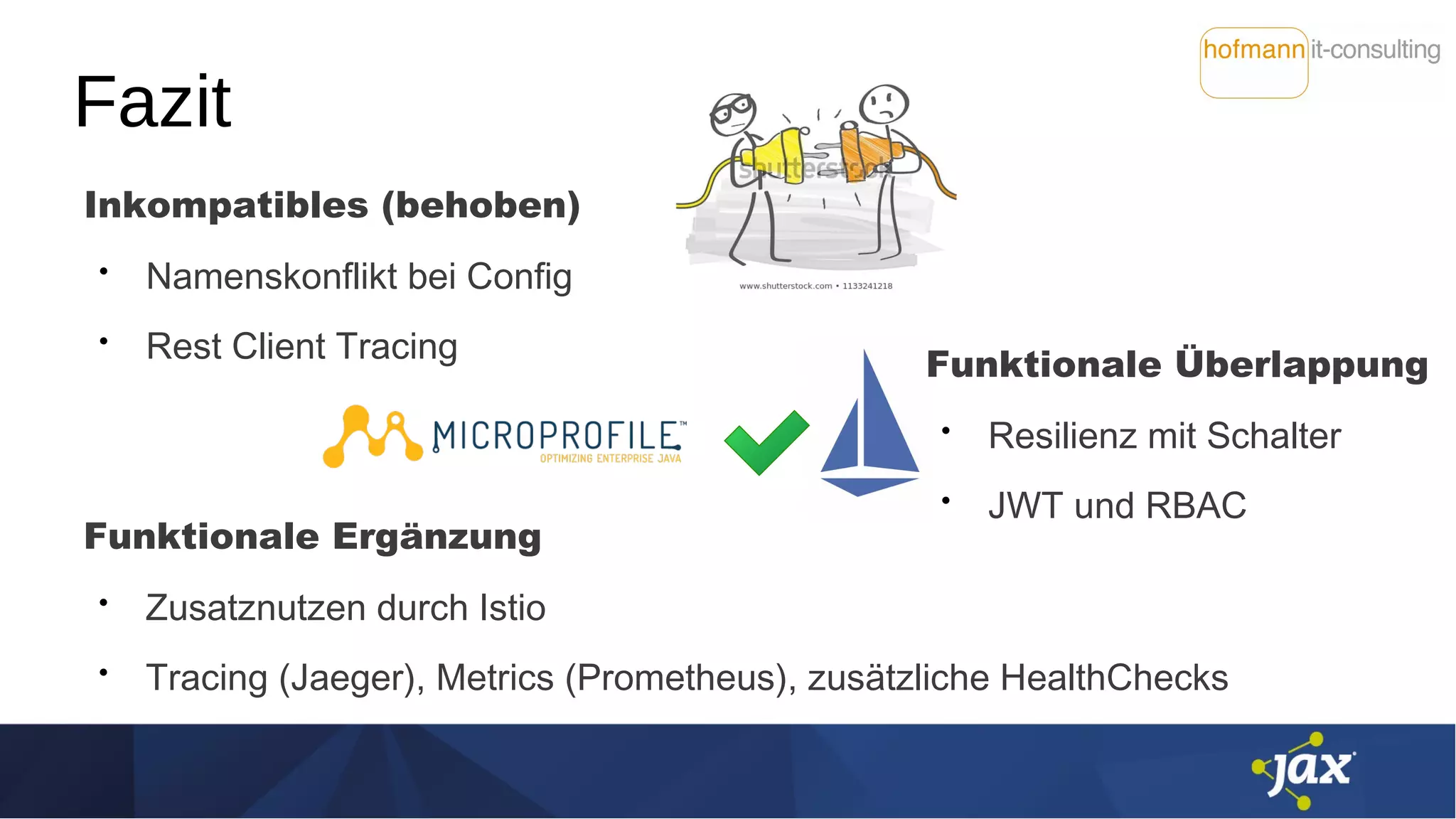
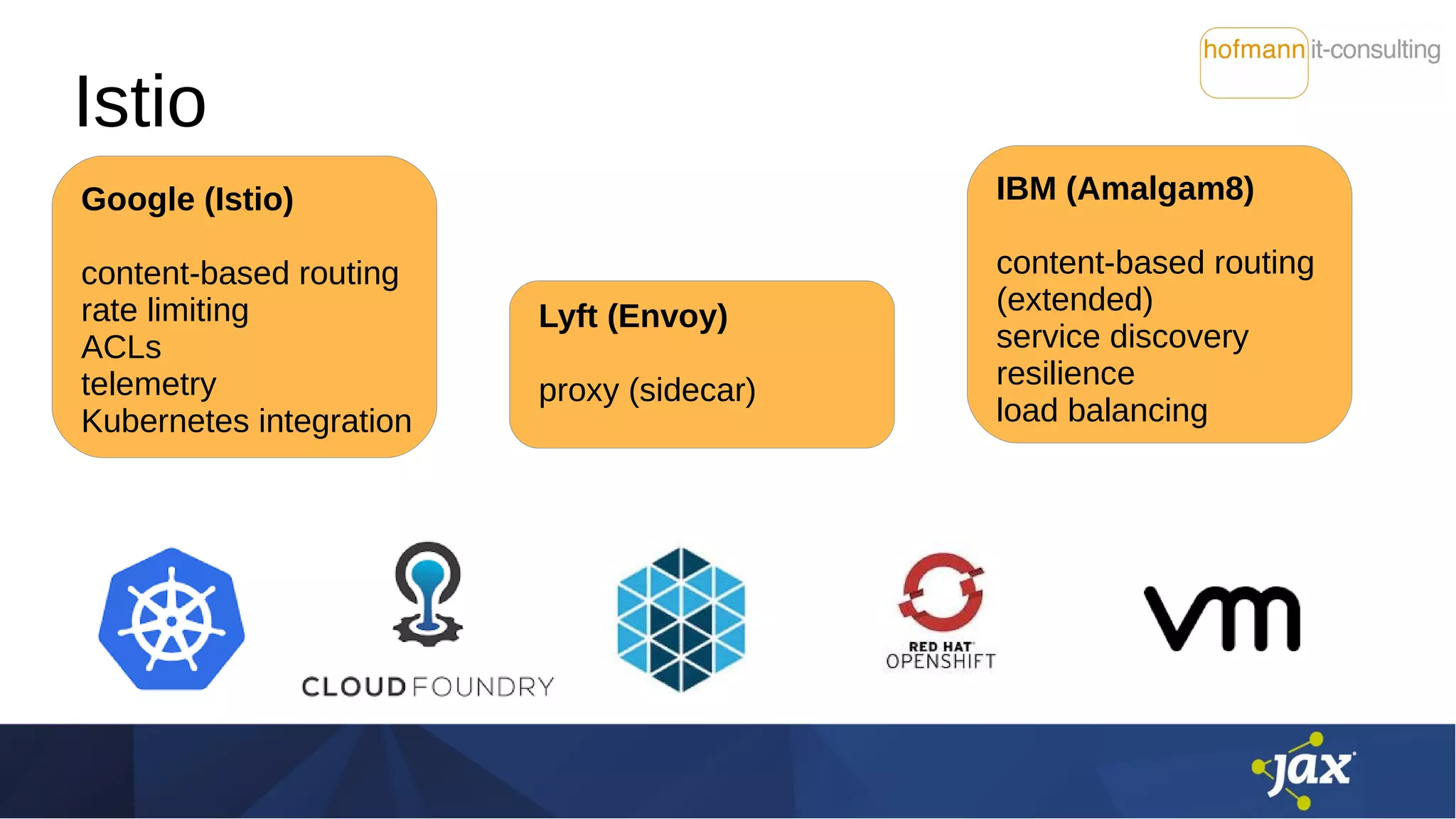
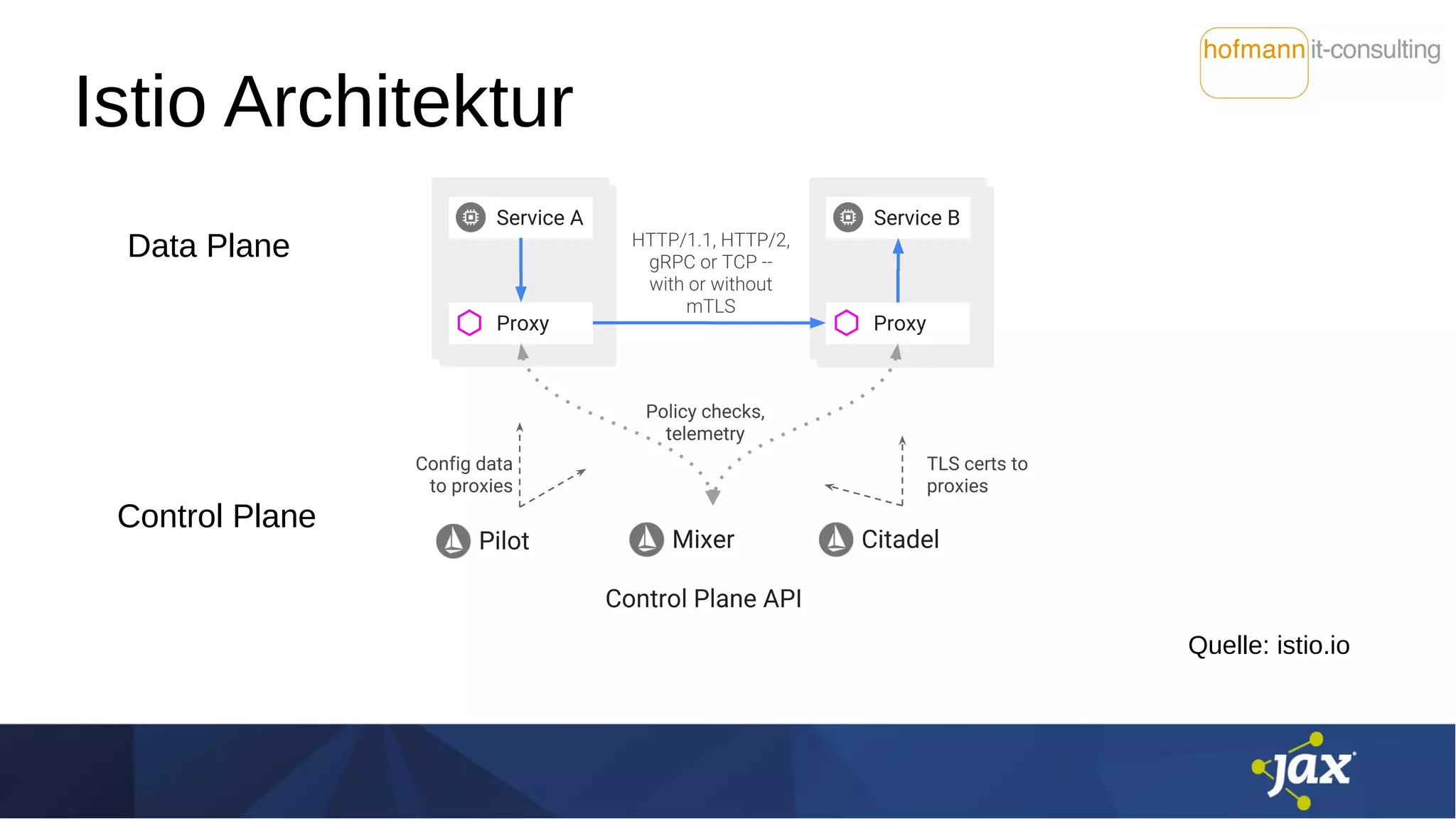
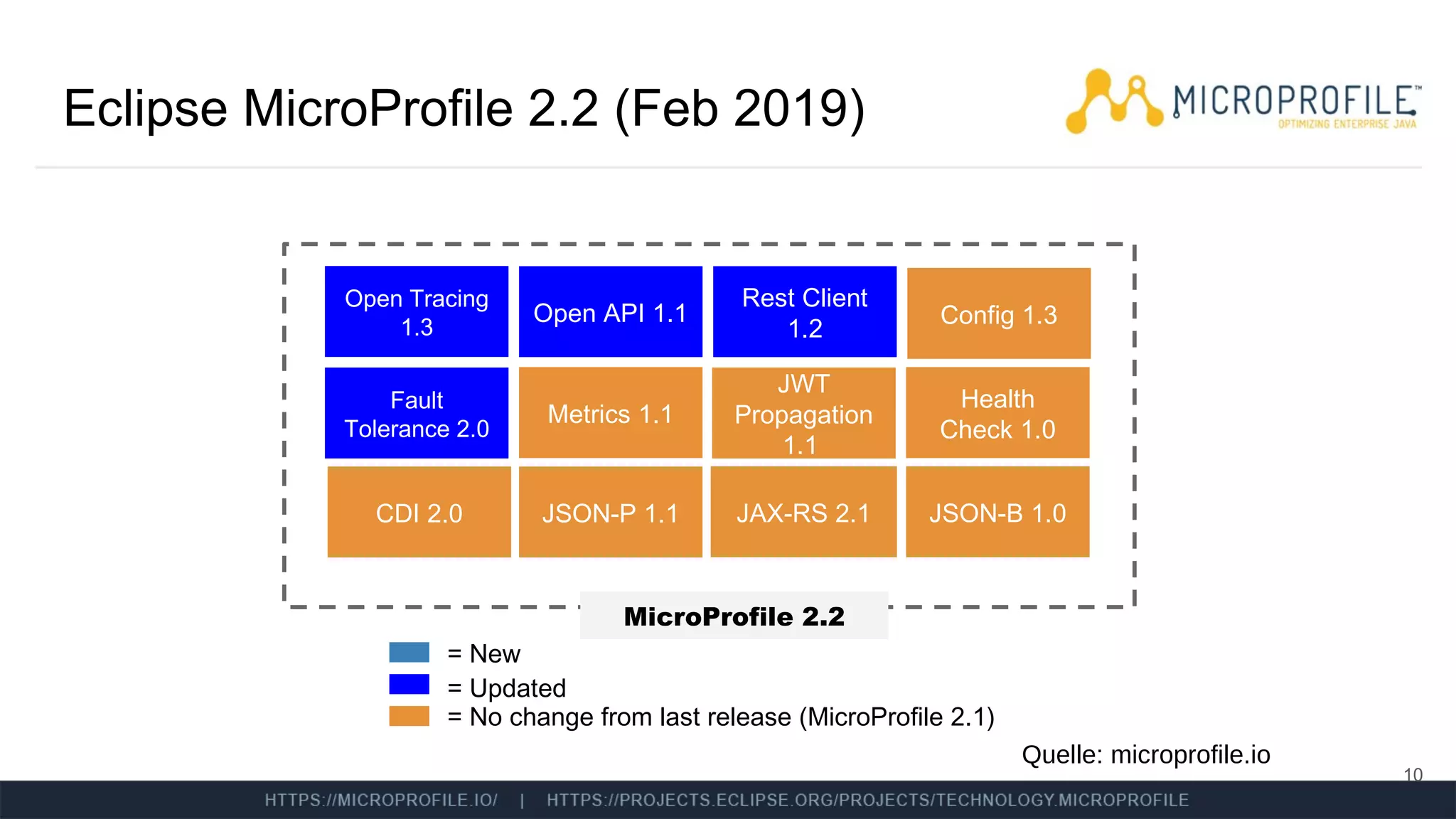
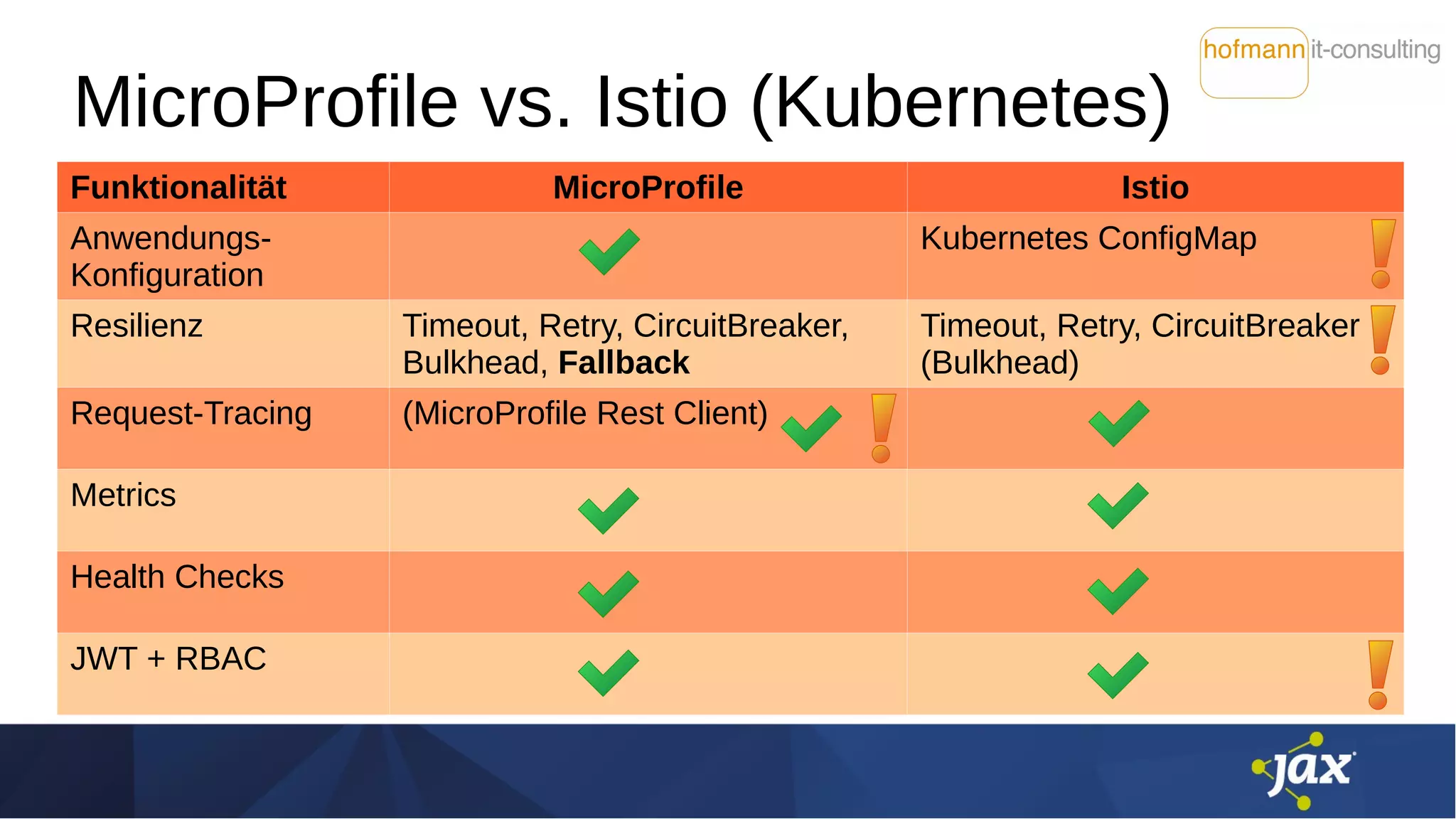
Das Dokument behandelt die Integration von Istio und MicroProfile in Service-Mesh-Architekturen und beleuchtet ihre Funktionen wie Service Discovery, Resilienz und Traffic Management. Es werden Unterschiede zwischen Istio und MicroProfile im Kontext von Kubernetes hervorgehoben, insbesondere hinsichtlich Konfiguration, Resilienzfunktionen und Sicherheitsmechanismen. Zudem werden verschiedene technische Aspekte, Herausforderungen und Möglichkeiten zur Optimierung der Zusammenarbeit zwischen diesen Technologien diskutiert.







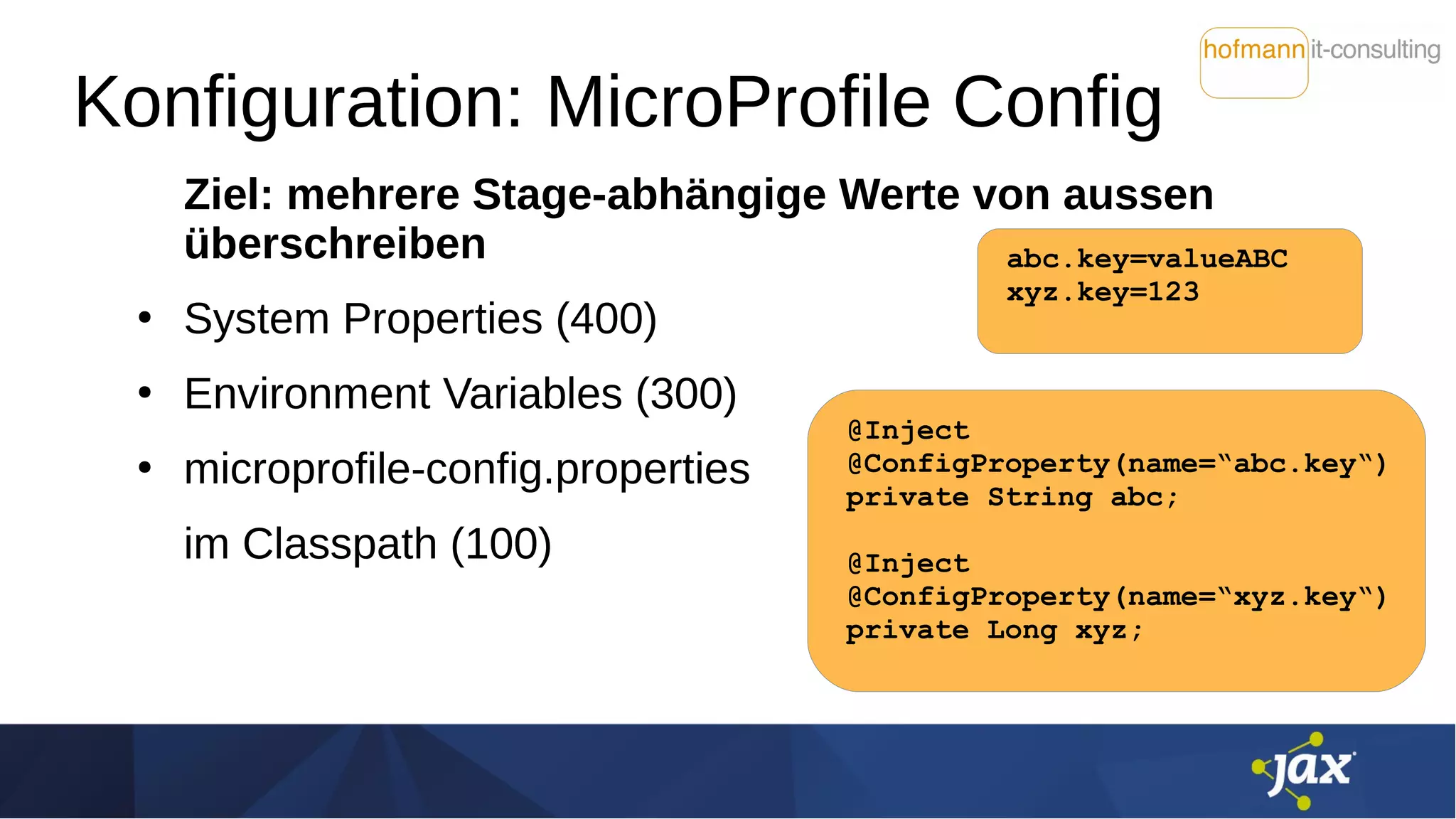
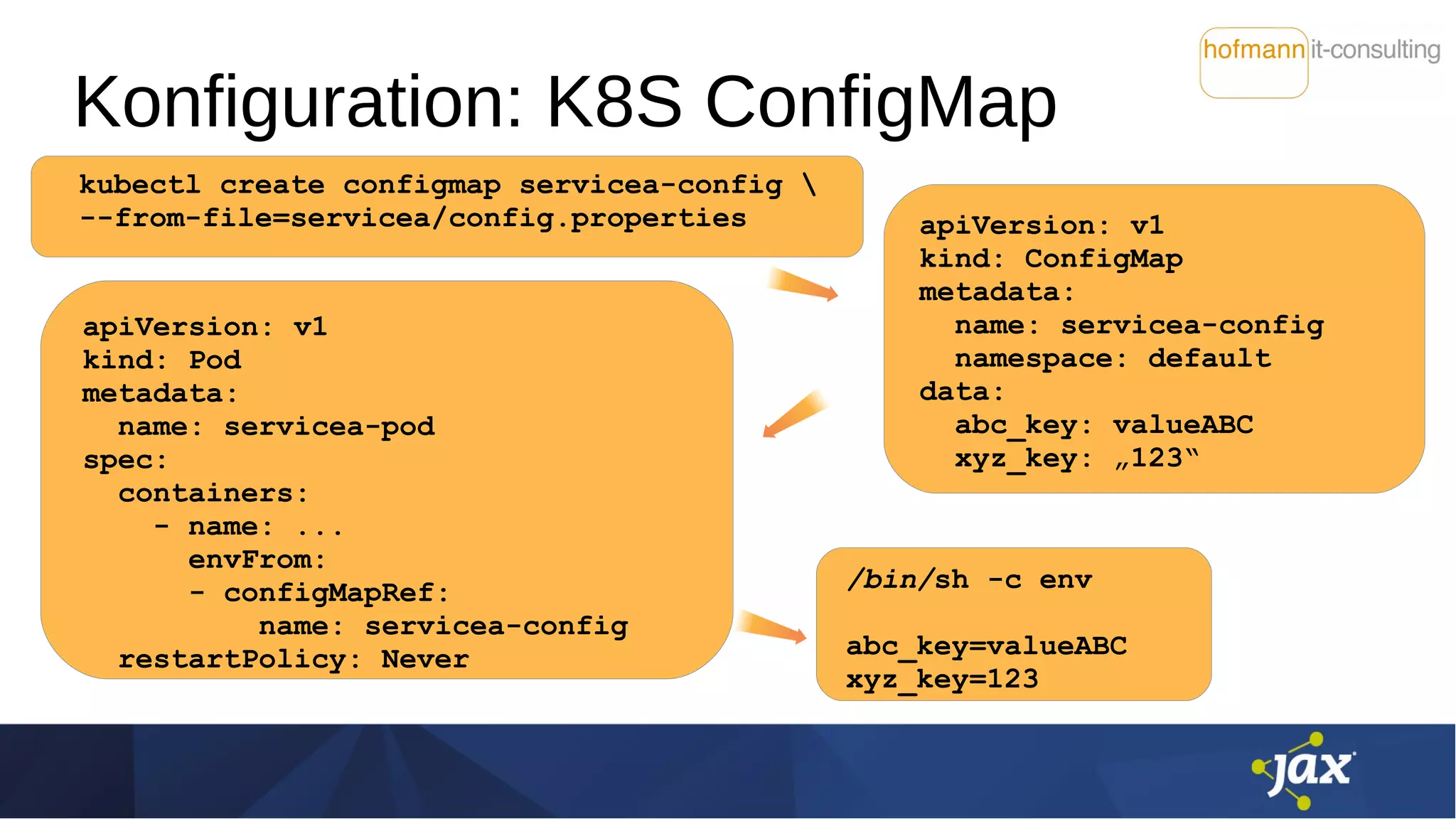
![Konfiguration: Stolperstein
Namenskonflikt der Variablen
K8S Environment Variables:
"must be a C identifier
(matching regex [A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)"
bei MicroProfile: entsprechend Package-Konvention mit .
Seit MicroProfile Config 1.3:
Mapping von non-alphanumeric auf .
(Mapping-Reihenfolge: abc.key, abc_key, ABC_KEY)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/istiomitmicroprofile2019-04-27-190510071112/75/Service-Mesh-mit-Istio-und-MicroProfile-eine-harmonische-Kombination-14-2048.jpg)