Cardiovascular
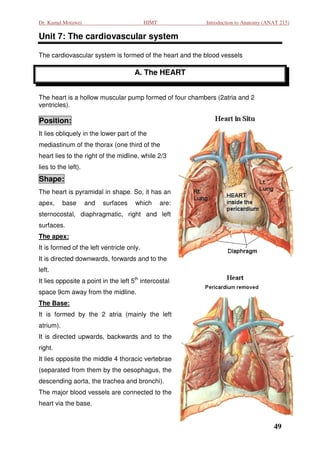
- 1. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Unit 7: The cardiovascular system : The cardiovascular system is formed of the heart and the blood vessels A. The HEART The heart is a hollow muscular pump formed of four chambers (2atria and 2 ventricles). Position: It lies obliquely in the lower part o the of mediastinum of the thorax (one third of the heart lies to the right of the midline, while 2/3 lies to the left). Shape: The heart is pyramidal in shape. So, it has an apex, base and surfaces which are: sternocostal, diaphragmatic, right and left surfaces. The apex: It is formed of the left ventricle only. It is directed downwards, forwards and to the left. It lies opposite a point in the left 5th intercostal space 9cm away from the midline. The Base: It is formed by the 2 atria (mainly the left atrium). It is directed upwards, backwards and to the right. It lies opposite the middle 4 thoracic vertebrae (separated from them by the oesophagus, the ted descending aorta, the trachea and bronchi) , bronchi). The major blood vessels are connected to the heart via the base. 49
- 2. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) The sternocostal surface: It is related to sternum and costal wall. It is formed of the left and right ventricles. The diaphragmatic surface: It lies on the diaphragm. It is formed of the 2 ventricles The right surface: It is formed by the right atrium It is related to the right lung. atrium. The left surface: It is formed of the left ventricle. It is related to the left lung. Chambers of the heart and their connections: The heart is formed of 4 chambers, Rt. & Lt. atria and Rt. & Lt. ventricles. The 2 atria are demarcated from the 2 ventricles by a groove called the coronary groove, while the 2 ventricles are separated from each other by the anterior and posterior interventricular grooves. There is no direct connection between the right side and the left side of the heart. side The right atrium: It forms the right surface of the heart. It is separated from the left atrium by the interatrial septum. During intrauterine life, this septum shows an oval foramen to allow passage of blood from the right atrium directl into the left directly atrium (as there is no respiration). This foramen is closed after birth. Connections: The right atrium receives non oxygenated blood from the whole body via: non-oxygenated 1. Superior vena cava (SVC) which collects venous blood from the upper half of the body. 2. Inferior vena cava (IVC) which collects venous blood from the lower half of the body. 3. Coronary sinus that collects venous blood from the heart itself. The right atrium pumps its blood content to the right ventricle through the right atrioventricular orifice (which is guarded by the tricuspid valve). ricular 50
- 3. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) The right ventricle: It forms most of the costo-diaphragmatic surface of the heart. It is separated from the left ventricle by the interventricular septum that bulges into the cavity of the right ventricle. Connections: It receives venous blood from the right atrium via the tricuspid valve. It pumps its blood content, via the pulmonary trunk, to the lungs. (The pulmonary valve prevents regurgitation of blood from the pulmonary trunk to the right ventricle). The left atrium: It forms most of the base of the heart. It receives two pulmonary veins from each lung. It pumps its blood content to the left ventricle via the left atrioventricular orifice (guarded by the mitral valve). The left ventricle: Its wall is thicker than that of the right ventricle. It receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium via the mitral valve. It pumps its blood content, via the aorta, to the whole body. (The aortic valve prevents regurgitation of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle). 51
- 4. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Blood Supply of the Heart: The heart is supplied with arterial blood by the right and the left coronary arteries, which are branches from the ascending aorta. A large vein called coronary sinus drains most of the heart, then it opens into the right atrium. Surface Anatomy of the heart: The heart can be projected to the surface by determining 4 points and connecting them together by four lines: First point (A)(The apex of the heart): it is a point drawn in the left 5th intercostal space, 9cm from the midline. Second point (B): on the 2nd left costal cartilage, 1.5 cm to the left of the sternal edge. Third point (C): on the 3rd right costal cartilage, 1.5 cm to the right of the sternal edge. Fourth point (D): on the 6th right costal cartilage, 1.5 cm to the right of the sternal edge. 52
- 5. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Coverings of the heart: The heart lies within a fibrous tissue envelope called the fibrous pericardium pericardium. The fibrous pericardium is continuos with the adventitia of the great vessels connected to the heart. A serous sac intervenes between the heart and its fibrous pericardium to prevent friction. This serous sac is called serous pericardium It is formed of pericardium. two layers and a cavity in between, visceral layer covering the heart surface and pari parietal layer lining the fibrous pericardium. The cavity of the serous pericardium contains nothing but few drops of fluid for lubrication. Structure of the Heart: The heart is formed of two myocardial muscles, one for the atria and another one for the ventricles. Both muscles are attached to the corresponding side of the fibrous ricles. rings surrounding the atrioventricular orifices. The atrial and ventricular muscles are completely separated from each other except for at the atrioventricular bundle, which represents the only communication between both muscles. nts The heart cavity is lined with endothelial layer. The conducting system: this is formed of some specialized cardiac muscle fibers, which are able to initialize and conduct cardiac impulses. It comprises the following structures: Sino-atrial node (pacemaker of the heart) in the right atrium close to the opening of the SVC Atrioventricular node: in the lower part of the interatrial septum. The atrioventricular bundle: It represents the only possible communicat bundle: communication between the atrial and ventricular muscles. It is divided into to two (Rt. &Lt.) branches for the Rt. and Lt. Ventricles. 53
- 6. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) B. The Blood Vessels The blood vessels are of three types: arteries, veins, and capillaries. 1. The arteries: They convey blood from the heart and distribute it to the body tissues. The smallest arteries (less than 0.1 mm in diameter, are called arterioles. The wall of an artery is formed of three layers; a) Tunica intema: it is formed of simple squamous endothelium. b) Tunica Media: It is formed of smooth muscle fibers and elastic fibers. Medium sized and small sized arteries contain more smooth muscles fibers than elastic fibers. On the other hand, Large sized arteries contain more elastic fibers than muscle fibers. c) Tunica adventitia: it is formed of fibrous connective tissue. 2. The veins: They convey blood back to the heart. The smallest veins are called venules. The wall of the vien is formed of the same layers as the artery but it is comparatively thin and very poor in muscle and elastic fibers. Veins may be deep or superficial. Medium-sized deep arteries are usually accompanied by two veins, one on each side, called venae comitantes. The superficial veins lie under the skin, they clinically important as they are used for intravenous injections. 3. The capillaries: they are microscopic vessels arranged in a network-form connecting the arterioles to the venules. The wall of the blood capillary is formed of a single layer of squamous cells on a basement membrane. 54
- 7. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Major arteries of the body The Aorta: it is the largest artery in the body. It conveys blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the whole body. It has three distinct parts: Ascending aor aorta, it gives left and right coronary arteries to the heart. Arch of the aorta, it giv three main arteries: brachiocephalic left common , gives brachiocephalic, carotid & left subclavian arteries to the head, neck and upper limbs. Descending aorta, the part of the descending aorta , that lies above the diaphragm is called thoracic aorta. The part below the diaphra . diaphragm is the abdominal aorta. The abominal aorta ends by . dividing into right and left common iliac arteries. The Common iliac arteries: Each one divides into Internal iliac artery (for the pelvis) and external iliac arteries (for the lower limbs). Arteries of the upper limb: The subclavian artery when passing the axilla is called axillary artery. It continues its course in the upper arm as the brachial artery, which is a superficial artery. The brachial artery divides into radial and ulnar arteries in the forearm (they are superficial in the lower part of the forearm. arm Arteries of the lower limb: The external iliac artery continues on the front aspect of the thigh as the femoral artery, then the artery passes behind the Knee joint as the popliteal artey The poplitea artey. artery divides in the back of the leg into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Arterial pulse Arterial pulse can be palpated at the superficial arteries especially those related to bones, e.g. the radial artery at the lower end of the radius, the common carotid artery in the neck and the femoral artery at the upper part of the front of the thigh. 55
- 8. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) The major deep veins The Superior vena Cava (SVC): it drains the upper part of the body. It is formed by the union of the the right and left brachiocephalic veins The right and left brachio cephalic veins: Each of which is formed by the union of the corresponding internal jugular and subclavian vein. The inferior vena cava (IVC): It drains the lower part of the body. It is formed in the abdomen by the union of the right and left common iliac veins. Superficial veins of clinical importance: External Jugular Vein: it lies in the neck extending obliquely backwards from the angle of the mandible to the middle of the clavicle. It is used as a monitor for the heart function. Also, it can be used for intravenous injections. Cephalic vein of the upper limb: It lies constantly under the skin immediately behind the styloid process of the radius. Median cubital vein: it lies obliquely in the cubital fossa (in front of the elbow joint). The great saphenous vein of the lower limb: It has a constant position in front of the medial malleolus. It is liable to be varicose (elongated and tortuous). 56
- 9. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Major Arteries 57
- 10. Dr. Kamal Motawei HIMT Introduction to Anatomy (ANAT 215) Major Veins 58
