Pc12 sol c06_6-1
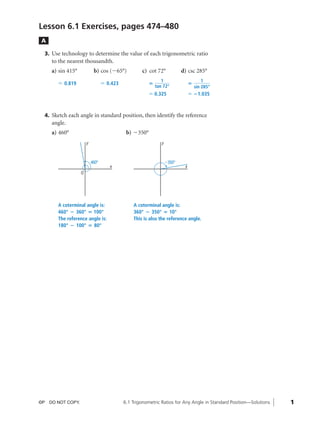
- 1. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 1 Home Quit Lesson 6.1 Exercises, pages 474–480 A 3. Use technology to determine the value of each trigonometric ratio to the nearest thousandth. a) sin 415° b) cos (Ϫ65°) c) cot 72° d) csc 285° 1 1 Џ 0.819 Џ 0.423 ؍ ؍ tan 72° sin 285° Џ 0.325 Џ ؊1.035 4. Sketch each angle in standard position, then identify the reference angle. a) 460° b) Ϫ350° y y 460° Ϫ350° x x O A coterminal angle is: A coterminal angle is: 460° ؊ 360° °001 ؍ 360° ؊ 350° °01 ؍ The reference angle is: This is also the reference angle. 180° ؊ 100° °08 ؍ ©P DO NOT COPY. 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions 1
- 2. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 2 Home Quit c) 695° d) Ϫ500° y y x x 695° Ϫ500° A coterminal angle is: A coterminal angle is: ؊720° ؉ 695° °52؊ ؍ 360° ؊ 500° °041؊ ؍ The reference angle is: 25° The reference angle is: 180° ؊ 140° °04 ؍ 5. For each angle in standard position below: i) Determine the measures of angles that are coterminal with the angle in the given domain. ii) Write an expression for the measures of all the angles that are coterminal with the angle in standard position. a) 75°; b) Ϫ105°; for Ϫ500° ≤ u ≤ 500° for Ϫ600° ≤ u ≤ 600° i) Between 500° and 0°, the i) Between 600° and 0°, the coterminal angles are: coterminal angle is: 75°; and 75° ؉ 360° °534 ؍ ؊105° ؉ 360° °552 ؍ Between 0° and ؊500°, the Between 0° and ؊600°, the coterminal angle is: coterminal angles are: 75° ؊ 360° °582؊ ؍ ؊105°; and ii) The measures of all the ؊105° ؊ 360° °564؊ ؍ angles coterminal with 75° ii) The measures of all the angles can be represented by the coterminal with ؊105° can be expression: represented by the expression: 75° ؉ k360°, k ç ޚ ؊105° ؉ k360°, k ç ޚ c) 215°; d) Ϫ290°; for Ϫ700° ≤ u ≤ 700° for Ϫ800° ≤ u ≤ 800° i) Between 700° and 0°, the i) Between 800° and 0°, the coterminal angles are: coterminal angles are: 215°; and ؊290° ؉ 360° ;°07 ؍ 215° ؉ 360° °575 ؍ ؊290° ؉ 2(360°) ;°034 ؍and Between 0° and ؊700°, the ؊290° ؉ 3(360°) °097 ؍ coterminal angles are: Between 0° and ؊800°, the 215° ؊ 360° ;°541؊ ؍and coterminal angles are: 215° ؊ 2(360°) °505؊ ؍ ؊290°; and ii) The measures of all the ؊290° ؊ 360° °056؊ ؍ angles coterminal with 215° ii) The measures of all the angles can be represented by the coterminal with ؊290° can be expression: 215° ؉ k360°, represented by the expression: kçޚ ؊290° ؉ k360°, k ç ޚ 2 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions DO NOT COPY. ©P
- 3. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 3 Home Quit B 6. Use exact values to complete this table. You will return to this table when U sin U cos U tan U csc U sec U cot U you complete Lesson 6.3 Exercises. 0°, 0 0 1 0 – 1 – √ 1 3 1 2 √ 30°, √ 2 √ 3 6 2 2 3 3 1 1 √ √ 45°, √ √ 1 2 2 1 4 2 2 √ 3 1 √ 2 1 60°, 3 √ 2 √ 3 2 2 3 3 90°, 1 0 – 1 – 0 2 √ 2 3 1 √ 2 1 120°, ؊ ؊ 3 √ ؊2 ؊√ 3 2 2 3 3 3 1 1 √ √ 135°, √ ؊√ ؊1 2 – 2 ؊1 4 2 2 √ 5 1 3 1 2 √ 150°, ؊ ؊√ 2 ؊√ ؊ 3 6 2 2 3 3 180°, 0 ؊1 0 – ؊1 – √ 7 1 3 1 2 √ 210°, ؊ ؊ √ ؊2 ؊√ 3 6 2 2 3 3 5 1 1 √ √ 225°, ؊√ ؊√ 1 ؊ 2 ؊ 2 1 4 2 2 √ 4 3 1 √ 2 1 240°, ؊ ؊ 3 ؊√ ؊2 √ 3 2 2 3 3 3 270°, ؊1 0 – ؊1 – 0 2 √ 5 3 1 √ 2 1 300°, ؊ ؊ 3 ؊√ 2 ؊√ 3 2 2 3 3 7 1 1 √ √ 315°, ؊√ √ ؊1 ؊ 2 2 ؊1 4 2 2 √ 11 1 3 1 2 √ 330°, ؊ ؊√ ؊2 √ ؊ 3 6 2 2 3 3 360°, 2 0 1 0 – 1 – ©P DO NOT COPY. 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions 3
- 4. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 4 Home Quit 7. Determine the exact values of the 6 trigonometric ratios for each angle. a) 480° A coterminal angle is: 480º ؊ 360º 021 ؍º From the completed table in question 6: sin 480º 021 √ ؍º sin cos 480º ؍cos 120º tan 480º ؍tan 120º 3 1 √ ؍ ؊؍ 3 ؊؍ 2 2 1 1 1 csc 480º ؍ sec 480º ؍ cot 480º ؍ sin 120° cos 120° tan 120° 2 1 √؍ 2؊ ؍ √؊ ؍ 3 3 b) Ϫ855° A coterminal angle is: 1080º ؊ 855º 522 ؍º From the completed table in question 6: sin (؊855º) ؍sin 225º cos (؊855º) ؍cos 225º tan (؊855º) ؍tan 225º 1 1 √؊ ؍ √؊ ؍ 1؍ 2 2 1 1 1 csc (؊855º) ؍ sec (؊855º) ؍ cot (؊855º) ؍ sin 225° cos 225° tan 225° √ √ 2 ؊؍ 2 ؊؍ 1؍ 8. For each point P(x, y) on the terminal arm of an angle u in standard position, determine the exact values of the six trigonometric ratios for u. a) P(2, 1) b) P(3, Ϫ4) Let the distance between the Let the distance between the origin and P be r. origin and P be r. Use: x2 ؉ y2 ؍r2 Use: x2 ؉ y2 ؍r2 Substitute: x ,2 ؍y 1 ؍ Substitute: x ,3 ؍y 4؊ ؍ 22 ؉ 12 ؍r2 32 ؉ (؊4) 2 ؍r2 √ r5 ؍ r5؍ The terminal arm lies in The terminal arm lies in Quadrant 1. Quadrant 4. 1 √ 4 5 sin U √ ؍ csc U 5 ؍ sin U ؊ ؍ csc U ؊ ؍ 5 5 4 √ 2 5 3 5 cos U √ ؍ sec U ؍ cos U ؍ sec U ؍ 2 5 3 5 4 3 tan U ؍ 1 cot U 2 ؍ tan U ؊ ؍ cot U ؊ ؍ 2 3 4 4 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions DO NOT COPY. ©P
- 5. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 5 Home Quit 9. For each point P(x, y) on the terminal arm of an angle u in standard position, determine possible measures of u in the given domain. Give the answers to the nearest degree. a) P(Ϫ4, 2); b) P(Ϫ4, Ϫ8); for Ϫ360° ≤ u ≤ 0° for Ϫ360° ≤ u ≤ 360° The terminal arm of angle U lies The terminal arm of angle U lies in Quadrant 2. in Quadrant 3. The reference angle is: The reference angle is: tan؊1 a b Џ 27° tan؊1 a b Џ 63° 2 8 4 4 So, U Џ 180° ؊ 27°, or 153° So, U Џ 180° ؉ 63°, or 243° The angle between ؊360° and The angle between ؊360° and 0° 0° that is coterminal with 153° is: that is coterminal with 243° is: ؊360° ؉ 153° °702؊ ؍ ؊360° ؉ 243° °711؊ ؍ Possible value of U is: Possible values of U are approximately ؊207° approximately: 243° and ؊117° 10. For each trigonometric ratio, determine the exact values of the other 5 trigonometric ratios for u in the given domain. 1 √ a) cos u ϭ √ ; b) cot u ϭ Ϫ 3; 2 for 0° ≤ u ≤ 180° for 90° ≤ u ≤ 270° Use the completed table in question 6. √ From the given domain, U °54 ؍ cot U 3 ؊ ؍for U °051 ؍or U °033 ؍ 1 √ Then: cos U , √ ؍sec U , 2 ؍ From the given domain, U °051 ؍ 2 √ 1 √ Then: cot U ,3 ؊ ؍tan U , √؊ ؍ 1 3 sin U , √ ؍csc U ,2 ؍ 1 2 sin U , ؍csc U ,2 ؍ 2 tan U ,1 ؍and cot U 1 ؍ √ 3 2 cos U ؊ ؍ , and sec U √؊ ؍ 2 3 11. For each value of the trigonometric ratio below, determine possible measures of angle u in the given domain. Give the angles to the nearest degree. 1 a) sin u ϭ Ϫ2 ; for Ϫ360° ≤ u ≤ 360° Since sin U is negative, the terminal arm of angle U lies in Quadrant 3 or 4. For the domain 0° ◊ U ◊ 360°, from the completed table in question 6, U 012 ؍º or U 033 ؍º For the domain ؊360° ◊ U ◊ 0°, U 051؊ ؍º or U 03؊ ؍º The angles are: ؊150°, ؊30°, 210°, and 330° ©P DO NOT COPY. 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions 5
- 6. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 6 Home Quit b) cot u ϭ 1; for 0° ≤ u ≤ 720° Since cot U is positive, the terminal arm of angle U lies in Quadrant 1 or 3. For the domain 0° ◊ U ◊ 360°, from the completed table in question 6, U 54 ؍º or U 522 ؍º For the domain 360° ◊ U ◊ 720°, U 54 ؍º ؉ 360° or U °063 ؉ °522 ؍ °504 ؍ °585 ؍ The angles are: 45°, 225°, 405°, and 585° c) sec u ϭ Ϫ11; for 0° ≤ u ≤ 360° Since sec U is negative, the terminal arm of angle U lies in Quadrant 2 or 3. The reference angle is: cos؊1 a b Џ 85º 1 11 For the domain 0° ◊ U ◊ 360°: In Quadrant 2, U Џ 180º ؊ 85º, or approximately 95º In Quadrant 3, U Џ 180º ؉ 85º, or approximately 265º To the nearest degree, the angles are: 95º and 265º C 12. Perpendicular lines are drawn from the y E F D axes to the terminal arm of an angle u B P in standard position. Lines DC and EF 1 are tangents to the unit circle. Explain x why each trigonometric ratio is equal O A C to the length of the indicated line segment. a) PA ϭ sin u b) PB ϭ cos u In right ^ OPA, In right ^ BOP, PA ∠BOP 09 ؍º ؊ U sin U ؍ So, ∠OPB ؍U OP PA PB sin U ؍ cos U ؍ 1 OP So, PA ؍sin U cos U ؍ PB 1 So, PB ؍cos U c) OF ϭ csc u d) DC ϭ tan u In right ^ OEF, In right ^ DOC, ∠EFO ؍U tan U ؍ DC EO OC sin U ؍ DC OF tan U ؍ 1 1 sin U ؍ So, DC ؍tan U OF So, OF ؍csc U 6 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions DO NOT COPY. ©P
- 7. 08_ch06_pre-calculas12_wncp_solution.qxd 5/22/12 6:37 PM Page 7 Home Quit e) FE ϭ cot u f) DO ϭ sec u In right ^ OEF, In right ^ DOC, ∠EFO ؍U cos U ؍ OC OE DO tan U ؍ 1 EF cos U ؍ 1 DO tan U ؍ So, DO ؍sec U EF So, EF ؍cot U ©P DO NOT COPY. 6.1 Trigonometric Ratios for Any Angle in Standard Position—Solutions 7