Cartilage (1)
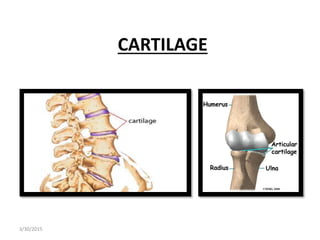
- 2. CARTILAGE • Cartilage is an avascular, flexible connective tissue located through out the body ,providing support and cushioning for adjacent tissues. • Cartilage is composed of cells & extracellular matrix ( ground substance & fibers) Chondrocytes • Cells of cartilage are called Chondrocytes. • Chondrocytes may occur singly but are frequently clustered. • Extracellular matrix is secreted by chondrocytes and composed of ground substance & connective tissue fibers. • Fibers are of collagen & elastic variety and are embedded in ground substance. • Cells occupy smallest spaces called Lacunae (singular lacuna) within the extracellular matrix . 3/30/2015
- 3. Perichondrium: It is a sheath of dense irrregular connective tissue that covers cartilage in most(but not all)places. Perichondrium contains blood vessels which are responsible for supply of nutrients and oxygen to the avascular cartilage. Perichondrium is composed of 2 layers 1. An outer fibrous layer which consist of collagen fibers and blood vessels,lymphatic vessels and nerves. 2. An inner cellular layer , in which are present fibroblast like cells called chondrogenic cells, which are capable of transformation into chondroblasts (cartilage forming cells) 3/30/2015
- 4. Cartilage is an avascular. Cartilage has no nerve supply or sensory receptors. The substances of cartilage is not traversed by any blood vessel or lymphatic vessel . The chondrocytes receive nutrition from blood vessels of surrounding connective tissue by diffusion through extracellular matrix. In synovial joints, the cartilage also receives nourishment from the synovial fluid that fills the joint cavities. 3/30/2015
- 5. Functions of cartilage Because of its resilient nature, cartilage performs 2 major functions in the adult human body. 1. Functions as shock absorber in various locations of the body . 2. Covers the articulating surfaces of those bones which participates in the formation of synovial joints. (friction-free movement of these joints) 3/30/2015
- 6. Types of Cartilage • Three varieties are distinguished on the basis of types of fibers/fibrils present in the extracellular matrix. • HYALINE CARTILAGE • FIBROCARTILAGE • ELASTIC CARTILAGE 3/30/2015
- 7. HYALINE CARTILAGE • Commonly called ‘’gristle’’ • Upon naked eye examination, the fresh hyaline cartilage gives a bluish – white translucent appearance resembling that of a frosted glass(hence the name hyaline i-e glass like) • When viewed through light microscope has a clear glassy like appearance. • CELLS OF HYALINE CARTILAGE : • Cells are chondrocytes, they are large (15-30 m in diameter) • Rough spherical cells. • Big centrally placed nucleus showing one or two nucleoli. • Cytoplasm is granular and basophilic • Chondrocytes are generally arranged into groups of two to four or more cells ,which are called isogenic groups. • All members of isogenic groups occupy a single lacuna 3/30/2015
- 9. Distribution of hyaline Cartilage: Articular cartilages which cover the articulating bone surfaces in the movable joints. Cartilage of trachea and bronchi Nasal cartilage forms flexible bridge called costal cartilage , between the anterior portion of each of the first 10 ribs and the sternum. Most of the bones of body first forms as hyaline cartilage and later become bone in the process called endochondral ossification. 3/30/2015
- 10. 3/30/2015
- 11. ELASTIC CARTILAGE • When fresh appears yellowish and more opaque than hyaline cartilage. • Numerous elastic fibers give it a yellow appearance. • Similar to hyaline cartilage except for presence of abundant elastic fibers that makes it very flexible without compromising its strength. • Found in outer ear , portion of larynx ,auditory canal. 3/30/2015
- 12. • Chondrocytes are similar in appearnce to those of to hyaline cartilage . • They lie within lacunae. • Occur singly or in isogenic groups of two to four cells. • Matrix contains large number of elastic fibers which branch and interlace with each other to form a closely woven network. • Elastic network is dense in region surrounding the chondrocytes. • Elastic cartilage is surrounded by perichondrium. • Unlike hyaline cartilage they don't become calcified with increasing age. 3/30/2015
- 13. 3/30/2015
- 14. 3/30/2015
- 15. 3/30/2015
- 16. FIBROCARTILAGE • Can be regarded as a combination of dense regular connective tissue and hyaline cartilage . • Found in body where great strength combined with flexibility and rigidity is required. • Chondrocytes have same structure as those of hyaline cartilage but the arrangement of cells in these two varieties of cartilage is different from each other. • Chondrocytes are arranged in parallel rows; each row comprising of 2,4,6 cells. • Fibrocartilage not surrounded by perichondrium • Matrix of fibrocartilage stains acidophilic due to abundance of collagen fibers. 3/30/2015
- 18. • Like ordinary collagenous connective tissue, the fibrocartilage develops from fibroblast. • After producing large quantities of collagen fibers, some of the fibroblasts differentiate into chondrocytes and begin to secrete cartilage matrix containing proteoglycans. • This amorphous matrix surrounds the chondrocytes and isolates then from bundles of collagen fibers. 3/30/2015
- 19. Distribution of Fibrocartilage • Found in • Intervertebral disc • Disc of pubic symphysis • Menisci of knee joint • sternoclavicular joint 3/30/2015
- 20. SUMMARY OF CARTILAGE TYPE STRUCTURE FUNCTION HYALINE CARTILAGE Homogenous matrix with extremely fine collagenous fibers provides flexible support, protects & is precursor to bone Articular surface of bones,nose,wall of respiratory passages,fetal skeleton FIBROCARTILAGE Abundant collagenous fibers within matrix, supports, withstands compression Symphysis pubis,intervertebral disc,knee joint ELASTIC CARTILAGE Abundant elastic fibers within matrix, provide flexibility Framework of outer ear ,portion of larynx 3/30/2015
- 21. BONE TISSUE • Is most rigid of all connective tissues. • Unlike cartilage, it has a rich vascular supply. • Bone tissue is composed of several type of bone cells embeded in a matrix of ground substance, inorganic salts (calcium & phosphorous) and collagenous fibers. • Hardness of bone is due to calcium phosphate deposited within intracellular matrix. • Numerous collagenous fibers also embedded within the matrix, give bone some flexibility. 3/30/2015
- 22. Spongy & Compact Bone Tissues Based on porosity ,bone tissue is classified as • Compact (dense) bone tissue • Spongy(cancellous) bone tissue 3/30/2015
- 23. Bone Cells • Five types of bone cells contained within bone tissues 1. Osteogenic 2. Osteoblasts 3. Osteocytes 4. Osteoclasts 5. Bone lining cells 3/30/2015
- 25. Shapes / Types of bones • Bones of skeleton are grouped on the basis of shape into four principle categories 1. Long Bones (femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, metatarsal & phalanges) 2. Short Bones (Lunate,pisiform,trapezoid) 3. Flat Bones (cranial bones, ribs,bones of shoulder girdle) 4. Irregular bones (vertebrae & certain bones of skull) 3/30/2015
- 26. Example of Bone types, as classified by shape 3/30/2015
- 28. 3/30/2015
- 29. STRUCTURE OF TYPICAL BONE 3/30/2015
- 30. Compact Bone • The outer covering or the periosteum is made up of an outer fibrous layer & inner cellular layer, which contains osteogenic cells. • Bony tissue is comprised of Haversian systems. • Each Haversian system consists of centrally situated Harvesian canal,surrounded by concentrically arranged lamella. • Each osteon consists of 5-15 lamellae of bone matrix that are concentrically arranged around a longitudinally running central canal called harvesian canal. 3/30/2015
- 31. Compact Bone • Osteocytes in their lacunae are found at regular intervals betweeen lamellae . • Neighbouring lacunae are connected with each other by narrow canaliculi . • Canaliculi form a network of channels that allow the flow of nutrients, ions, hormones & waste products between osteocytes and nearby blood vessels. • Between osteons there are imcomplete remnants of osteons,called interstitial systems. • Perforating (Volkmann’s canal penetrates compact bone,connecting osteons with blood vessels & nerves 3/30/2015
- 32. 3/30/2015
- 33. MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF TYPICAL BONE 3/30/2015
- 34. Spongy Bone • E.g Sternum,ends of long bones • Its outermost covering is periosteum • Haversian systems are absent. • Bone tissue is made up of trabecule of varying shapes & sizes joined with each other enclosing small spaces containing red bone marrow. • Inside the trabeculae are osteocytes which lie within the lacunae 3/30/2015
