Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie fundamentos da cinesioterapia (20)
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
fundamentos da cinesioterapia
- 2. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 1
STARTING POSITION
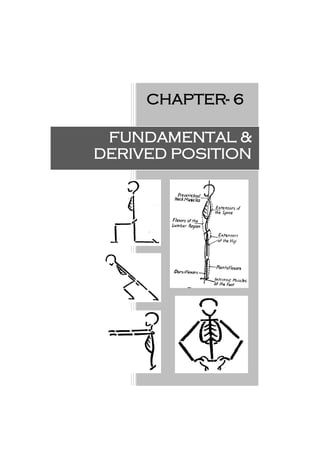
Posture follows movement like a shadow. Every movement begins in posture & ends in
posture (Sherrington). The posture from which movement is initiated is known as starting
position and they may be either active or passive in character. Equilibrium & stability is
maintained in this position.
Starting position mainly two types:
1. Fundamental starting position
2. Derived position
FUNDAMENTAL POSITION
There are five basic fundamental starting positions. These are:
1. Standing (st)
2. Kneeling (Kn)
3. Sitting (Sitt)
4. Lying (ly)
5. Hanging (hg)
Standing (st)
This is the most difficult fundamental starting position to maintain
Joint position:
1. The heels are together & on the same line,
the toes slightly apart
2. The knees are together & straight
3. The hips are extended & laterally rotated
slightly
4. The pelvis is balanced on the femoral heads
5. The spine is stretched to its maximum
length
6. The vertex is thrust upwards, the are level
is same & the eyes look straight forwards
7. The shoulders are down & back
8. The arms hang loosely to the sides, palms
facing inwards towards the body
- 3. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 2
Muscle work:
1. Ankle planter flexors: Balance the lower leg on the foot
2. Ankle dorsiflexors: Counter balance the action of the planter flexors & support the
medial longitudinal arch of the foot
3. Knee extensors: Work slightly
4. Hip extensors: Maintain hip extension & balance the pelvis on the femoral heads
5. The extensors of the lumber spine: Work to keep the trunk upright
6. Flexors of the lumber spine (abdominal muscle): Prevent over action of extensors,
also maintain the correct angle of pelvic tilt & support the abdominal viscera.
7. Prevertebral neck muscle: Control excessive extension of the neck & straighten the
cervical spine
8. Flexors & extensors of the A-0 joint: Reciprocally balance the head
Stability:
All the muscles group mentioned above stabilized the body in anterior & posterior direction.
In addition there must be a balanced contraction of the lateral muscles to maintain
equilibrium.
Effects & uses:
1. As the base of support (BOS) is small & gravity is high so it is effective starting
position for exercise for those who can maintain it correctly.
2. The muscle work is minimal when perfect balance is achieved, therefore practice in
attaining & holding in a satisfactory pattern of standing posture reduce fatigue & also
condition the postural reflex.
3. In this position the thorax is free & the abdominal viscera are welled supported.
4. Patient feels joy & efficiency during performing exercise in standing position.
Kneeling (kn):
Joint position:
1. Body is supported on the knees which may be together or slightly apart
2. The low leg rests on the floor with the feet planter flexed.
3. The hips are extended
4. The pelvis is balanced on the femoral heads
5. The spine is stretched to its maximum length
6. The vertex is thrust upwards, the are level is same & the eyes look straight forwards
7. The shoulders are down & back
8. The arms hang loosely to the sides, palms facing inwards towards the body
- 4. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 3
Muscles work:
1. Flexors & extensors of knees: Balance the femur vertically on the knee.
2. Knee extensors: Work slightly.
3. Hip extensors: More strongly maintain the hip extension &
balance the pelvis on the femoral heads.
4. Spine extensors: Working to keep the trunk upright.
5. Flexors of lumbar spine: Prevent more strongly the action
of the extensors & maintain the correct angle of pelvic tilt.
6. Prevertribral neck muscle: Control the excessive extension
of neck & straighten the cervical spine.
7. Flexors & extensors of A-0 joint: Reciprocally balance the
head.
Stability: The body is stabilized on the both knees
Effects & uses: Use for controlling the hip joint & lower trunk in preparation for the
standing position.
Sitting (sitt)
Joint position:
1. Position is taken on a chair or stool
2. Hip & knee is flexed in right angle
3. Femurs are parallel & the feet rest on the floor
4. Pelvic is anteriorly tilted
5. Spine is straight & maintains appropriate curvature in each
region
6. The arms either hang loosely to the sides, or rest on the both
thigh
Muscle work:
1. No muscle work for holding the leg
2. Hip flexors: Maintain right angle flexion & prevent the tendency to slump
3. Extensors of spine: Keep the trunk upright
4. Prevertribral neck muscles: Control excessive extension of the neck & straighten
the cervical spine
5. Flexors & extensors of A-0 joint: Working reciprocally to balance the head.
- 5. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 4
Effects & uses:
1. Comfortable, neutral, stable position
2. Commonly used for those who, lack the necessary strength & control to maintain
more difficult position.
3. For pelvic mobility
4. Effective for those who has contraindication in knee & ankle weight bearing
Lying (ly)
Joint position:
1. Same as the standing position but on the bed (Supine lying)
2. In this position the body is completely supported
Muscle work:
1. Minimal muscles are involve to maintain this posture
2. Head rotators: Work reciprocally to stabilize the head
3. Hip medial rotators: Keep the leg in neutral position
Effects & uses:
1. Most relax position
2. For treatment of spinal deformity
3. Effective for those who are suffering from respiratory & cardiac problem
4. Patient who has low muscle tone after stroke
Hanging (hg)
Joint position:
1. Body is supported by griping over the horizontal bar.
2. Fore arm: Pronated
3. Shoulder: Full flexion & apart
4. The trunk & legs: Hang straight
5. Knees: Together, Extension & maintain traction.
6. Ankle: Together & planter flexed
- 6. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 5
Muscle work:
1. Fingers flexors: Work strongly to grip the bar.
2. Wrist Muscles round the wrist work as a synergists to prevent strain
of finger joints.
3. Elbow flexor: Reduce the strain of the joint
4. Shoulder abductors: Work strongly to lift the body to the arms.
5. Pre-vertebral neck muscles: Work reciprocally to maintain the
position of the head & neck.
6. The flexors of the lumber spine & the extensors of the hip: Work to
correct the tendency to arch the back as the result of the over action
of Latissimus dorsi, working on the sacrum.
7. Hip adductor: Keep the hip together
8. Knee extensors: Maintain knee extension
9. Ankle planter flexors: Work to point the toes to the floor
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for whom, who have well muscle strength & balance
2. Useful for limb traction
3. Useful for gymnast
4. Contraindicated for those who have respiratory & cardiac problems
- 7. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 6
DERIVED POSITION
We know there are five basic fundamental starting positions, from where we start our
exercise. Sometimes we need to change or modify the fundamental position by altering the
arm, leg & trunk position for some exercise purpose. In this way a new starting position
comes out which is called derived position.
Purpose of derived position:
To increase or decrease the size & stability of the base (BOS)
To raise or low the center of gravity
To ensure the maximum local or general relaxation
To provide a convenient position from which a particular exercise is to be
performed
To increase or decrease leverage
POSITION DERIVED FROM STANDING
By alteration of the arms
Wing standing ( wg.st)
Joint position
1. Hands rest on the iliac crest
2. Shoulder: Abducted
3. Elbow: Flexed
4. Wrist: Extended
5. Finger: Extended, Abducted finger face anteriorly &
thumb in posterior side
6. Another joint position is same as the standing position
Muscle work:
1. Shoulder abductor (Deltoid, Supra spinatus)
2. Elbow extensors work slightly to press hand on iliac
crest
Effects &uses:
1. As the shoulder is abducted so during some trunk exercise it is easy to the therapist
to grasp the trunk
2. Prevent the swinging of hand during trunk exercise
- 8. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 7
Reach standing (rch.st)
Joint position
1. Shoulder: Forward flexed, Parallel right angles to the body
2. Elbow: Extended
3. Wrist & finger: Neutral position
Muscle work:
1. Shoulder: Flexors maintain position against gravity
2. Elbow extensors
3. Finger & wrist extensors work slightly
Effects & uses:
1. Assists balance during balance walking side ways
2. As the hand is forward so gravity & there is a natural tendency to overcompensate
for this by extension of lumbar spine
Yard standing (yd.st)
Joint position:
1. Shoulder: Abducted
2. Elbow: extended
3. Fore arm: pronated
4. Wrist: Neutral position
5. Finger: Neutral position
6. Other position is same as fundamental standing position
Muscle work:
1. Shoulder: Abductor, Extensors, Lateral rotators, Rotator of scapula work to
stabilized the arms
2. Elbow: Extensors keep the elbow straight
3. Wrist, Finger: Extensors to hold the limbs in a straight line
Effects & uses:
1. Facilitates body balance
2. Convenient for arm swing exercise
- 9. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 8
Stretch standing (str.st)
Joint position:
1. Arm is fully elevated so that they are in line with the body, parallel to each other &
with palm facing.
2. Elbow: Extended
3. Wrist & finger: Neutral position
Muscle work:
1. Shoulder abductors, extensors & lateral rotators
2. Lateral rotators of scapula to hold the arms position
3. Elbow extensors: Keep straight
4. Wrist & fingers extensors
By alteration of leg
Close standing (cl.st.)
Joint position:
1. The hip joints are rotated internally so that the both are adjacent together
2. Rest of the joint position is same as fundamental standing position
Muscles work:
1. Leg muscles work more strongly than fundamental standing
position
Effects & uses:
1. For advance standing training
Toe standing (toe.st.)
Joint position:
1. The heel are closed together & raised from the floor
2. DIP: extended
3. Ankle: planter flexion
Muscles work:
1. Ankle planter flexors work strongly
Effects & uses:
2. More balance exercise
3. Useful for postural flat feet patient
- 10. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 9
Stride standing (std.st.)
Joint position:
1. Both hip joints are abducted (Body weight equally distributed)
Muscles work:
1. Hip abductor: work strongly to prevent further sliding
Effects & uses:
1. More stable position when performing exercise in frontal plane
Walk standing (wlk.st.)
Joint position:
1. One leg is forward just two foot-length apart
2. Another leg is backward in the same line
Muscles work:
1. Extensors of hip & knee of rare leg work strongly to maintain this position
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for sagittal plane exercise
2. Useful for localized rotation of spine
Half standing (1/2 st.)
Joint position:
1. The whole weight of the body is supported on one leg
2. The other leg may be free or supported in variety in position
Muscles work:
1. Abductor of hip: maintain COG by slightly lateral tilting of pelvic
2. Opposite lumbar side flexors: Bring the trunk alignment
3. Supportive leg muscles work more strongly than fundamental position
Effects & uses:
1. Unsupported leg is free, so useful for some one leg exercise
2. For more balance exercise
[Stride standing, Walk standing, Step standing]
- 11. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 10
By alteration of trunk
Lax stoop standing (lax.stp.st)
Joint position:
1. Hip & trunk flexion
2. Head & arms are relaxed so that they hang forward &
downward
Muscle work:
1. Ankle dorsiflexors stabilized the position & intrinsic foot
muscles grip the floor
Effects & uses:
1. For local relaxation of upper limb
2. For expiration
Stoop standing (stp.st.)
Joint position:
1. Hip joints are flexed
2. Head, trunk & arm remain in alignment & are inclined forward
Muscle work:
1. Ankle dorsiflexors stabilized the position & intrinsic
foot muscles grip the floor
2. Back muscles, extensors of shoulders & elbow
maintain the position against pull of gravity
3. Pre-vertebral neck muscles support the head
Effects & uses:
1. For strong work of back muscles
Fallout standing (fallout.st.)
Joint position:
1. One leg is placed directly forward to the distance of three foot lengths & knee is
bent
2. The back leg is remaining straight & the body is inclined forwards in line with it
Muscles work:
1. Forward leg: extensors & foot muscles work strongly
2. Back leg: extensors work to keep the trunk straight, dorsiflexors keep heel on
ground
3. Head & trunk muscles work as stoop standing
- 12. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 11
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for treatment of spine curvature
POSITION DERIVED FROM KNEELING
Half kneeling (1/2 kn.)
Joint position:
1. One knee supports most of the weight, other leg bent forward right angle at hip,
knee, ankle
Muscle work:
1. Supported leg: abductors & lumbar spine flexors of
opposite side
2. Opposite leg: extensors of hip & knee
Effects & uses:
1. For trunk side bending & rotation exercise
Kneel sitting (kn. sitt.)
Joint position:
1. Knees & hip are flexed so that patient sit on heels
Effects & uses:
1. This position is comfortable for children
2. But uncomfortable for adult
Prone kneeling (pr. Kn.)
Joint position:
1. Trunk is horizontal & supported under the shoulders by the arms
2. Pelvis supported by the thighs
Muscles work:
1. Shoulder & hip joint muscles stabilize the supporting limb
2. Lumbar spine flexors prevent the hollowing the back
3. Extensors of head neck & preventable neck muscles
- 13. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 12
Effects & uses:
For trunk & head exercise
POSITION DERIVED FROM SITTING
Stride sitting (std. sitt.)
Joint position:
1. This is exactly similar to the fundamental position, except
that the legs are abducted so that the feet are up to two
foot-lengths apart.
Effects & uses:
1. This position increases the stability
Crook sitting (crk.sitt.)
Joint position:
1. The knees are bent so that the feet are together & flat on the floor
2. The knees are together or apart
Muscles work:
1. Hip flexors: work strongly to prevent the excessive flexion of
the lumbar region & to support the thighs
2. The flexors of the knees & the planter flexors of ankle to
maintain this position
3. The longitudinal & transverse back muscles work strongly to
maintain the upright position of the trunk
Effects & uses:
1. As the pelvis is posteriorly tilted & the lumbar spine is flexed so useful for upper
trunk localized exercise
2. Treatment for kypho-lordosis
3. Strong work for the extensors of thoracic spine
- 14. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 13
Long sitting (lg.sitt.)
Joint position:
1. Both hips are flexing as right angle to the trunk
2. Both knees are extended & ankles are in neutral position
3. The legs are totally supported to the ground
Muscles work:
1. Hip flexors: keep the trunk right angle to the
lower limb
2. Knee extensors: keep the both leg straight
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for sitting balance practice
Cross sitting (X sitt.)
Joint position:
1. Both hip are flexed, strongly abducted & laterally rotated
2. Both knees are flexed & the both ankles cross each other so that the lateral part of
both knees touch the floor
Effects & uses:
1. To stretch the adductors of hip
2. Useful for children during sitting balance practice
Side sitting (s. sitt.)
Joint position:
1. In right side sitting the right leg position is same as cross sitting
2. Left leg: hip is flexed & medially rotated & knee is
flexed so that the medial aspect of the left leg touch the
floor
3. The pelvis is tilted in to the right side
4. The lumbar flexed left side to keep the balance
5. Total body weight on the right side
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for increase lateral mobility of the lumbar spine
2. Useful for weight transferring
- 15. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 14
Stoop sitting (stp. sitt.)
Joint position:
1. Same as fundamental sitting position except the trunk is
lean forward by maintaining it curvature
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for arms & upper back exercise
2. Sometimes useful for giving back massage when prone
lying is impossible
Fallout sitting (fallout sitt.)
Joint position:
1. Same as fallout standing except the hip & thigh of the forward leg are supported
across a stool.
Effects & uses:
1. Here balance is easier than the fallout standing
POSITION DERIVED FRO LYING
Crook lying (crk.ly)
Joint position:
1. From lying hip & knee are bent so that the feet rest on the floor
Muscles work:
1. Adductor & medial rotators of hip work together to prevent the knees from falling
apart
Effects & uses:
1. Reduce tension of anterior aspect of knee & thigh, pelvis & lumbar spine
2. Useful for relaxation exercise
3. Appropriate for chest physiotherapy
- 16. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 15
Bridging
Joint position:
1. From the crook lying elevate the trunk from the ground so that the trunk rests on
the shoulders & is brought in to line with the thighs
Muscles work:
1. Hip & lumbar extensors
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for re-education of muscles in pelvic floor
2. Useful for pelvic control of stroke patient
Half lying (1/2 ly.)
Joint position:
1. The trunk is supported in the oblique position by inclination of the long end of the
plinth, or by the arrangement of pillows
2. Both knees may be extended of flexed
Effects & uses:
1. Relaxed & comfortable in this position
2. Breathing is easier in this position so useful for
breathing exercise
3. Useful for word exercise
Prone lying (pr. Ly.)
Joint position:
1. Lying face downward, the body is fully supported anteriorly on the plinth
2. It may be active & passive
3. When this position is used as an exercise purpose at that time the head is kept
slightly raise
Muscles work (During active position):
1. The pre & post vertebral neck muscles work together to maintain the head position
2. The retractors & depressors of the scapula work to brace the upper back
3. The lateral rotators of the hips keep the heel together
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for patient who have a back pain
2. Some unloading lumbar extension
exercise
3. Contraindicated for cardiac patient
- 17. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 16
Leg prone lying (L. pr. Ly.)
Joint position:
1. Same as prone lying except from the ASIS to the leg is supported on the plinth &
strap
2. The rest of the trunk is free in the space
3. A stool is placed under the trunk for safety
Muscles work:
1. The Prevertebral neck muscles, extensors of
hip & longitudinal & transverse back muscles
work strongly to maintain the position of the
trunk against gravity
2. The extensors of shoulder & elbow hold the arm to the side
Effects & uses:
1. Advance back muscle strengthening exercise
2. For sports man
Side lying (s. ly.)
Joint position:
1. From lying roll on side
2. Under arm support the head
3. Some times rotates the trunk more & keep the upper hip & knee flex
Effects & uses:
1. Useful for relaxation
2. Sometimes use for gravity elimination position of limb
Sit lying (sit. ly.)
Joint position:
1. Supine lying position except the both knee is out from the plinth.
2. The whole trunk up the knee is supported on the plinth.
3. Both knees are flexed right angle at the edge of the bed
Effects & uses:
1. Knee extensor strengthening exercise
- 18. CHAPTER: 6 FUNDAMENTAL & DERIVED POSITION
© T h e r a p e u t i c E x e r c i s e H a n d B o o k Page 17
Study question:
1. What is starting position? What are the types of starting position?
2. How many types of fundamental position?
3. What is the most difficult fundamental position? Write down its Joint position,
Muscle work, Stability, Effects & uses with picture.
4. Write down the Joint position, Muscles work, Effects & uses of five fundamental
positions.
5. What is derived position? What is the purpose of derived position?
6. Write down the positions derived from standing.
7. Write down the positions derived from sitting.
8. Write down the positions derived from lying.
9. Write down the positions derived from kneeling.
10. Write down the value of fundamental & derived positions.