Chapter 2
- 3. 1)1) ElementElement isis a substance that consists of identical atoms •there are 116 known elements •of these, 88 occur in nature •their symbols consist of one or two letters Element Symbol Carbon C Calcium Ca Oxygen O Titanium Ti •Symbols and element names are derived from a variety of sources Pure Substances
- 5. Relative Abundance of Elements in Earth
- 6. 2)2) CompoundCompound is a pure substance made up of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass • The formula of a compoundThe formula of a compound tells us the ratios of its constituent elements and identifies each element by its atomic symbol. NaCl: the ratio of sodium atoms to chlorine atoms in sodium chloride is 1:1 H2O: the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in water is 2:1
- 8. • are a combination of two or more pure substances •the substances may be present in any mass ratio •each substance has a different set of physical properties •if we know the physical properties of the individual components of the mixture, we can use appropriate physical means to separate the mixture into its component parts Mixtures
- 10. Homogenous - uniform composition throughout -gases, solutions, alloys Heterogeneous - nonuniform composition throughout -salad, trail mix, granite, chicken noodle soup
- 11. The symbol CO represents which of the following? 1. element 2. compound 3. homogeneous mixture 4. heterogeneous mixture
- 12. Monatomic elements:Monatomic elements: consist of single atoms; for example, helium (He) and neon (Ne). Diatomic elements:Diatomic elements: there are seven elements that occur as diatomic molecules: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 Polyatomic elements:Polyatomic elements: some elements have three or more atoms per molecule
- 13. 1. monoatomic element 2. diatomic element 3. polyatomic element 4. compound S8 is an example of a ________.
- 14. All matter is composed of tiny ATOMSATOMS. Atoms in an element have the same chemical properties. Atoms of different elements have different properties. COMPOUNDSCOMPOUNDS are formed by the chemical combination of two or more different kinds of atoms. A MOLECULEMOLECULE is a tightly bound combination of two or more atoms that acts as a single unit. Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- 15. 1) Law of Conservation of Mass1) Law of Conservation of Mass : matter can be neither created or destroyed. A chemical reaction just changes the attachments among atoms, but does not destroy the atoms themselves. Evidence for Dalton’s Atomic Theory:
- 16. 2) Law of Constant Composition2) Law of Constant Composition: any compound is always made up of elements in the same proportion by mass Ex. The mass ration of oxygen to hydrogen in pure water is always 8:1 Evidence for Dalton’s Atomic Theory: H2O
- 17. The unit of mass is the atomic mass unit (amu)atomic mass unit (amu) 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of a carbon atom 1 amu = 1.6605 x 10-24 g What are atoms made of? Subatomic Particles
- 18. + + + + + + + + - - - - - - - - • Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, and electrons are found as a cloud outside the nucleus
- 19. I’m Professor Thomson and I discovered the electrons in 1897 I used to be his graduate student. Now I’m famous myself . I, Ernest Rutherford discovered positive charges in the nucleus in 1911
- 20. Cathode ray experiment (Thomson’s) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_nLESblUAHY Gold foil experiment (Rutherford’s) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5pZj0u_XMbc
- 21. Mass number:Mass number: number of protons plus neutrons Atomic number:Atomic number: number of protons A carbon atom of this composition is referred to as carbon-12. Mass and Atomic Number
- 22. What is the mass number for an atom that contains 7 electrons, 7 protons, and 8 neutrons? 1. 0 2. 7 3. 8 4. 15
- 23. What is the atomic number for an atom that contains 7 electrons, 7 protons, and 8 neutrons? 1. 0 2. 7 3. 8 4. 15
- 24. Isotopes:Isotopes: atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons C13 6 C12 6 C14 6 Isotopes
- 25. Atomic weight:Atomic weight: the weighted average of the masses (in amu) of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. -Chlorine is 75.77% chlorine-35 and 24.23% chlorine-37 Atomic Weight
- 27. Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) – arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic weight (rearranged by atomic number in 1913). – He observed that when elements are arranged in this manner, certain sets of properties recur periodically. – He then arranged elements with recurring sets of properties in the same columncolumn (vertical row).
- 29. • MetalsMetals – solids at room temperature (except mercury), shiny, conduct electricity, and are ductile and malleable. – form alloys (solutions of one metal dissolved in another); brass, for example, is an alloy of copper and zinc. – In chemical reactions, they tend to give up electrons. • NonmetalsNonmetals – Except for hydrogen (H), they lie on the right side of the Periodic Table. – Except for graphite, do not conduct electricity. – In chemical reactions, they tend to accept electrons. Classification of Elements
- 30. • MetaloidsMetaloids – Share some of the properties with metals and nonmentals; for example, they are shiny like metals but do not conduct electricity – Boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium are classified as metalloids – One of the metalloids, silicon, is a semiconductor; it does not conduct electricity under certain applied voltages, but becomes a conductor at higher applied voltages
- 32. Oxygen is an example of a(n) ________ element. 1. Main-group 2. Halogen 3. Transition metal 4. Noble gas
- 33. • The noble gases, Group 8A elements Examples of Periodicity:
- 36. Shell 4 3 2 1 32 18 8 2 Relative energies of electrons in each shell lower higher. nucleus 1st shell 2nd shell 3rd shell 4th shell Number of electrons shell can hold How are electron in an atom arranged? Bohr’s Model
- 37. Electron configuration:Electron configuration: the exact arrangement of electrons in the extranuclear space The energy of electrons in an atom is quantizedquantized, which means that an electron in an atom can have only certain allowed energies. Ground-State electron configuration:Ground-State electron configuration: the electron configuration of the lowest energy state of an atom
- 38. Shell Subshell Orbital Electron configuration continued…..Electron configuration continued….. Within shells electrons are further groupedWithin shells electrons are further grouped into 4 differentinto 4 different subshellssubshells, identified in, identified in order of increasing energies:order of increasing energies: s, p, d, fs, p, d, f Shell number: 1 2 3 4 Orbital designation: s s,p s,p,d s,p,d,f Within each subshell electrons are groupedWithin each subshell electrons are grouped intointo orbitalsorbitals, regions of space within an, regions of space within an atom where the specific electrons are mostatom where the specific electrons are most likely foundlikely found
- 39. ORBITALS HOLDS S 1 orbital P 3 orbitals D 5 orbitals F 7 orbitals • each orbital hold only 2 electrons that differ in spin
- 42. • OOrbitals fill in the order of increasing energy from lowest to highest. • EEach orbital can hold up to two electrons with spins paired Pauli’s principle. • WWhen there is a set of orbitals of equal energy, each orbital becomes half filled before any of them becomes completely filled Hund’s principle.
- 45. Orbital box diagramsOrbital box diagrams Order: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p and so on……
- 46. Order: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p and so on……
- 47. Order: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p and so on……
- 48. Noble gas notationNoble gas notation The symbol of the noble gas immediately preceding the particular atom indicates the electron configuration of all filled shells Electron Configuration (condensed)O rbital box diagram Noble G as Notation 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 [He]2s 2 2p 2
- 51. Valence shell:Valence shell: the outermost incomplete shell. Valence electron:Valence electron: an electron in the valence shell. Lewis structure:Lewis structure: the symbol of the element represents the nucleus and filled shells. Dots represent valence electrons.
- 53. The Lewis Dot Structure for sulfur will contain _____ dots. 1. 4 2. 6 3. 8 4. 16
- 54. Periodicity of chemical properties can be explained in terms of periodicity in electron configuration. The Periodic Table works because elements in the same column (group) have the same configuration in their outer shells.
- 55. The size of an atom is determined by the size of its outermost occupied orbital. The size of a chlorine atom is determined by the size of its three 3p orbitals, the size of a carbon atom is determined by the size of if its three 2p orbitals. 198 pm Cl Cl C C 1.54 pm The radius of a chlorine atom is 99 pm The radius of a carbon atom is 77 pm
- 56. Atomic Size (picometers) Explanation for this trend can be found on page 56
- 57. • Ionization energy:Ionization energy: the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an atom in the gaseous state. When lithium loses one electron, it becomes a lithium ion; it still has three protons in its nucleus, but now only two electrons outside the nucleus.
- 58. Increases across a row; valence electrons are in the same shell and subject to increasing attraction as the number of protons in the nucleus increases. Increases going up a column; the valence electrons are in lower energy levels, which are closer to the nucleus and feel the nuclear charge more strongly.
Hinweis der Redaktion
- There are 116 known elements. Of these, 88 occur in nature; the others have been made by chemists and physicists. Their symbols consist of one or two letters. Names are derived from a variety of sources: the English name of the element, people important in atomic science, geographic locations, planets, mythological sources, etc. Compound: a pure substance made up of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass. Formula of a compound: tells us the ratios of its constituent elements and identifies each element by its atomic symbol.
- the mass of the electrons in an atom is so small compared to that of its protons and neutrons that electrons are not counted in determining mass number.
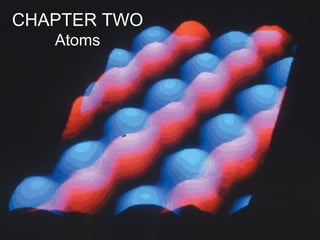
- The STM is a non-optical microscope which employs principles of quantum mechanics. An atomically sharp probe (the tip) is moved over the surface of the material under study, and a voltage is applied between probe and the surface. Depending on the voltage electrons will "tunnel" (this is a quantum-mechanical effect) or jump from the tip to the surface (or vice-versa depending on the polarity), resulting in a weak electric current. The size of this current is exponentially dependent on the distance between probe and the surface. For a current to occur the substrate being scanned must be conductive (or semiconductive). Insulators cannot be scanned through the STM, as the electron has no available energy state to tunnel into or out of due to the band gap structure in insulators.