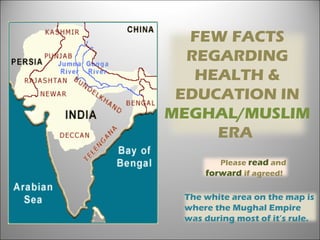
Muslim mughal era_india
- 1. The white area on the map is where the Mughal Empire was during most of it’s rule. FEW FACTS REGARDING HEALTH & EDUCATION IN MEGHAL/MUSLIM ERA Please read and forward if agreed!
- 2. We need to provide exact/correct knowledge of the legacy of the Muslims and Mughals era in the field of education and Medicines beside other fields as well, since this is vital to our nation
- 3. especially new generations as libraries and a reading culture is now missing from our lives of ordinary Pakistanis.
- 4. Our corrupt and paid media as representative of Non-Muslims and Jews trying to change the mind of our youth in favour of them and against the Muslims. Most of the so called intellectuals, writers and anchors etc playing vital role in emphasizing to present Muslims as negative and narrow minded rulers.
- 5. let us take an overview of the life and times of the Muslims/Mugha To correct the obvious
- 6. Tughluq Dynasty Hospitals •70 hospitals alone in Delhi •1200 physicians-as state employees Muhammad bin Tughluq (CE 1325-1352)
- 7. •great interest in building hospitals. •great kindness and humanity. •established a hospital for the sick and troubled •both for natives and strangers •Arab physicians were appointed to superintend it. Feroz Shah Tughluq
- 8. •36 lacs spends against Salaries •4200 afflicted persons receives •monthly allowances •Medicine •food and drinks (Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi composed by Shams-i-Siraj Afif)
- 9. • accommodation for 4000 patients • many physicians were appointed • the biggest hospital in the world • 52 rest houses for travellers •Provided food and other necessities Source: According to the journal Mahanama The Grand Hospital Dar-ul-Shifa (the house of cure) Sultan Muhammad Qutab Shah IV (CE 1595)
- 10. Highly qualified expert in diagnosis of diseases and looked after the patients •Scholars learned and well-read in the branches of sciences and medicines. Physicians categories
- 11. The British rule of India highlighted as being the real benefactor of the modern states of Pakistan and India The Mughal India from the layman’s perception is often defame to a baser level Whether the Mughals had contributed to India anything other than buildings and gardens Argument commonly arose While praising the British rulers for developing India through education, roads and railways
- 12. Mughal empire classic period • 1526-1530 Babur • 1530-1556 Humayun • 1556-1605 Akbar • 1605-1627 Jahangir • 1628-1658 Shah Jahan • 1659-1707 Aurangzeb
- 13. • In present language that would mean • economic superiority • and prosperity of the people of that nation state • today’s context: • a large arsenal • technological advancement • and a stable, viable, democratic governance with a literate population The Super Power of the era Mughal Empire No doubt about
- 14. Mughal Era Hospitals The Mughul Dynasty changed India into one of the greatest empires. It was stretched out over almost two centuries In the field of Health Take a tour of the era
- 15. System spread all over the India • Many renowned hakims and scholars from Persia and Central Asian countries • Good number of government hospitals & private clinics in operation by many physicians • Services for deprived people without distinction of • Caste and creed. Akbar’s period Unani medicine
- 16. Jahangir and Shah Jahan • Both not only continued the hospitals built by Akbar, but also built more hospitals for the help of the sick and needy people • By providing more medical facilities to the people. During Aurangzeb’s period many hospitals were situated in the capital and even in the outlying cities. Aurangzeb did the same
- 17. Besides the emperors Individuals also built hospitals Prosperous personalities Nobles personalities Many Citizens Nawab Khayr Andish Khan Kumbha built such a hospital at Etawah the population out of reach of such expensive medication
- 18. Thus we see that in mughal/muslim India, the state, as well as the rich/noble people, provided medical facilities for the poor and the common man without any distinction of caste or creed. The state in India always realized its responsibility to its citizens and functioned as a welfare state. In contrast, even the richest nations like the USA have made medicinal facilities a totally private enterprise, placing half the population out of reach of such expensive medication Conclusion Sources: Jaggi, O.P. 2000. Hospitals in India. In Medicine in India: Modern Period, D.P. Chattopadhyaya (Ed.). New Delhi: PHISPC. Pp. 70-74. Verma, R.L. 1992. Indian –Arab relations in medical sciences. In P.V.Sharma (Ed.) History of Medicine in India. New Delhi: Indian National Science Academy. Pp. 465-484.
- 19. In the field of Education Before the advent of the Muslims/Mughals in India Indian had already developed a system of education Confined to small groups of people only Private individuals who set up educational institutions for the spread of education in a limited section of society Where no government considered it to be its duty to promote public education.
- 20. Muslim Educational System in India The Muslim educational system in India has developed in the eight century. in Punjab in the twelfth century The Islamic pattern of education was well developed before the Muslim rules developed India. The Madarsahs مدرسہ as the centers of orthodoxy صحیح عقیدہ , and they aimed at a stabilizing a body of beliefs and a discipline prescribed by Islam
- 21. The Slave Dynasty (1206-1286) Qutubuddin Aibak (1206-210 A.D) • He loved education • Maktabs (primary school) attached to Mosques • means network of Maktabs (primary school) • Muslim religion was principally taught also Razia Sultana (1236-1242 A.D) an able female administrator • She also loved education • Learned person greatly honured in her court • Education was encouraged and expanded • Maktabs (primary school) attached to Mosques • A big educational institution “Mauiji Madarsa” was established at Delhi
- 22. The Slave Dynasty (1206-1286) Nasiruddin (1246-1265 A.D) • Greatest lover of education • Himself a learned man • Encouraged education • Hounoured learned persons who adorned his court • Persian was developed further • Many books were written in his tenure including Tabkati Nasiri the famous historical document • Used to copy Quran e Pak and prepare caps for earning his livelihood http://www.developindiagroup.co.in/PDFs/General%20Knowledge%20English %202012.pdf
- 23. •Balban (1266-1285 A.D) Strongest sultan of Salve dynasty • An ardent lover of literature • Encouraged education • Patronized a number of Scholars in his court • Reward to Scholars on their great work • Number of learned people fled to India Asia (becasuse of Changes Khan) • Amir Khusro was most influential and bright scholar of his court • Literature was greatly encouraged The Slave Dynasty (1206-1286)
- 24. Jalaluddin Khilji (1290-1296 A.D) Founder of Dynasty • Encouraged education • Hounored learned persons • Established a library at Kiluguri ner Delhi • Head of library was Amir Khusro Alauddin Khilji (1296-1316) • Worst period for education The Khilji Dynasty (1290-1316) Entire Dynasty was lover of education
- 25. The Tughlaq Dynasty (1320-1389) Ghasauddin Tughlaq (1320-1325 A.D) • Great lover of education • Developed Literature • Encouraged education • Respected Scholars • Developed a cultural society • Rewarded a number of scholars for their work • Extended many facilities to learned persons All three were Great lover of education
- 26. Muhammad Bin Tughlaq (1325-1351 A.D) • Himself was a great writer and scholar • Great lover of education • Principally consisted of learned persons, writers, artists and philosophers • Big Assembly of learned persons • Encouraged scholars to create literacy work • Built a number of Maktab and Madarsas. • Maulana Moinuddin was a great literacy figure of his time The Tughlaq Dynasty (1320-1389) All three were Great lover of education
- 27. Firoz Shah Tughlaq (1351-1389 A.D) 38 years’ of rule • also a great lover of education • peace loving and liberal • Opened a number of Maktabs and Madarsas • Used to Grant stipends to poor student • Rewarded scholars and literacy persons • Built a number of Maktab and Madarsas. • Established a great Maktab in Firozabad The Tughlaq Dynasty (1320-1389) All three were Great lover of education
- 28. Bahlol Lodhi (1451-1481 A.D) • an able ruler also a great lover of education • Literacy works were encouraged • Started few Madarsas also Sayyed Dynasty (1414-1451) Did not do anything worth mentioning in the field of education The Lodhi Dynasty (1451-1526 A.D)
- 29. The Sikandar Lodhi (1481-1517 A.D) • an able ruler also a great lover of education • Generous ruler-cared his subject • Fair system of Administration • Himself was a Great writer, poet • Lover of arts • Respected scholars • Rewarded them for new writings • Many foreign scholars visited his court • writer of Dewan of 9000 poems(pen-name GULRUKH) • Translated persian book on Ayunda under the title of “Tibbat-e-Sikandri” The Lodhi Dynasty (1451-1526 A.D)
- 30. Ibrahim Lodhi (1481-1517 A.D) • Could not pay due attention to education and literature due to the war and other difficulties • He loved arts and education The Lodhi Dynasty (1451-1526 A.D)
- 31. By the thirteenth century •Ghazni was adopted •spread all over the country Pattern of education Whole • Culture of Islamic world transformed in India • Delhi established as greatest learning centre in the east
- 32. Muslim Education under the Mughals Babur founded a Madarasah at Delhi that taught mathematics, astronomy, geography, and the theological courses beside Persian He included new subjects such as; Indian philosophy ethics , arithmetic domestic or home science, agriculture menstruation, the study of government, physiognomy, astronomy geometry and other physical sciences (tabi’i) Sanskrit and Sanskrit literature Akbar reforms through the efforts Shah Fathullah Shirazi Cont’d
- 33. Indian philosophy ethics , arithmetic domestic or home science, agriculture menstruation, the study of government, physiognomy, astronomy geometry and other physical sciences (tabi’i) Sanskrit and Sanskrit literature Akbar reforms Cont’d Nyaya (Indian logic) Vyakarana (Grammar) Yoga (Patanjala Yoga) Vedanta (The Study of Upanishadic philosophy) Persian (official language of the government) medium of study Akbar included new subjects such as:
- 35. Key Features The method of teaching was laid on training the mind of the student to understand Teacher was liable to pay special attention to each student • Islamic schools were attached to • Mosques • Khanqah of Safi & Tombs • Special Building were construct • Expenses were met from endowments. • Scholars from Persia and Central Asia also attracted Key Features Cont’d
- 36. • Free of cost education to every Students • Famous scholars received stipends from the royal treasury Key Features • To create such ability in the scholar who: • Able to acquire perfection in any branch of learning through self-study and personal efforts. Leitner’s report 1882 having 330,000 pupils learning “all the sciences in Arabic and Sanskrit schools and colleges, as well as Oriental literature, Oriental law, Logic, Philosophy and Medicine were taught to the highest standard Confirms the educational status of just the Punjab Key Features cont’d
- 37. Paid high tribute to the quality of Muslim education in India Colonel Sleeman He wrote: Perhaps there are few communities in the world among whom education is more generally diffused than among Mohammadans in IndiaHe who holds an office worth twenty rupees a month commonly gives his sons an education equal to that of a Prime Minister They learn, through the medium of Arabic and Persian languages, what young men in our colleges learn through those of Greek and Latin—that is, grammar, rhetoric, and logic. After his seven years of study, the young Mohammadan binds his turban upon a head almost as well filled with the things which appertain to these branches of knowledge as the young man raw from Oxford He will talk as fluently about Socrates and Aristotle, Plato and Hippocrates, Galen, and Avicenna (alias Sokrat, Aristotalis, Aflatun, Bukrat, Jalinus, and Sina).
- 38. Paid high tribute to the quality of Muslim education in India Colonel Sleeman Perhaps there are few communities in the world among whom education is more generally diffused than among Mohammadans in India He wrote: He who holds an office worth twenty rupees a month commonly gives his sons an education equal to that of a Prime Minister They learn, through the medium of Arabic and Persian languages, what young men in our colleges learn through those of Greek and Latin—that is, grammar, rhetoric, and logic. After his seven years of study, the young Mohammadan binds his turban upon a head almost as well filled with the things which appertain to these branches of knowledge as the young man raw from Oxford he will talk as fluently about Socrates and Aristotle, Plato and Hippocrates, Galen, and Avicenna (alias Sokrat, Aristotalis, Aflatun, Bukrat, Jalinus, and Sina)
- 39. Quoted paid high tribute to the quality of Muslim education in India Bernier, French Traveler • Free of cost education to every Students • Famous scholars received stipends from the royal treasury • To create such ability in the scholar who: • Able to acquire perfection in any branch of learning through self-study and personal efforts.
- 40. Father Manrque • To create such ability in the scholar who: • Mughal understand that knowledge and intellectual development is linked up with growth of libraries • The royal palaces contained immense libraries • The library of Agra in 1641 contained 24,000 volumes valued at six and half million rupees • Hundred of calligraphists (Katib) were available • no Muslim noble would be considered cultured, unless he possessed a good library.
- 41. Ghazi-ud-din Khan Firuz Jang Shara-ud-din Raushan-ud-daulah in delhi etc During Aurangzeb’s period large grants rent-free lands to Ulema for setting up madrasas • Educational institutions • Foundation and colleges were established by him Prosperous personalities Nobles personalities Many Citizens Beside Aurangzeb
- 42. Aim & Organization of Education • Aim of Education – extension of knowledge and socio economic behavior of Students Organization of Education (main Institutions) • Maktab - primary education • Children were made to remember ‘Ayats’ of Quran e Pak • Reading, Writing and primary arithmetic • After Arabic script education in Persian continues • Stories of Prophets and Muslim ‘Fakirs’ were also told • Children were also imparted knowledge Formal Institutions
- 43. • Madarsas – higher education (after completing primary education) • Equal emphasis on religious and secular subjects • Religious education included : a. Quran Pak b. Seerat c. Ahadees d. Islamic laws e. Islamic history, etc • Secular education included : • Arabic literature • Grammar • History • Philosophy • Mathematics • Geography • Politics • Economics • Greek Language • Astrology • Agriculture etc Organization of Education • After Maktab Pupil could go Madarsa (centers of higher education ) • Madarasas were granted land and villages as jagir from king to meet the expenses • beside jagirs, Madarsas were used to receive financial grants beside also • Learned scholars were appointed as head of the Madarsas and with regular teacher as well • Noble and rich persons were also used to give financial assistance • The king never interfered the matters of Madarsa (any educational institution) 1. Formal Institutions
- 44. • Madarsas – higher education (after completing primary education) • Equal emphasis on religious and secular subjects Organization of Education • After Maktab Pupil could go Madarsa (centers of higher education ) • Madarasas were granted land and villages as jagir from king to meet the expenses • beside jagirs, Madarsas were used to receive financial grants beside also • Learned scholars were appointed as head of the Madarsas and with regular teacher as well • Noble and rich persons were also used to give financial assistance • The king never interfered the matters of Madarsa (any educational institution) 1. Formal Institutions Secular education included : • Arabic literature • Grammar • History • Philosophy • Mathematics • Geography • Politics • Economics • Greek Language • Astrology • Agriculture etc Religious education included: a. Quran Pak b. Seerat c. Ahadees d. Islamic laws e. Islamic history, etc
- 45. • Mosques • Almost every “mosque” served as an elementary school • In big cities and towns there used to grand and specious mosque (Jamia masjid) with series of rooms (hujrahs) on atleast two sides which were meant mainly for the students and teachers Organization of Education 1. Formal Institutions (cont’d)
- 46. • Private teachers • Muallim • Muaddib • Ataliq Organization of Education • Khanqahs (Sufi centers) • Sufi showed keen interest work and daily spared some times for this purpose at their place of work or residence • Private Houses • Eminent scholars (large Number) • Large Number of Eminent scholar and men of letter taught independently and even supported the 3. Individual centers of learning 2. Informal Institutions (Very Large number) these informal institutions very well served the purpose of madaris
- 47. Organization of Education • Teacher-Pupil Relation • Great teacher-pupil relationship was observed during Muslims’ rule • Discipline and Punishment • The teachers were empowerment to different types of physical punishment • Examination • Examination system was totally dependent on teacher • Degrees • There was also the system of awarding degrees after education as follows : • Alim: Who acquired special /advance knowledge in “Religion” • Fazil : Who completed knowledge of “Logic”
- 48. In brief, the madrasah education is very deeply rooted in the Muslim civilization and in India this noble tradition originated in the pre-Muslim period and was firmly established during the Muslim rule. As a matter of fact, series of madrasas flourished in modern India are continuation of the same well established practice for which the significant contribution of ulama, scholars and rulers of medieval India cannot be forgotten.
- 49. Organization of Education • Education of Women • Although there was “Pardah” system during the Muslim rule, yet Islam did not opposed the education of women. • The girls were entitled to receive equal to boys up to a definite age • Thereafter, they used to continue their higher studies at home Military Education During the Muslim rules, Military Education was compulsory for every students
- 50. Organization of Education Compulsory education : Education was compulsory, specially for boys Co-ordination: There was proper co-ordination between religious values and material or worldly needs and well-being Character : Great stress was laid on character building Personal Touch: There was a personal touch between the teacher and the taught Curriculum: Curriculum included arrangement for the teaching of various subjects Practical: Remarkable stress was laid on practical utility Merits of Muslim education
- 51. • Separate teachers for different subjects • Special/equal attention was given to religious education & Secular subjects • Great State Patronage was received during Muslim period in shape of • Scholarships • Stipends to many/most Scholars • Establishment of libraries • Aim of the system was to create such ability in the scholars so that he is able to acquire perfection in any branch of learning through self-study and personal efforts • Hindus had their Pathslas for imparting religious instructions Merits of Muslim education
- 52. • In the same way Sultan Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Khalji (1469-1500), an independent ruler of Malwa, took special care of providing religious education to female slaves and for this purpose he appointed a number of teachers Following examples proves that the Muslim rulers of India had interest in the education of different sections of society and further dispel the misgiving that they were only concerned with the education of the elite • some of the Rulers had made special arrangement for the education and even for male and female slaves • In the reign of Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1351-1388), Thousands of slaves got education and training at the state’s expenses not only in traditional sciences (ulum-i-naqliyyah) , but also in crafts and mechanical works (Afif, Tarikh-i-Firuzshahi pp.339-340) (Tarikh-i-Farishta, 2/255)
- 53. The historian Rawlinson says that “the high degree of culture in Mughal India was largely the result of the excellent system of education.” The madrasah education is very deeply rooted in the Muslim civilization and in India this noble tradition was firmly established during the Muslim rule A large number of prominent Irani poets, including Urfi, Naziri, Talib, and Kalim, migrated to India, and at times the level of Persian literature was higher in Mughal India than in Iran Great literary activity in the regional languages like Bengali, Deccani, Hindi, Sindhi, Pushto, Kashmiri, and other regional languages along with the cultivation of Persian Following examples proves that the Muslim rulers of India had interest in the education of different sections of society and further dispel the misgiving that they were only concerned with the education of the elite
- 54. numerous buildings at Fatehpur Sikri, the seat of the imperial court from 1569 to 1584. Some of the buildings there are dominated by the Hindu style of architecture, reflecting the emperor's regard for the Hindu tradition The monuments, tombs, forts, and mosques that Mughal architecture left to India is a testament to the highly-skilled craftsmanship and engineering marvels of the era. The water systems of the gardens and forts were developed for the heat of the subcontinent and their planning can only be attributed to an educated mind The architectural ethereal beauty of the Taj Mahal has not been surpassed to this day and has earned it the position of one of the wonders of the world. In modern times it has managed to contribute to the Indian economy as a tourist attraction that cannot be overlooked Skill examples other than education field
- 55. In contrast with so called progressive
- 56. • The Indian economy boomed under the Mughals, because of the creation of a road system and a uniform currency, together with the unification of the country • The Mughals developed the Mansabdar system to generate land revenue. • The emperor would grant revenue rights to a Mansabdar in exchange for promises of soldiers in war-time. • The greater the size of the land the emperor granted, the greater the number of soldiers the Mansabdar had to promise. • The Mansab was both revocable and non-hereditary. • This gave the center a fairly large degree of control over the Mansabdars. ECONOMY Beside health and education
- 57. Conclusion Muslims/Mughals (several distinctive features) • The credit for organizing education on a systematic basis goes to Akbar (1542–1605) a contemporary of Queen Elizbeth-I of England and undoubtedly the greatest of Mughal emperors. • He treated all his subjects alike and opened a large number of schools and colleges for Muslims as well as for Hindus hroughout his empire. • He also introduced a few curricular changes, based on students’ individual needs and the practical necessities of life. The scope of the curriculum was so widened as to enable every student to receive education according to his religion and views of life. • later part of Mughal rule there was a great outburst of literary activity in Bengali, Deccani, Hindi, Sindhi, Pushto, Kashmiri, and other regional languages. • The adoption of Persian as the court language gave further encouragement to the Hindus and the Muslims to study Persian. Akbar reforms Cont’’d
- 58. Conclusion Akbar reforms Cont’d Muslims/Mughals (several distinctive features) • Muslim rulers of India were great patrons of literature • Considerable impetus to its development • Education was documentised • Principle was established that the poor should also be educated • Education in Mosque, Maktab or Madarsah are equal • Muslim rule influenced the system of elementary education of the Hindus, which had to accommodate itself to changed circumstances by adopting a new method of teaching and by using textbooks • Hindus and Muslims were studied side by side • During the entire Mughal period, girls received their education at home or in the house of some teacher living in close proximity. • Special arrangements for the ladies of the royal household • Some of the princesses were distinguished scholars. • Vocational education was imparted through a system of apprenticeship either in the house of ustads (teachers) or in karkhanahs (manufacturing centres).
- 59. Conclusion Muslims/Mughals (several distinctive features) • There were one hundred thousand elementary schools in Bengal and Bihar alone • A school for every four hundred persons during the fourth decade of the nineteenth century • For higher education there were 1800 colleges in Bengal • Akbar well-advanced of his age, built a girls’ school at Fatehpur Sikri • This development was observed even at the twilight of the Mughal Empire by the English, and it reflects the keen interest the Mughal rulers had taken in the promotion of educati
- 60. • Women had a significant role in family life • Significant policy maker • Promoted widow marriage • Hindu women were consequently allowed to • Engage in business • Also to own land • Banned customs such as ”SATI ” (the Hindu custom of a widow voluntarily being burned alive upon her husband's funeral pyre) • Discouraged early/child marriage • Women received : • Salaries • Owned land • Participated in business transactions • Literary activities. • Aristocratic women: • Painted • Wrote poetry • Played music because they received a higher education. • Conclusion Women's condition in Muslim/Mughal era
- 61. • Some women even fought in wars, right beside the men • Women of course were not treated equally, but the Mughals brought the Indian society closer to the equality of men and women than they had ever been before • Due to many of the Hindu laws remained intact, so women were clearly not treated equal to men Women's condition in Muslim/Mughal era Conclusion
- 62. Conclusion The credit for organizing education on a systematic basis goes to Akbar (1542–1605)a contemporary of Queen Elizabeth I of England and undoubtedly the greatest of Mughal emperors. He treated all his subjects alike and opened a large number of schools and colleges for Muslims as well as for Hindus throughout his empire. He also introduced a few curricular changes, based on students’ individual needs and the practical necessities of life. The scope of the curriculum was so widened as to enable every student to receive education according to his religion and views of life. The adoption ... (100 of 123,990 words) http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/179408/education/47523/The-Mughal-period
- 63. Nowadays, universities or colleges are established only in big cities, but in those days living colleges could be established in each town, village and even in huts (Maqalat-i-Shibli, 3/102-3) Conclusion Muslims/Mughals (several distinctive features) In present days, (learned) persons are ascribed to a college or an institution and at that (Muslims)time they were ascribed to a person (teacher) Whatever was expressed by him in day and night that served a lecture and in this way his talking, movement, manners and behavior all formed part of his silent lectures
- 64. • Ministers were well read and empire functioned effectively with separate departments like: • Agriculture • Trade • Justice • Education • Military and • running of the royal households etc Conclusion Muslims/Mughals (several distinctive features) In present days, (learned) persons are ascribed to a college or an institution and at that (Muslims)time they were ascribed to a person (teacher) Whatever was expressed by him in day and night that served a lecture and in this way his talking, movement, manners and behavior all formed part of his silent lectures
- 67. •Literacy in Mughal times is gauged by a reading public among whom the most commonly read books were 1. Gulistan, 2. Bostan, 3. Akhlaq-i-Nasiri and 4. Anwaar-i-Suhaili etc. •Education is also visible in the conduct of governance and administration. • Ministers were well read.
- 68. The empire functioned effectively with separate departments dealing with • Agriculture, • Trade, • Justice, • Education, • Military and the running of the royal households. • Law and order was maintained throughout the empire with justice accorded by Qazis and Muftis, a system later emulated by the British.
- 69. Maulana Manazir Ahsan Gilani’s famous book – Hindustan mein Musalmanon ka Nizam- i-Talim wa Tarbiyat (Nadwatul Mussanefin, Delhi, 1944, 1/ 13-15) Maulana Manazir Ahsan Gilani’s famous book – Hindustan mein Musalmanon ka Nizam- i-Talim wa Tarbiyat (Nadwatul Mussanefin, Delhi, 1944, 1/ 13-15) Tarikh-i-Firuzshahi pp.339-340) http://www.developindiagroup.co.in/PDFs/General%20Knowledge%20English %202012.pdf Sources: Jaggi, O.P. 2000. Hospitals in India. In Medicine in India: Modern Period, D.P. Chattopadhyaya (Ed.). New Delhi: PHISPC. Pp. 70-74. Verma, R.L. 1992. Indian –Arab relations in medical sciences. In P.V.Sharma (Ed.) History of Medicine in India. New Delhi: Indian National Science Academy. Pp. 465-484.
