Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie Dacj 4 2-a (20)
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Dacj 4 2-a
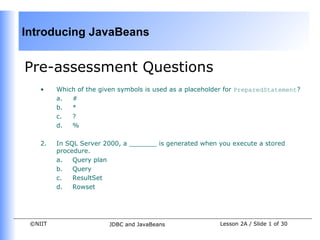
- 1. Introducing JavaBeans
Pre-assessment Questions
• Which of the given symbols is used as a placeholder for PreparedStatement?
a. #
b. *
c. ?
d. %
2. In SQL Server 2000, a _______ is generated when you execute a stored
procedure.
a. Query plan
b. Query
c. ResultSet
d. Rowset
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 1 of 30
- 2. Introducing JavaBeans
Pre-assessment Questions (Contd.)
1. Which of the following parameters cannot be used in a stored procedure?
• IN
• OUT
• OUTIN
• INOUT
• Which of the following enables you to retrieve the information about a
ResultSet?
a. DatabaseMetaData
b. ResultSetData
c. RowSetData
d. ResultSetMetaData
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 2 of 30
- 3. Introducing JavaBeans
Pre-assessment Questions (Contd.)
1. The batch update operations can throw two types of exceptions,
__________and ___________.
• SQLException and BatchUpdateException
• SQLException and UpdateException
• BatchException and BatchUpdateException
• BatchException and SQLException
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 3 of 30
- 4. Introducing JavaBeans
Solutions to Pre-assessment
Questions
• c. ?
• a. Query plan
• c. OUTIN
• d. ResultSetMetaData
• a. SQLException and BatchUpdateException
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 4 of 30
- 5. Introducing JavaBeans
Objectives
In this lesson, you will learn about:
• Features of JavaBeans
• Associating predefined events with sample JavaBeans
• Testing JavaBeans using BDK
• Creating sample JavaBean applet using BDK
• Creating user-defined JavaBean
• Creating manifest and JAR files for a JavaBean
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 5 of 30
- 6. Introducing JavaBeans
JavaBean Concepts
• A software component is a reusable object that can be plugged into any target
software application.
• You can develop software components using various programming languages,
such as C, C++, Java, and Visual Basic.
• JavaBeans are reusable and platform-independent software components
developed using the Java programming language.
• The classes and interfaces defined in the java.beans package enable you to
create JavaBeans.
• The JavaBean components can exist in one of the following three phases of
development:
• Construction phase
• Build phase
• Execution phase
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 6 of 30
- 7. Introducing JavaBeans
JavaBean Concepts (Contd.)
• Elements of a JavaBean
• Properties: Refer to the private data members of a JavaBean that define
the behavior of the JavaBeans.
• Methods: Refer to public member functions of a JavaBean that are used to
modify the JavaBean properties.
• Events: Refer to the messages that one JavaBean components sends to
another JavaBean components.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 7 of 30
- 8. Introducing JavaBeans
JavaBean Concepts (Contd.)
• The JavaBean Component Specification
• Customization: Is the ability of JavaBean to allow its properties to be
changed in build and execution phase.
• Persistence: Is the ability of JavaBean to save its state to disk or storage
device and restore the saved state when the JavaBean is reloaded.
• Communication: Is the ability of JavaBean to notify change in its
properties to other JavaBeans or the container.
• Introspection: Is the ability of a JavaBean to allow an external application
to query the properties, methods, and events supported by it.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 8 of 30
- 9. Introducing JavaBeans
JavaBean Concepts (Contd.)
• Services of JavaBean Components
• Builder support: Enables you to create and group multiple JavaBeans in
an application.
• Layout: Allows multiple JavaBeans to be arranged in a development
environment.
• Interface publishing: Enables multiple JavaBeans in an application to
communicate with each other.
• Event handling: Refers to firing and handling of events associated with
a JavaBean.
• Persistence: Enables you to save the last state of JavaBean.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 9 of 30
- 10. Introducing JavaBeans
JavaBean Concepts (Contd.)
• Types of JavaBeans
• Control JavaBeans: Are used to create GUI components that can be
plugged into any application.
• Container JavaBeans: Are used to hold other JavaBeans.
• Invisible Runtime JavaBeans: Are used to create components that
perform a specific task in the background of an application.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 10 of 30
- 11. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit
• Is a development environment to create, configure, and test JavaBeans.
• The features of BDK environment are:
• Provides a GUI to create, configure, and test JavaBeans.
• Enables you to modify JavaBean properties and link multiple
JavaBeans in an application using BDK.
• Provides a set of sample JavaBeans.
• Enables you to associate pre-defined events with sample JavaBeans.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 11 of 30
- 12. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit (Contd.)
• Identifying BDK Components
• Execute the run.bat file of BDK to start the BDK development
environment.
• The components of BDK development environment are:
• ToolBox
• BeanBox
• Properties
• Method Tracer
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 12 of 30
- 13. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit (Contd.)
• ToolBox window: Lists the sample JavaBeans of BDK.
• The following figure shows the ToolBox window:
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 13 of 30
- 14. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit (Contd.)
• BeanBox window: Is a workspace for creating the layout of JavaBean
application.
• The following figure shows the BeanBox window:
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 14 of 30
- 15. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit (Contd.)
• Properties window: Displays all the exposed properties of a JavaBean.
You can modify JavaBean properties in the properties window.
• The following figure shows the Properties window:
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 15 of 30
- 16. Introducing JavaBeans
Beans Development Kit (Contd.)
• Method Tracer window: Displays the debugging messages and method
calls for a JavaBean application.
• The following figure shows the Method Tracer window:
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 16 of 30
- 18. Introducing JavaBeans
Demonstration-Creating Sample
JavaBean Applet using BDK
(Contd.)
• Solution
• To create an applet that shows a Molecule JavaBean rotating
along its X-axis, you need to perform the following tasks:
1. Associating pre-defined event with sample JavaBeans.
2. Converting the JavaBean to an applet.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 18 of 30
- 19. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean
• The coding conventions to create a user-defined JavaBean are:
• Implement the java.io.Serializable interface.
• Define an empty constructor to initialize the instances of a JavaBean.
• Define the accessor and mutator methods for the exposed properties
of a JavaBean.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 19 of 30
- 20. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean (Contd.)
• Accessor and Mutator Methods:
• Are used to access the exposed properties of a JavaBean.
• The accessor methods:
• Are used to retrieve the values of JavaBean properties.
• Are also called get methods.
• The mutator methods:
• Are used to specify the values of JavaBean properties.
• Are also called set methods.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 20 of 30
- 21. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean (Contd.)
• Manifest and JAR Files
• Manifest File
• The manifest file for a JavaBean application contains a list of all the
class files that make up a JavaBean.
• The entry in the manifest file enables the target application to
recognize the JavaBean classes for an application.
• For example, the entry for the SpellCheck JavaBean in the manifest
file is as shown:
Name: SpellCheck.class
Java-Bean: True
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 21 of 30
- 22. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean (Contd.)
• Manifest File (Contd.)
• The rules to create a manifest file are:
• Press the Enter key after typing each line in the manifest file.
• Leave a space after the colon.
• Type a hyphen between Java and Bean.
• No blank line between the Name and the Java-Bean entry.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 22 of 30
- 23. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean (Contd.)
• Java Archive File
• The files of a JavaBean application are compressed and grouped as
JAR files to reduce the size and the download time of the files.
• The syntax to create a JAR file from the command prompt is:
jar <options> <file_names>
• The file_names is a list of files for a JavaBean application that are
stored in the JAR file.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 23 of 30
- 24. Introducing JavaBeans
User-Defined JavaBean (Contd.)
• Java Archive File (Contd.)
• The various options that you can specify while creating a JAR file are:
• c: Indicates the new JAR file is created.
• f: Indicates that the first file in the file_names list is the name
of the JAR file.
• m: Indicates that the second file in the file_names list is the
name of the manifest file.
• t: Indicates that all the files and resources in the JAR file are to
be displayed in a tabular format.
• v: Indicates that the JAR file should generate a verbose output.
• x: Indicates that the files and resources of a JAR file are to be
extracted.
• o: Indicates that the JAR file should not be compressed.
• m: Indicates that the manifest file is not created.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 24 of 30
- 26. Introducing JavaBeans
Demonstration-Creating User-Defined
JavaBean (Contd.)
• Solution
• To create a user-defined JavaBean that changes the caption of a
label, you need to perform the following tasks:
1. Code the user-defined JavaBean
2. Package the JavaBean
3. Load and test the JavaBean
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 26 of 30
- 27. Introducing JavaBeans
Summary
In this lesson, you learned:
• A component is a reusable object that can be plugged into any target
software application.
• JavaBeans are reusable and platform-independent software components that
are created using the Java programming language.
• The various features of JavaBean are:
• Customization
• Persistence
• Communication
• Introspection
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 27 of 30
- 28. Introducing JavaBeans
Summary (Contd.)
• JavaBean components provide the following services to the container in
which they are grouped together:
• Builder support
• Layout
• Interface publishing
• Event handling
• Persistence
• There are three types of JavaBeans, Control JavaBeans, Container
JavaBeans, and Invisible runtime JavaBeans.
• BDK is a development environment to test and create JavaBeans.
• The ToolBox window of BDK displays the sample JavaBeans defined in the
BDK.
• The BeanBox window of BDK enables you to test JavaBeans and create
applications using various JavaBeans as components.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 28 of 30
- 29. Introducing JavaBeans
Summary (Contd.)
• The properties window displays the properties of the currently selected
JavaBean component.
• The method tracer window of BDK displays the debugging messages and
method calls for the BDK environment.
• BDK provides pre-defined events that can be associated with the sample
JavaBean components in an application.
• The pre-defined events for the sample JavaBeans are displayed in the
EventTargetDialog window of BDK.
• The MakeApplet utility of BDK enables you to create an applet file for a
JavaBean application. The applet file can be run using a Web browser or the
applet viewer utility of Java.
• You can also create user-defined JavaBeans using the classes and interfaces
provided by the java.beans package.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 29 of 30
- 30. Introducing JavaBeans
Summary (Contd.)
• The accessor and mutator methods of user-defined JavaBean are used to
retrieve and specify the value of JavaBean properties.
• The user-defined JavaBean implements the java.io.Serializable
interface.
• A manifest file is a text file that provides information about the class files
that represent a JavaBean.
• JAR files are platform-independent files that are used to package all the
classes and the associated resources for a JavaBean application.
• The JAR file for the user-defined JavaBean is loaded in the ToolBox window
using the FileLoadJar command of the BeanBox window.
©NIIT JDBC and JavaBeans Lesson 2A / Slide 30 of 30