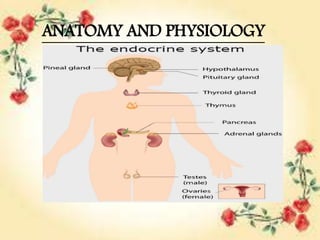
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF Endocrine SYSTEM
- 2. PRESENTATION ON ENDOCRINE SYSTEM SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: DR. PALLAVI PATHANIA MS. SAPNA THAKUR ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR M.Sc. (N) 1ST YEAR SHIMLA NURSING COLLEGE SHIMLA NURSING COLLEGE
- 3. TODAY WE WILL DISCUSS ABUOT Sr. no. Content 1. Meaning of endocrinology 2. Introduction of endocrine system 3. Hormones 4. Regulation of hormones 5. Types of endocrine system
- 4. Sr. no. Content 6.I Endocrine gland: •To Define endocrine glands •To explain types endocrine gland: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Pancreas Liver Heart Kidney Adrenal gland Prostaglandin Ovaries Testes Placenta Ghrelin
- 5. Sr. no. Content 6.II Exocrine gland: •To Define exocrine glands •To explain Classification of exocrine gland •To explain the type of exocrine gland Sweat gland Parotid gland Submadibular gland Sublingual gland Sebaceous gland Pyloric gland.
- 6. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Meaning of endocrinology • Endo- within • Crino- secrete • Logy- study
- 7. Cont.. • Introduction of endocrine system: • Endocrine system consists of glands widely separated from each other with no physical connections . • The endocrine system performs the same general function as the nervous system.
- 8. CONT.. • The nervous system provides a more rapid response than the endocrine system. • Nerve signals are sent via electrical impulses while the endocrine system (ES) communicates via circulating hormones.
- 9. HORMONE • Two main classes of hormones are: Steroid Non steroid
- 10. CONT.. • Non steroid hormones : are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or versions of a single amino acid. • Non steroid hormones are first messengers that act on target cells. • With this system hormones are release, the interaction of the target cell with receptors causes chemical changes to occur within the cell.
- 11. CONT.. • This creates a second messenger within the cell that other reactions to take place. • With in the second messenger system ATP with inside the cell is turned into cAMP causes the cells to respond to secreting the hormone.
- 12. CONT.. • Steroid hormone: The action of lipid soluble do not occur by second messenger systems. • Because they are soluble in lipids they can pass directly through the Plasma membrane of their target cells.
- 13. CONT.. • Once inside the cell’s nucleus, the steroid hormone can bind to receptors – lock and key model. • This hormone receptor complex acts on DNA which causes the formation of a new protein in the cytoplasm that produces specific effect in the target cell. • An example of this type of hormone class would be estrogen.
- 14. HORMONE REGULATION • Negative feedback system can regulate hormone levels within the blood. • As you recall, positive feedback system amplify the condition instead of reversing them to normal levels. Negative feedback mechanism Positive feedback mechanism
- 15. CONT.. • Most PGs regulate cells by the production of cAMP. • Play roles in the treatment of various conditions including high blood pressure, ulcers and asthma. • Aspirin cause their effect by altering the function of PGs in the body.
- 16. TYPE OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Endocrine system consist of two type of glands Endocrine gland Exocrine gland
- 17. ENDOCRINE GLANDS
- 18. CONT.. • Endocrine: These are ductless glands secrete hormone into the blood or into the blood or into fluid surrounding cells. E.g. pineal gland, thyroid gland . • Endocrine glands secrete hormone into intercellular spaces. • Hormone can diffuse into the blood and be carried throughout the body.
- 19. CONT.. • Hormone may bind to cells that have hormone specific receptors on their surface. • These cells are known as target cells. The binding of the hormone with the receptor of the hormone with the receptor initiates a chemical reaction. • Hormone play an important role in homeostasis and metabolism. • Disease may cause a gland to secrete too much or too little hormone.- Hyper secretion or hypo secretion.
- 20. HYPOTHALAMUS
- 21. CONT.. • Location: • The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. • Anatomy: • The hypothalamus is a region of the brain composed of many small nuclei with diverse functions.
- 22. CONT.. • Physiology: • The hypothalamus is a small area in the ventral diencephalon of the forebrain, in the floor of the third ventricle, and is a functional link between the nervous and endocrine systems. • Hypothalamus produces many hormones, some of which are given below • ADH (vasopressin) • DA (dopamine) • CRH (corticotrophin releasing hormone)
- 23. Cont.. • The hypothalamus produces Releasing hormone (RHs) and Inhibiting hormone (His) • They travel to the adenohyposis via a specialized capillary system. • They can cause the release of anterior pituitary hormones or inhibit their production and release into the general circulation. • The hypothalamus plays a dominant role in regulating many body function including: • Body temperature • Appetite • Thirst
- 24. PITUITARY GLAND
- 25. Cont.. • The pituitary gland is endocrine gland smaller than a pea in size but carries out very important functions. • It is called as master gland. • It measure only 1.2-1.5cm its length and weight is 1.5 gram. • It has well protected location with in the skull ventricle surface of brain.
- 26. CONT.. • It lies in the hypophyseal fossa of sphenoid bone below hypothalamus. • It consists of two glands- each of different type. • -Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophyssi) • -Posterior pituitary gland (neurohpophysis)
- 27. Cont.. • Anterior pituitary gland: • The anterior pituitary gland secretes several major hormones. • Tropic hormones stimulates another endocrine gland to grow and secrete its hormones. • It consist of epithelial cell.
- 28. CONT.. • Thyroid stimulating hormone- TSH stimulate the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone. • T3- tri-idothyroxine • T4- thyroxine • Calcitonin
- 29. CONT.. • Adenocorticotrophic hormone- • ACTH acts on the adrenal cortex to increase in size and to secrete larger amounts of cortisol.
- 30. CONT.. • Gonadotrophin hormone – • Two Gonadotrophin hormone release in response of GnRH i.e. LH and FSH. • LH acts with FSH to perform various functions. • Causes estrogen production increase and ovulation. • Stimulate the formation of the corpus luteum and its production of progesterone. • Stimulate the interstitial cells of the testes to secrete testosterone.
- 31. CONT.. • Growth hormone- GH speeds up the movement of amino acids out of the blood and into cells to promote anabolism of amino acids into tissue proteins. • GH also promotes fat catabolism and slow down glucose catabolism.
- 32. CONT… • Less glucose leaves the blood to enter cells. GH therefore increases blood glucose concentration. • Hyper secretion of insulin produces hypoglycemia. • Hyper secretion of GH produces hyperglycemia
- 33. CONT.. • Prolactin- PRL or lactogenic hormone. • Stimulate the development of the breasts for producing milk during pregnancy.
- 34. CONT.. • Melanocyte stimulating hormone- It work with other hormones to control pigmentation of the skin. In response to UV rays, its production by the skin and pituitary gland is enhanced and provide pigmentation to the skin, eye and hair.
- 35. Cont… • Posterior pituitary • Two group of neurons make the posterior gland hormones and pass them along axons to the neurohypophysis. Release is controlled by nervous stimulation. • The neurohypophysis releases two hormones. • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) • Oxytocin (OT)
- 36. CONT.. • ADH: Accelerates the reabsorption of water from urine in the kidneys back into the blood. • More water moves out of the kidney tubules into the blood, less water remains in the kidneys and therefore less urine is excreted from the body. • ADH acts to decrease urine volume. • Hypo secretion of ADH result in diabetes insipidus- Large volume of urine are produced- dehydration
- 37. CONT.. • Ocytocin therapy: Is secreted by the posterior pituitary of a female before and after she has a baby. • OT stimulate uterine contractions to initiate and maintain labor. • It stimulate glandular cells of the breast to release milk into ducts from which the baby can obtain nutrients.
- 38. PINEAL GLAND
- 39. CONT.. • Introduction: • Pineal gland is small body attached to the roof of the 3rd ventricle of the brain. • Pineal gland is about 10mm long is reddish brown in color and surrounded by a capsule. • The gland tends to atrophy after puberty and may become calcified in later life.
- 40. CONT.. • Function: • Production of melatonin-regulates onset of puberty and menstrual cycle. • It act on the hypothalamus to inhibit Gonadotrophin releasing hormone when the growth development. • Regulation of endocrine system & Cause feeling of sleepiness. • Its level highest at night and lowest around midday, because secretion is influenced by the number of daylight hours i.e. seasonal variation.
- 41. THYROID GLAND
- 42. Cont.. • Introduction: • It is endocrine gland. • Its weight about 15-25gm • It situated anteriorly in the lower part of neck. • It lies in front of larynx and trachea at the level of lower three cervical and first thoracic vertebrae. • It consist of two lobes join together by a narrow isthmus.
- 43. CONT. • Structure: • The thyroid gland is cover by fibrous capsule. • It look a butterfly shape. • It is composed of right and left lobes. • It is highly vascular i.e. 80- 120ml/min. • Thyroid tissue is composed of tiny structural units called follicles. • Each lobe is 5cm. Long, 3cm. Wide and 12 cm. thick.
- 44. CONT.. • Thyroid hormone : • T3- tri-idothyroxine • T4- thyroxine • Calcitonin
- 45. CONT… • Thyroid hormone help to increase cell metabolism. • All body function depend on thyroid secretion.
- 46. CONT.. • Clacitonin decrease the amount of calcium in the blood by acting on bone to inhibit its breakdown. • Less calcium will move out of bone into the blood. • Concentration of blood Ca+ levels will decrease. • Clacitonin helps to maintain homeostasis of blood Ca+ levels will decrease.
- 48. Cont.. • Introduction: • There are 4 Small glands found on the back of the thyroid gland. • Each has a mass of about 140mg. • Each gland is about the size of split pea. • Secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- 49. CONT.. • Structure: microscopically the parathyroid gland contain 2 kind of epithelial cell. • Chief cell Oxyphil cell • Chief cell: these called chief cells which produce parathyroid hormone celled parathormone. • Oxyphil cell: these cells first appear at puberty and their function is still not clear.
- 50. CONT.. • Functions: • PTH regulate the level of Ca+, Mg, phosphate level in blood an regulate muscle contraction, nerve transmission, blood clotting. • PTH increase Ca+ concentration in the blood. • The opposite effect of Calcitonin. • PTH stimulates osteoclasts (bone resorbing cells) to increase their breakdown of bone matrix. This moves Ca+ out of bone into blood.
- 51. CONT.. • Low levels of Ca+ in the blood can cause: Overactive nerve cells ,muscle spasms resulting from constant nervous stimulation • High levels of Ca+ can cause : The death of brain and heart cells.
- 52. THYMUS GLAND
- 53. CONT.. • Introduction: • Thymus gland lies in the upper part of the behind the sternum and extend upward into the root of the neck. • Weight: • in infant- 10-15 gm • In adolescence- 30-40gm • In middle age – it shrink approximately to its weight 10-15gm
- 54. CONT.. Organ associated with the thymus: • Anteriorly: sternum & upper 4 costal cartilage • Posterior: aortic arch & its branch • Laterally: lungs • Superiorly: structure in the root of neck • Inferiorly: heart Structure: thymus consist of 2 lobes joined by areolar tissue.
- 55. CONT.. • Function: • Thymus gland hormone is thymosin for development and function of immune system. • It is also known as T- lymphocyte (cell mediated immunity). • It help to protect the body against foreign organism.
- 56. PANCREAS
- 57. CONT.. • Introduction : • Pancreas is grayish pink color gland about 12 to 15 cm. long and its weight about 60 gm. • It resemble a fish with its head and neck in C shape curve of the duodenum. • it’s body extending horizontally below and behind the stomach and its tail touching the spleen. • According to old anatomical style romance of the abdomen is the pancreas lying in the arm of duodenum.
- 58. TYPE OF PANCREAS • Pancreas is composed of two different type of tissue. • Exocrine • Endocrine • The duodenal opening is controlled by hepatic pancreatic sphincter Oddi.
- 59. CONT.. • Endocrine: it is distributed throughout the gland are group of specialized celled the pancreatic islet of langerhans. • The endocrine pancreas secrete the hormone insulin and glucogens which are principally concerned with control by blood glucose level. • It contain 3 types of cells: • Alpha cells: It secrete glucagon. It stimulate conversion by glycogen to glucose in the liver and skeletal muscle.
- 60. CONT.. • Beta cells: It secrete insulin. When the nutrient especially glucose are in excess the insulin promote their storage by acting an cell membrane and membrane and stimulating uptake and use of glucose by muscles and connective tissue. • Delta cells: it secrete somatostatin. It inhibit the secretion of both insulin and glycogen.
- 61. CONT.. • Exocrine gland: • This consist of a large no. of lobules. • The walls of which consist of secretary cells. • Each lobule drained in to duct and these links eventually to from the pancreatic duct when extent the whole length of the gland and opens into the duodenum.
- 62. CONT.. • Normal glucose levels= 70 to 100 mg per 100 ml of blood. • Hypo secretion of insulin: • type 1 diabetes mellitus • Type 2 diabetes mellitus- some decrease in insulin and abnormalities in insulin target cell receptors. Blood glucose levels are increased.
- 63. LIVER
- 64. CONT.. • Location: • It is always located immediately caudal to the diaphragm and tends to be located on the right side. • Anatomy: • The liver is the largest gland of the body and is 1-2% of the total body weight.
- 65. CONT.. • Physiology: • It secrete two hormones • Insulin like growth factor (GF): Insulin like effect Regulate cell growth and development • Angiotensiogen and angiontension: Vasoconstriction Release of Aldosterone from adrenal cortex
- 66. HEART
- 67. CONT.. • Location: • It is situated in the middle mediastinum and is enclosed with the pericardium. • Anatomy: • It is a conical hollow muscular organ. That pumps blood.
- 68. CONT.. • Physiology: • It secrete following hormones • Artial- natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Reduce blood pressure Increase Na+ excretion by kidney • Brain- natriuretic peptide: (BNP) Reduce blood pressure to minor degree than ANP
- 69. KIDNEY
- 70. CONT.. • Location: • It usually lie ventral to the first three lumber transverse process; against the dorsal wall of the abdominal cavity. • Anatomy: • The kidney are a pair of excretory organs and is a bean shaped.
- 71. CONT.. • Physiology: • It secrete following hormones: • Erythropoietin Stimulates erythrocyte production • Thrombopoientin: Stimulate megakaryotes to produce platelets
- 72. ADRENAL GLAND
- 73. Cont.. • Introduction: • The adrenal glands are located on the top of each kidney. • These are 2 in number • Length- 4cm, width- 3cm. • The are composed of two glands: • Adrenal cortex • Adrenal medulla • The two glands produce different hormones.
- 74. CONT.. • Adrenal cortex • It is divided into three zones or layers. • Hormones secreted by all three layers are called corticoids. • Mineral corticoids • Gluco corticoids • Sex hormone
- 75. CONT.. • Mineral corticoids: • The outer zone secrete mineral corticoids- MCs. • Main Mc is Aldosterone. • It help to control the amount of NaCl in the blood. It increase the amount of Na+ in the blood and decreases the amount of K+ in the blood. More K+ will be lost in urine. • Aldosterone speeds up the kidneys reabsorption of water. Mineral corticoid receptor
- 76. CONT.. • Glucocorticoids: • The middle zone secretes glucocorticoid- GCs • Hydrocortisone or cortisol is the chief glucocorticoid. • Glucocorticoids help to maintain blood glucose concentration by the process of gluconeogenesis.
- 77. CONT.. • Amino acids or fatty acids are converted to glucose within the liver. • Glucocorticoids promote the catabolism of tissue proteins into amino acids- transported to the liver and turned into glucose and enters blood. • Act as weak mineral corticoids effect Maintain normal blood pressure .
- 78. CONT.. • Some pathological and pharmacological function. • Delayed wound healing. • Produce anti-inflammatory effect- example: hydrocortisone cream/ ointment. • Production of anti-immunity or anti- allergy effects- Decrease in the production of antibodies. • Responding to stress
- 79. CONT.. • Sex hormone: • The innermost, deepest zone of the cortex secretes small amount of sex hormones are mainly androgen (male sex hormone ) that resemble testosterone.
- 80. CONT… • Adrenal medulla is the inner portion of the adrenal gland. • It is stimulated by its extensive sympathetic nerve supply • It secretes: • Epinephrine hormones • nor epinephrine hormones
- 81. CONT. • These hormone are released directly into the blood and are involved in the body’s flight or fight response by • Increasing heart rate. • Increase blood pressure. • Diverting blood to essential organs, including heart , brain, skeletal muscle. • Increase metabolic rate. • Dilating pupil.
- 82. CONT.. • In response to stress the hypothalamus causes the anterior pituitary to release ACTH. • This causes the adrenal cortex to release glucorticoids. In addition, the adrenal medulla will release nor epinephrine and epinephrine. • Adrenaline has a great effect on the heart and metabolic processes. • Nor adrenaline has more influence on blood vessels.
- 83. PROSTAGLANDINS (PGS) • PGs are tissue hormones that are found in a large variety of tissues. • They perform many important function but are not like typical hormones. • PGs are produced within tissues and diffuse a short distance to act on cells within that tissue.
- 84. CONT.. • PGs typically influence the activities of neighboring cells. Hormones can influence the activities of widely separated targets. • PGs can be divided into separate classes- A, E and F. • PGs can have influences on many body functions such as: • Respiration • Blood pressure • GI secretion • Inflammation • Reproductive system
- 85. CONT.. • Most PGs regulate cells by the production of cAMP. • Play roles in the treatment of various conditions including high blood pressure, ulcers and asthma. • Aspirin cause their effect by altering the function of PGs in the body.
- 86. OVARIES
- 87. CONT.. • The ovary (from Latin: ovarium, literally “egg” or “nut”) is an ovum- producing reproductive organ. • Location: • Ovaries found in pairs at the lower back of the female as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system.
- 88. CONT.. • Anatomy: • They are almond –shaped and about 3.5cm. (1.5 inches) long. • Physiology: • The ovaries have 2 main functions. They produce mature eggs. They also make the female sex hormones, which control reproduction and sexual development.
- 89. CONT.. • It mainly produces two hormones: • Estrogen: • Is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics, such as the growth of breasts. • Progesterone: • Prepares the body for conception by causing the buildup of the uterine lining (endometrium) and other changes.
- 90. TESTES
- 91. CONT.. • Anatomy: • Like the ovaries to which they are homologous, testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system. • Physiology: • The primary functions of the testes are to produce • sperm (spermatogenesis) • Androgen • Primarily testosterone
- 92. CONT.. • Testosterone: • It is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in human and other vertebrates. • In humans and other mammals, testosterone is secreted primarily by the testicles of males and, to a lesser extent the ovaries of females. • Small amount are also secreted by the adrenal glands. It is principal male sex hormone and an anabolic steroid.
- 93. CONT.. • In men, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive issues such as- testis and prostate • As well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased- muscle, bone mass, growth of body hair. • In addition, testosterone is essential for health and well-being as well as the prevention of osteoporosis.
- 94. PLACENTA • Temporary endocrine gland hormone: • Chronic gonadotrophins • Secreted in urine/ pregnancy test • Estrogen and progesterone
- 95. GHRELIN • Secreted by stomach- boosts appetite and slows metabolism. • ANH strial natriuretic hormone-loss of Na+ ions and water from kidney • Antagonist to Aldosterone
- 96. EXOCRINE GLANDS
- 97. CONT.. • Definition: • Exocrine system includes Exocrine glands are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. • Example of exocrine gland include: • Sweat • Slivery Parotid Submadibular Sublingual • Lacrimal sebaceous • Pyloric gland
- 98. CONT.. • Classification : • By structure: • Exocrine glands contains a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. • The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called simple) • The glandular portion may be tubular or acrinar, or may be a mix of the two (called tubloacinar). If the glandular potion branches, then the gland is called a branched gland.
- 99. CONT. • By method of excretion: • Exocrine glands are named apocrine glands, holocrine glands, or Merocrine glands based on how their products are excreted. • Merocrine secretion: cells excrete their substances by exocytosis; e.g. pancreatic acinar cells.
- 100. CONT.. • Apocrine secretion: a portion of the cell membrane that contains the excretion buds off. • Holocrine secretion: the entire cell disintegrates to excrete its substance; e.g., subcutaneous glands of the skin and nose.
- 101. CONT.. • By product excreted: • Serous cells excrete portions, often enzymes. Example include gastric chief cells and Paneth cells. • Mucous cells excrete mucus. Example include Bruner’s gland, esophageal glands, and pyloric glands. • Mixed glands excrete both protein and mucus. Example include the slivery glands, through the parotid glands is predominantly serous, the sublingual gland.
- 102. SWEAT GLAND • It produce sweat from skin Name (S) Location Product Structure Apocrine sweat glands Skin Sweat Coiled tubula
- 103. PAROTID GLAND • Its production rises to 50% during stimulation Name(S) Location Product Structure Parotid gland Mouth Serous Tubulo- alveolar
- 104. SUBMADIBULAR GLAND They contribute some 60-67% of on stimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decrease in proportion as the parotid secretion rises to 50% Name(S) Location Product Structure Submadibula r gland Mouth Mixed (M+S) Tubulo- alveolar
- 105. SUBLINGUAL GLAND They provide only 3-5% of the total salivary volume Name(S) Location Product Structure Sublingual gland Rivini’s gland Mouth Mucus (primarily) Tubulo- alveolar
- 106. SEBACEOUS GLAND It secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals. Name(S) Location Product Structure Sebaceous gland Skin Sebum Acinar branched
- 107. PYLORIC GLAND • The pyloric glands are located in the antrum of the pylorus. • They secrete gastrin produced by their G cells • Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCI) Name(S) Location Product Structure Pyloric gland Stomach Mucous Simple branched tubular
- 108. CONCLUSION Hormones are special chemical messenger in the body that are created in the endocrine glands. These messengers control most major bodily functions, fro simple basic needs like hunger to complex system like reproduction, and even the emotions and mood. understanding the major hormone functions will help patients take control of their health.
- 109. SUMMARIZATION
- 111. Recapitalization
- 113. BIBLIOGRAPHY Wilson and Ross, “Textbook of Anatomy and Physiology in health and illness,” 11th edition, Churchill Livingstone publisher; 2010, Page no.207-219 https://www.slideshare.net?mobile/mrhunterspage /natomy-nd-physiology-he-endocrine-system-02- 19-13 viewed on 25/05/2019 http://www.slideshare.net/mobile/beekaboo/endoc rine-system-overview-hs-anatomy-and- physiology
- 114. ASSIGNMENT Complete endocrine system diagram function of exocrine glands
