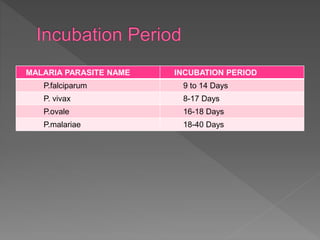
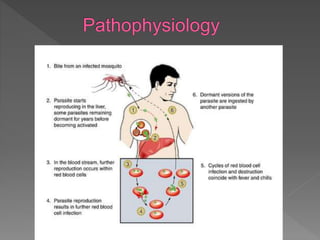
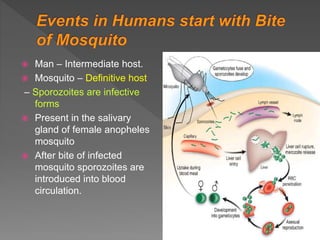
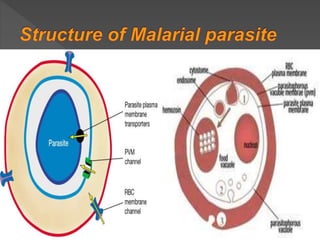
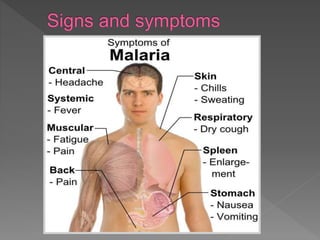
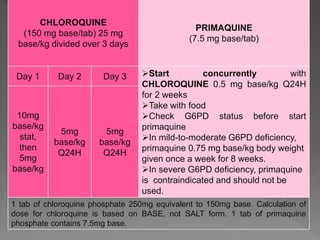
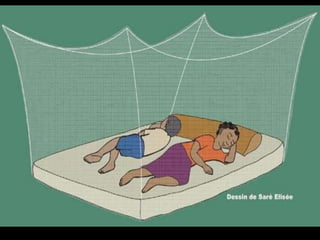
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. It is transmitted via the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. The most common symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, and flu-like illness. There are four species of malaria parasite that infect humans - P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. Treatment involves antimalarial medications such as chloroquine and primaquine. Prevention focuses on mosquito control measures like insecticide spraying and source reduction as well as the use of insecticide-treated bed nets.