3 - + 6H+ + 6e- → CI- + 3H2O 2I- → I2 2I- → I2 + 2e- 6I- → 3I2 + 6e- CIO3 - + 6H++ 6I- → 3I2 + 3H2O
- 27. ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+5) (+2)NO3 - red - ON ↓ (0) Cu oxi – ON ↑ (+2) 2NO3 - + 3Cu + 8H+ → 3Cu2+ + 2NO + 4H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction NO3 - + 3e- → NO Reducing Agent Oxidation Cu → Cu2+ + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 3x 2 2NO3 - + 8H+ + 6e- → 2NO + 4H2O 3Cu → 3Cu2+ + 6e- + 2NO3 - + 3Cu + 8H+ → 3Cu2+ + 2NO + 4H2O NO3 - → NO NO3 - → NO + 2H2O NO3 - + 4H+ → NO + 2H2O NO3 - + 4H+ + 3e- → NO + 2H2O 2NO3 - + 8H+ + 6e- → 2NO + 4H2O Cu → Cu2+ Cu → Cu2+ + 2e- 3Cu → 3Cu2+ + 6e- 2NO3 - + 8H+ + 3Cu → 3Cu2+ +2NO + 4H2O
- 28. HNO3 +3Fe2+ + 3H+ → 3Fe3+ + NO + 2H2O ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (+5) (+2)HNO3 red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe oxi – ON ↑ (+3) HNO3 + 3Fe2+ + 3H+ → 3Fe3+ + NO + 2H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction HNO3 + 3e- → NO Reducing Agent Oxidation Fe 2+ → Fe3++ e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 3x 1 HNO3 + 3H+ + 3e- → NO + 2H2O 3Fe2+ → 3Fe3+ + 3e- + HNO3 → NO + 2H2O HNO3+ 3H+ → NO + 2H2O HNO3 + 3H+ + 3e- → NO + 2H2O HNO3 + 3H+ + 3e- → NO + 2H2O Fe2+ → Fe3+ HNO3 + 3Fe2+ + 3H+ → 3Fe3+ + NO + 2H2O HNO3 → NO Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- 3Fe2+ → 3Fe3+ + 3e-
- 29. H2O2 + 2Fe2+ +2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (-1) (-2)H2O3 red - ON ↓ (+2) Fe oxi – ON ↑ (+3) H2O2 + 2Fe2+ + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction H2O3 + e- → H2O Reducing Agent Oxidation Fe 2+ → Fe3++ e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer x 2x 1 H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → 2H2O 2Fe2+ → 2Fe3+ + 2e- + Fe2+ → Fe3+ Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- 2Fe2+ → 2Fe3+ + 2e- H2O2 + 2Fe2+ + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O H2O2 → H2O H2O2 → 2H2O H2O2 + 2H+ → 2H2O H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → 2H2O H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → 2H2O
- 30. CI2 + SO2 + 2H2O → 2CI- + SO4 2- + 4H+ ConstructingHalf and complete redox equations (0) (-1)CI2 red - ON ↓ (+4) SO2 oxi – ON ↑ (+6) CI2 + SO2 + 2H2O→ 2CI- + SO4 2- + 4H+ Oxidizing agent ↓ Reduction Reducing agent ↓ Oxidation Oxidizing Agent Reduction CI2 + 2e → 2CI- Reducing Agent Oxidation SO2 → SO4 2- + 2e- Loss electron Increase ON ↑ Gain electron Decrease ON ↓ Completefull eqn Oxidation half eqnReduction half eqn 1. Balance # O - add H2O 2. Balance# H add H+ 3. Balance# charges - add electrons 4. Balance# electron transfer SO2 → SO4 2- x 1x 1 CI2 + 2e- → 2CI- SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- + SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- CI2 + SO2 + 2H2O→ 2CI- + SO4 2- + 4H+ CI2 → 2CI- CI2 + 2e- → 2CI- CI2 + 2e- → 2CI- SO2 + 2H2O → SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e-
- 31. MnO4 - (Acidic medium) - Strong oxidizing agent - Gain 5 e- MnO4 - - (Neutral medium) - Moderate oxidizing agent - Gain 3 e MnO4 - + 2H2O + 3e- →MnO2 + 4OH- MnO4 - - (Basic medium) - Weak oxidizing agent - Gain 1 e DisproportionalReaction Substance both oxidized and reduced simultaneously Substance acts as oxidizing and reducing agent Redox Reaction (-1) Br - oxi – ON ↑ (0) (0) CI red – ON ↓ (-1) CI2 + 2KBr-→ 2KCI + Br2 Reducing agent - oxidized Oxidizingagent – reduced Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent Concept Map Redox Reaction in diff medium (-1) H2O2 red – ON ↓ (-2) H2O2 → H2O + 1/2O2 (-1) H2O2 oxi – ON ↑ (0) (0) CI2 red – ON ↓ (-1) CI2 + H2O → HOCI + HCI (0) CI2 oxi – ON ↑ (+1) (+3) HNO2 red – ON ↓ (+2) HNO2 → HNO3 + 2NO + 2H2O (+3) HNO2 oxi – ON ↑ (+5) Cu2SO4 → CuSO4 + Cu (+1) Cu red – ON ↓ (0) (+1) Cu oxi – ON ↑ (+2) MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O (+7) ON decrease ↓ (+2) (+7) ON decrease ↓ (+4) MnO4 - + e- → MnO4 2- (+7) ON decrease ↓ (+6)
- 32. Sn2+ + 2Fe3+ → Sn4+ + 2Fe2+2Fe2+ + CI2 → 2Fe3+ + 2CI-Ca + 2H+ → Ca2+ + H2 IB Redox Questions Deduce half eqn of oxidation and reduction for the following Ca + 2H+ → Ca2+ + H2 2Fe2+ + CI2 → 2Fe3+ + 2CI- Sn2+ + 2Fe3+ → Sn4+ + 2Fe2+ 0 +1 +2 0 Ca → Ca2+ + 2e 2H+ + 2e → H2 oxidation reduction +2 0 +3 -1 2Fe2+ → Fe3+ + 2e CI2 + 2e → 2CI- oxidation reduction +2 +3 +4 +2 Sn2+ → Sn4+ + 2e 2Fe3+ + 2e → 2Fe2+ Substancesacting as oxidizingand reducing agent 2MnO4 - + 5H2O2 + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5O2 + 8H2O H2O2 + 2Fe2+ + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O H2O2 + 2I- + 2H+ → I2 + 2H2O Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent MnO4 - Fe2+ Cr2O7 2- SO2 HNO3 I- H2O2 H2S CI2 SO3 2- Acidified H2O2 act as oxidizing agent - Oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+ - Oxidizes I- to I2 Acidified MnO4 - act as more powerful oxidizing agent - Oxidizes weaker oxidizing agent H2O2 to H2O and O2 - H2O2 act as reducing agent Identify oxidizingand reducing agentfor followingrxn. 5As2O3 + 2MnO4 - + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5As2O5 + 8H2O 2NO3 - + 3Cu + 8H+ → 3Cu2+ + 2NO+ 4H2O Cr2O7 2- + 3NO2 - + 8H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3NO3 - + 4H2O 1 2 3 oxidizing agent oxidizing agent oxidizing agent reducing agent reducing agent reducing agent
