Network topologies
•Als PPT, PDF herunterladen•
0 gefällt mir•1,406 views
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Andere mochten auch
Andere mochten auch (20)
Ähnlich wie Network topologies
The layout pattern of the interconnections between computers in a network is called network topology. ... Network topology is illustrated by showing these nodes and their connections using cables. There are a number of different types of network topologies, including point-to-point, bus, star, ring, mesh, tree and hybrid.Network Topologies in Simple (Logical, Physical and Types)

Network Topologies in Simple (Logical, Physical and Types)Amity University | FMS - DU | IMT | Stratford University | KKMI International Institute | AIMA | DTU
Ähnlich wie Network topologies (20)
For Introduction to Network1.What is computer networking means2.pdf

For Introduction to Network1.What is computer networking means2.pdf
Network Topologies in Simple (Logical, Physical and Types)

Network Topologies in Simple (Logical, Physical and Types)
basiccomponentsofacomputernetwork-210820131631.pptx

basiccomponentsofacomputernetwork-210820131631.pptx
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...

Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...
ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges

ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges
Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...

Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...
Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving

Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving
TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery

TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery
Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood

Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood
AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform

AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform
Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...

Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...
EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY GRADE 11 QUARTER 2 REVIEWER

EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY GRADE 11 QUARTER 2 REVIEWER
Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher

Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher
Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...

Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...
Emergent Methods: Multi-lingual narrative tracking in the news - real-time ex...

Emergent Methods: Multi-lingual narrative tracking in the news - real-time ex...
TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments

TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments
Apidays New York 2024 - Scaling API-first by Ian Reasor and Radu Cotescu, Adobe

Apidays New York 2024 - Scaling API-first by Ian Reasor and Radu Cotescu, Adobe
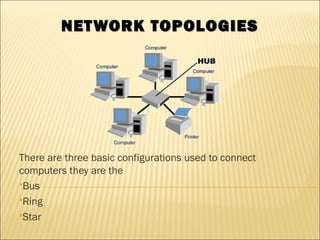
Network topologies
- 1. NETWORK TOPOLOGIESNETWORK TOPOLOGIES There are three basic configurations used to connect computers they are the Bus Ring Star
- 2. This type of network was widely used in the 1980’s In this configuration every computer (node) shares the networks total bus capacities. In this configuration adding more computers will reduce the access speed on the network. Each computer communicates to other computers on the network independently this is referred to as PEER-TO-PEER networking
- 3. HOW A BUS PEER TO PEERHOW A BUS PEER TO PEER NETWORK WORKSNETWORK WORKS All computers on a network have a distinct address just like your house does a message would be send from one computer with the address of another computer attached to the message The message is broadcasted to all the computers on the network until the addressed PC accepts the message
- 4. HOW IT WORKEDHOW IT WORKED The type of wires used for Bus Networks in the 80’s were called Thicknet and Thinnet A Thicknet cable (very large about 1 inch in diameter usually yellow was hung around a room) Thinnet cables were connected to the PC’s NIC and a Transceiver. The Transceiver was tapped into the Thicknet cable To stop the message from bouncing back and forward down the wire (known as signal bounce) both ends of the network are terminated with 50Ω resistors
- 5. PROBLEMSPROBLEMS One of the main problems with this type of network is that it is not very fault tolerant, a break or defect in the bus would affect the whole network
- 6. In Ring topology each node is connected to the two nearest nodes so the entire network forms a circle Data only travels in one direction on a Ring network
- 7. a node has information to send to another computer on the network so it sends the information out on the network to the PC it is connected to, if the information is for this PC (the recipients NIC address is attached to the message, which is like putting an address on an envelope) then the PC accepts the data otherwise it passes the information on to the next PC by repeating the data back out on the line This method of repeating the data helps keep the integrity of the data readable by other computers
- 8. HOW IT WORKSHOW IT WORKS As it is better to have computers take turns using the connecting Data cable, Ring topologies incorporated a system called Token passing In this topology, to transmit on the wire your computer must have control of the token or wait for the token to be free Larger Token Ring networks use multiple tokens
- 9. PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONSPROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS The drawback to this type of topology is that a single malfunctioning workstation can disable the whole network To make sure all the information is sent the receiving PC sends the token back to the sending PC after it has received all the data If the sending PC is finished sending it passes the token to the next PC This type of network was also widely used in the 1980’s This type of network used Thinnet cable joining nodes. In the mid 1980’s Thinnet cable was replaced by Category 3 Ethernet cable capable of handling up to 10Mbps
- 10. In a Star topology every node is connected through a central device such as a Hub, Switch or Router Compared to a Ring or Bus topology a Star topology requires that more thought be put into its setup
- 11. THE GOOD AND BAD OF ATHE GOOD AND BAD OF A STAR NETWORKSTAR NETWORK The upside of a star network is that if any one cable fails then only the node connected on that cable would be affected Another positive point to this type of network is that it is very simple to join two star networks together by connecting their central devices to each other
- 12. THE GOOD AND BAD OF ATHE GOOD AND BAD OF A STAR NETWORKSTAR NETWORK As each computer is connected to a central device (Hub) the location of the Hub must be made as central as possible, so as to reduce cable lengths The drawback to this type of topology is if a central device was to fail then all computers connected to that device would not be able to see the network
- 13. WHAT IS A HUB?WHAT IS A HUB? A hub is usually a small rectangular box, often made of plastic, which receives its power from an ordinary wall outlet A hub joins multiple computers (or other network devices) together to form a single network segment
- 14. WHAT IS A NETWORK SWITCH?WHAT IS A NETWORK SWITCH? A network switch is a small hardware device that joins multiple computers together within one local area network (LAN) Technically, network switches operate at layer two (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model
- 15. WHAT IS A ROUTER?WHAT IS A ROUTER? Routers are physical devices that join multiple wired or wireless networks together Technically, a wired or wireless router is a Layer 3 gateway, meaning that the wired/wireless router connects networks together