Cycling of materials in ecosystem
- 1. Cycling of Materials in Ecosystems
- 2. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: Humans throw away tons of garbage every year as unwanted, unneeded, and unusable. Nature, however, does not throw anything away. Most energy flows through Earth’s ecosystems from the sun to producers to consumers. The physical parts of the ecosystems, however, cycle constantly. Carbon atoms are passed from one organism to another in a great circle of use.
- 3. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: In an ecosystem cycle; producers are eaten by herbivores, herbivores are eaten by carnivores, and carnivores eaten by larger top carnivores. Eventually the top (tertiary) carnivores die and decay; their bodies broken down by decomposers. (bacteria, fungi) Their carbon atoms become part of the soil. This carbon in the soil than becomes part of the nutrients that feed the roots of the plants, the next generation of producers. This completes the cycle, returning some of the energy that started with the producer, back to the producer.
- 4. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: Carbon is not the only element that is recycled in this loop. Other recycled elements include many of the inorganic (noncarbon) substances that make up the soil, water, and air; such as nitrogen, sulfur, calcium, and phosphorus. All materials that cycle through living organisms are important in maintaining the health of ecosystems; but four elements are particularly important: water, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus.
- 5. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: All organisms require carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur in relatively large quantities. Organisms require other elements such as magnesium, sodium, calcium, and phosphorus. Some elements are required in smaller amounts; such as magnesium, sodium, calcium, and iron. Some elements are required in trace amounts; such as cobalt and magnesium.
- 6. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: The paths of water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus pass from the nonliving environment to living organisms; such as trees, and than back to the nonliving environment. These paths form closed circuits, or cycles, called biogeochemical cycles. In each biogeochemical cycle, a pathway forms when a substance enters living organisms such as trees from the atmosphere, water, or soil; stays for a time in the living organism, than returns to the nonliving environment.
- 7. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: Ecologists refer to such substances as cycling within an ecosystem between a living reservoir ( an organism that lives in the ecosystem) and a nonliving reservoir. In almost all biogeochemical cycles, there is much less of the substance in theliving reservoir than in the nonliving reservoir.
- 8. Biogeochemical changes Biogeochemical changes: Ecologists refer to such substances as cycling within an ecosystem between a living reservoir ( an organism that lives in the ecosystem) and a nonliving reservoir. In almost all biogeochemical cycles, there is much less of the substance in theliving reservoir than in the nonliving reservoir.
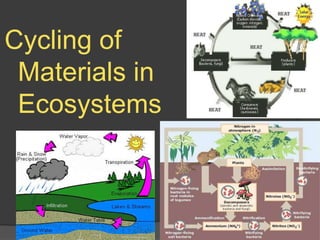
- 9. The Water Cycle: The Water Cycle: Of all the nonliving components of an ecosystem, water has the greatest influence on the ecosystem’s inhabitants. In the nonliving portion of the water cycle, water vapor in the atmosphere condenses and falls to Earth’s surface as precipitation as snow or rain. Some of this water seeps into Earth’s surface (infiltration) and becomes part of groundwater, which is water retained beneath the surface of the Earth.
- 10. The Water Cycle: The Water Cycle: Most of the remaining water that falls to Earth does not stay on the surface. Instead, heated by the sun, it reenters the atmosphere by evaporation. In the living portion of the water cycle, much water is taken up by the roots of plants. After passing through a plant, the water moves into the atmosphere by evaporating from the leaves, a process called transpiration.
- 11. The Water Cycle: The Water Cycle: Transpiration is a sun driven process. The sun heats the Earth’s atmosphere , creating wind currents that draw moisture from the tiny openings in the leaves of plants.
- 12. The Water Cycle: In aquatic ecosystems (lakes, rivers and oceans) the nonliving portion of the ecosystem is the most important. In terrestrial ecosystems, the nonliving and living parts of the water cycle both play important roles. In thickly vegetated ecosystems, such as tropical rainforests, more than 90 percent of the moisture in the ecosystem passes through plants and is transpired from their leaves.
- 13. The Water Cycle: In a rain forest; rain falls and infiltrates soil, moisture travels from soil through plant’s roots, out the leaves through transpiration into the atmosphere, and falls back as rain in a complete cycle.
- 14. The Carbon Cycle: The Carbon Cycle: Carbon also cycles between the nonliving environment and living organisms. Carbon dioxide in the air or dissolved in water is used by photosynthesizing plants, algae, and bacteria as a raw material to build organic molecules. Carbon cycle
- 15. The Carbon Cycle: The Carbon Cycle: Carbon atoms may return to the pool of carbon dioxide in the air and water in three ways Respiration Combustion Erosion Carbon cycle
- 16. The Carbon Cycle: Respiration: Nearly all living organisms, including plants, engage in cellular respiration. They use oxygen to oxidize organic molecules during cellular respiration, and carbon dioxide is a product of this reaction. Carbon cycle
- 17. The Carbon Cycle: Combustion: Carbon also returns to the atmosphere through combustion, or burning. The carbon contained in wood may stay there for many years, returning to the atmosphere only when the wood is burned. Sometimes carbon can be locked away beneath the Earth for millions of years, as in fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas. The carbon in these is released when these fossil fuels are burned. Carbon cycle
- 18. The Carbon Cycle: Erosion: Marine organisms use carbon dioxide dissolved in sea water to make calcium carbonate shells. Over millions of years, the shells of dead organisms form sediments, which form limestone. As the limestone becomes exposed and erodes, the carbon becomes available to other organisms. Carbon cycle
- 19. The Carbon Cycle: Phosphorus or Nitrogen Cycles: Organisms need nitrogen and phosphorus to build proteins and nucleic acids. Phosphorus is an essential part of both ATP and DNA. Phosphorus is usually present in soil and rock as calcium phosphate, which dissolves in water to form phosphate ions. This phosphate is absorbed by the roots of plants and used to build organic molecules.
- 20. The Carbon Cycle: Phosphorus Cycle: The atmosphere is about 78 percent nitrogen gas. However, most organisms are unable to use it in this form. The two nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen gas are connected by a strong triple covalent bond that is very difficult to break. However, a few bacteria have enzymes that can break it, and they bind nitrogen atoms to hydrogen to form ammonia.
- 21. The Carbon Cycle: Nitrogen Cycles: The process of combining nitrogen with hydrogen to form ammonia is called nitrogenfixation. Nitrogen fixing bacteria live in the soil and are also found within swellings, or nodules, on the roots of beans, alder trees, and a few other kinds of plants.
- 22. The Carbon Cycle: Nitrogen Cycles: The nitrogen cycle is a complex process with four stages: 1: Assimilation is the absorption and incorporation of nitrogen into organic compounds by plants 2: Ammonificationis the production of ammonia by bacteria during the decay of organic matter. 3: Nitrification is the production of nitrate from ammonia. 4: Denitrificationis the conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas. Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) carry out many Important steps in the nitrogen cycle
- 23. The Carbon Cycle: Nitrogen Cycles: The growth of plants in ecosystems is often limited by the availability of nitrate and ammonia in the soil. Today most of the ammonia and nitrate that farmers add to soil is produced chemically in factories, rather than by bacterial nitrogen fixation. Genetic engineers are trying to place nitrogen-fixing genes from bacteria into the chromosomes of crop plants using genetic engineering.
- 24. The Carbon Cycle: Nitrogen Cycles: If these attempts by genetic engineers are successful, the plants themselves will be able to fix nitrogen, thus eliminating the need for nitrogen-supplying fertilizers. Some farmers adjust their farming methods to increase natural recycling of nitrogen.