Wool fibers assi
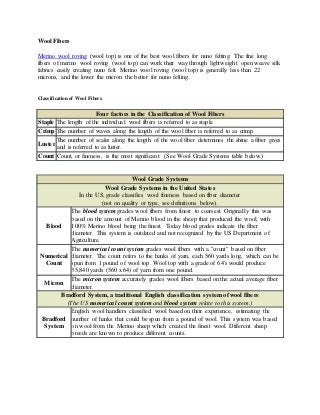
- 1. Wool Fibers Merino wool roving (wool top) is one of the best wool fibers for nuno felting. The fine long fibers of merino wool roving (wool top) can work their way through lightweight open weave silk fabrics easily creating nuno felt. Merino wool roving (wool top) is generally less than 22 microns, and the lower the micron the better for nuno felting. Classification of Wool Fibers Four factors in the Classification of Wool Fibers Staple The length of the individual wool fibers is referred to as staple. Crimp The number of waves along the length of the wool fiber is referred to as crimp. Luster The number of scales along the length of the wool fiber determines the shine a fiber gives and is referred to as luster. Count Count, or fineness, is the most significant. (See Wool Grade Systems table below.) Wool Grade Systems Wool Grade Systems in the United States In the US, grade classifies wool fineness based on fiber diameter (not on quality or type, see definitions below). Blood The blood system grades wool fibers from finest to coarsest. Originally this was based on the amount of Merino blood in the sheep that produced the wool, with 100% Merino blood being the finest. Today blood grades indicate the fiber diameter. This system is outdated and not recognized by the US Department of Agriculture. Numerical Count The numerical count system grades wool fibers with a "count" based on fiber diameter. The count refers to the hanks of yarn, each 560 yards long, which can be spun from 1 pound of wool top. Wool top with a grade of 64's would produce 35,840 yards (560 x 64) of yarn from one pound. Micron The micron system accurately grades wool fibers based on the actual average fiber diameter. Bradford System, a traditional English classification system of wool fibers (The US numerical count system and blood system relate to this system.) Bradford System English wool handlers classified wool based on their experience, estimating the number of hanks that could be spun from a pound of wool. This system was based on wool from the Merino sheep which created the finest wool. Different sheep breeds are known to produce different counts.
- 2. United States Standards for Grades of : WOOL WOOL TOP Numerical Count System Micron System Micron System Finer than 80's ≤ 17.69 ≤ 18.09 80's 17.70 - 19.14 18.10 - 19.59 70's 19.15 - 20.59 19.60 - 21.09 64's 20.60 - 22.04 21.10 - 22.59 62's 22.05 - 23.49 22.60 - 24.09 60's 23.50 - 24.94 24.10 - 25.59 58's 24.95 - 26.39 25.60 - 27.09 56's 26.40 - 27.84 27.10 - 28.59 54's 27.85 - 29.29 28.60 - 30.09 50's 29.30 - 30.99 30.10 - 31.79 48's 31.00 - 32.69 37.80 - 33.49 46's 32.70 - 34.39 33.50 - 35.19 44's 34.40 - 36.19 35.20 - 37.09 40's 36.20 - 38.09 37.10 - 38.99 36's 38.10 - 40.20 39.00 - 41.29 Coarser than 36's ≥ 40.21 ≥ 41.30 (source: United States Standards for Grades of Wool) Processing Methods of Wool Fibers (Sliver, Tops, and Roving) Sliver, tops, and roving are produced as an intermediate step in the processing of wool for manufacturing. Wool fibers are processed into products via one of two methods. The worsted system of manufacturing, utilizes the longer length wools within a grade. The woolen system of manufacturing, utilizes the shorter length wools within a grade. The wool is scoured to remove the bulk of the impurities by washing. Then, the wool is carded. The clean dry wool passes through rollers that have thin wire teeth which untangle the fibers and arrange them into a flat sheet called a web. The web is then formed into narrow ropes, or slivers. If the batch of wool is for the woolen system, the slivers are gently twisted into ropelike strands called roving and wound into balls. If the batch of wool is for the worsted system, the slivers are combed to remove the shorter fibers or noils and create smooth parallel fibers producing wool top. The wool top is also gently twisted into ropelike strands called roving and wound into balls.
- 3. Definitions of Wool Fibers Definitions of Wool Fibers (source: United States Standards for Grades of Wool) Card sliver Wool that has been scoured and carded and formed into a continuous, untwisted strand of loosely assembled fibers. Fineness This term refers to fiber diameter. Fleece The wool of one sheep obtained by shearing. Grade (1) With respect to wool, this term means a numerical designation of wool fineness based on average fiber diameter and variation of fiber diameter. It does not include characteristics such as length, crimp, strength, elasticity, luster, hand, and color--all of which affect the spinnability of wool and the properties of the yarn and fabric and which are usually referred to as "quality." Neither does it apply to wool by geographic origin, breed of sheep, manner of preparation for market, or a combination of characteristics which makes wool appropriate for a specific use. These characteristics are usually referred to as "type." (2) With respect to wool top, this term means a numerical designation of wool top fineness based on average fiber diameter dispersion. It does not include characteristics such as length, crimp, strength, elasticity, luster, hand, and color--all of which affect the spinnability of wool and the properties of the yarn and fabric. The characteristics are usually referred to as "quality." Grease wool Wool, as obtained from living sheep. Micron A unit of linear measurement equal to 1/1000 millimeter or 1/25400 inch. Pulled wool Wool obtained from the pelts of sheep by pulling or similar means after subjecting the pelt to sweating, the use of a depilatory, or other auxiliary treatment to loosen the wool fibers from the skin. Scoured wool Wool from which the bulk of the impurities have been removed by washing in warm water, soap, and alkali or by an equivalent process. Skirted fleece A fleece from which the belly, britch, and stained portions have been removed. Sorted wool Wool removed from various parts of fleeces and combined into different groups or sorts, each of which has closely similar fineness, length, and other qualities. Wool The fiber from the fleece of sheep. Wool top A continuous untwisted strand of scoured wool fibers from which the shorter fibers or noils have been removed by combing.
