Vocab Flash Cards
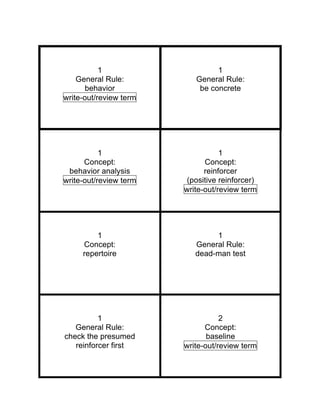
- 1. 1 1 General Rule: General Rule: behavior be concrete write-out/review term 1 1 Concept: Concept: behavior analysis reinforcer write-out/review term (positive reinforcer) write-out/review term 1 1 Concept: General Rule: repertoire dead-man test 1 2 General Rule: Concept: check the presumed baseline reinforcer first write-out/review term
- 2. • Always pinpoint specific • A muscle, glandular, or behaviors neuro-electrical activity. • when you deal with a behavioral (psychological) problem. • A stimulus • The study of the • that increases the frequency • principles of behavior. of a response it follows. • If a dead man can do it, it • A set of skills. probably isn’t behavior. • The phase of an experiment • Before spending much time or intervention trying to reinforce behavior, • where the behavior is • make sure you have a true measured reinforcer. • in the absence of an intervention.
- 3. 2 2 Concept: Concept: medical model myth behavioral contingency 2 2 Concept: General Rule: reinforcement contingency the don't say rule write-out/review term 2 2 Concept: General Rule: the error of reification reinforce behavior 3 3 Concept: Concept: escape contingency aversive stimulus write-out/review term (negative reinforcer) write-out/review term
- 4. • The occasion for a response, • An erroneous view of • the response, and human behavior • the outcome of the response. • that behavior is always a mere symptom of • an underlying psychological condition. • With nonverbal organisms, don't say, • expects, • The response-contingent • knows, • presentation • thinks, • figures out, • of a reinforcer • in order to (or so that he, she, or it could ...), • trying to, • resulting in an increased • makes the connection, • associates, frequency of that response. • learns that, • imagines, • or understands. • With any organisms. don't say, • wants. • Reinforce behavior, • To call a behavior or • not people. process a thing. • A stimulus • The response-contingent • that increases the future • removal of frequency of a response • an aversive stimulus • its removal (termination) • resulting in an increased follows. frequency of that response.
- 5. 3 3 Concept: False General Rule: differential reinforcement the toothpaste theory of alternative behavior (DRA) of abnormal behavior write-out/review term 3 3 Concept: Principle: functional assessment parsimony write-out/review term 3 4 General Rule: General Rule: the sick social cycle the sick social cycle (victim’s escape model) (victim’s punishment model) 4 4 Concept: Concept: punishment contingency overcorrection write-out/review term
- 6. • Abnormal behavior flows out • The replacement of an of sick people inappropriate response • like toothpaste squeezed • with a specific appropriate from a tube. response • The abnormal behavior • that produces the same results from inner pressure. reinforcing outcome. • The use of no unnecessary • An assessment concepts, principles, or • of the contingencies assumptions. • responsible for • behavioral problems. • The perpetrator’s aversive • In escaping behavior punishes • the perpetrator’s aversive • the victim’s appropriate behavior, behavior. • the victim unintentionally • And the victim’s stopping the reinforces appropriate behavior • that aversive behavior. • unintentionally reinforces that aversive behavior. • A contingency • Response-contingent • on inappropriate behavior • presentation of • requiring the person • an aversive condition • to engage in an effortful (negative reinforcer) response • resulting in a decreased • that more than corrects frequency of that response. • the effects of inappropriate behavior.
- 7. 4 4 Concept: Concept: dependent variable informed consent write-out/review term 4 4 Concept: Concept: independent variable social validity write-out/review term write-out/review term 4 4 Concept: Concept: multiple baseline design reliability measurement 5 5 Concept: Concept: penalty contingency response-cost contingency write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 8. • Consent to intervene in a • A measure of the subject's way behavior. • that is experimental or • risky. • The participant or guardian • is informed of the risks and benefits • and of the right to stop the intervention. • The goals, • The variable the • procedures, and experimenter systematically • results of an intervention manipulates • are socially acceptable to • to influence the dependent • the client, variable. • the behavior analyst, and • society. • The comparison of • An experimental design measurements • in which the replications • of dependent variables and involve • independent variables • baselines of differing • obtained by independent durations observers. • and interventions of differing starting times. • The response-contingent • The • removal of • response-contingent • a tangible reinforcer. • removal of • a reinforcer (positive reinforcer) • resulting in a decreased frequency of that response.
- 9. 5 5 Concept: Concept: time-out contingency reversal design write-out/review term 5 6 Principle: Principle: the law of effect recovery from punishment write-out/review term write-out/review term 6 6 Principle: Concept: spontaneous recovery forgetting procedure write-out/review term 6 6 Principle: General Rule: extinction Forget Forgetting write-out/review term
- 10. • An experimental design • The response-contingent • in which we reverse • removal of • between intervention and • access to a reinforcer. baseline conditions • to assess the effects of those conditions. • Stopping the punishment or • The effects of our actions penalty contingency • determine whether we will • for a previously punished repeat them. response • may cause the response frequency to increase • to its frequency before the punishment or penalty contingency. • Preventing the opportunity • A temporary recovery of the (or occasion) for a response. extinguished behavior • during the first part of each of the extinction sessions • that follow the first extinction session. • There’s no such thing. • Stopping the reinforcement or escape contingency • for a previously reinforced response • causes the response frequency to decrease.
- 11. 6 6 Concept: Concept: to confound variables control condition write-out/review term 7 7 Concept: Concept: response topography Latency write-out/review term write-out/review term 7 7 Concept: Concept: task analysis duration write-out/review term 7 7 General Rule: Concept: process vs. product response dimensions
- 12. • A condition not containing • To change or allow to the presumed crucial value change two or more of the independent variable. independent variables at the same time, • so you cannot determine what variables are responsible for the change in the dependent variable. • The time between • The sequence (path of • the signal or opportunity for movement), a response • form, • and the beginning of the • or location response. • of components of a response • relative to the rest of the body • An analysis of complex • The time from behavior • the beginning • and sequences of behavior • to the end • into their component • of a response. responses. • Sometimes you need to • The physical properties of a response. • make reinforcers and feedback contingent on • the component responses of the process, • not just the product (outcome).
- 13. 7 7 Concept: Concept: response class single-subject write-out/review term research design write-out/review term 7 7 Procedure: Concept: the differential- group research design reinforcement procedure write-out/review term 7 7 Concept: Concept: the differential punishment control group procedure 7 8 Concept: Concept: experimental group fixed-outcome shaping
- 14. • The entire experiment is • A set of responses that conducted with a single either subject, • a) are similar on at least one • though it may be replicated response dimension, or with several other subjects. • b) share the effects of reinforcement and punishment, or • c) serve the same function (produce the same • The experiment is conducted with • outcome). one set of Reinforcing at least two groups of subjects. responses and • And the data are usually • withholding reinforcement presented in terms of the mean (average) for another set of • of the performance of all subjects responses. • combined for each group. • A group of subjects • Punishing one set of • not exposed to the presumed responses crucial value of the • and withholding punishment independent variable. of another set of responses. • Shaping that involves • A group of subjects • no change in the value of • exposed to the presumed • the reinforcer crucial value • or aversive condition, • of the independent variable. • as the performance criterion more and more closely resembles the terminal behavior.
- 15. 8 8 Concept: Concept: terminal behavior shaping write-out/review term with reinforcement write-out/review term 8 8 Concept: Concept: operant level shaping with punishment 8 8 Concept: Concept: initial behavior variable-outcome shaping write-out/review term 8 9 Concept: Concept: intermediate behavior unlearned aversive condition
- 16. • The differential • Behavior not in the reinforcement of only that repertoire behavior • or not occurring at the • that more and more closely desired frequency; resembles the terminal • the goal of the intervention behavior. • The differential punishment • The frequency of of all behavior responding • except that which more and • before reinforcement more closely resembles the terminal behavior. • Shaping that involves • Behavior that resembles • a change in the value of • the terminal behavior • the reinforcer • along some meaningful • or aversive condition, dimension • as performance more and • and occurs with at least a more closely resembles the minimal frequency. • terminal behavior. • A stimulus that is aversive, • Behavior that more closely • though not as a result of approximates the terminal pairing with other aversive behavior. stimuli.
- 17. 9 9 Concept: Procedure: unlearned reinforcer motivating operation write-out/review term write-out/review term 9 9 Principle: Principle: Satiation Premack principle write-out/review term write-out/review term 9 10 Principle: Concept: Deprivation addictive reinforcer write-out/review term 10 10 Concept: Principle: aggression reinforcer the aggression principle
- 18. • A stimulus that is a • A procedure or condition reinforcer, • that affects learning and • though not as a result of performance pairing with another • with respect to a particular reinforcer. reinforcer or aversive condition. • If one activity occurs more • Consuming a substantial often than another, amount of a reinforcer • the opportunity to do the • temporarily decreases more frequent activity relevant learning and • will reinforce the less performance. frequent activity. • A reinforcer for which • Withholding a reinforcer • repeated exposure • increases relevant learning • is an motivating operation. and performance. • Aversive stimuli and • Stimuli resulting from acts of extinction are motivating aggression. operations • for aggression reinforcers.
- 19. 11 11 Concept: Concept: generalized learned reinforcer conditional stimulus (generalized secondary/conditioned reinforcer) write-out/review term 11 11 Concept: Concept: learned reinforcer token economy (secondary or conditioned write-out/review term reinforcer) write-out/review term 11 11 Procedure: Concept: pairing procedure learned aversive stimulus 11 12 Principle: Concept: value-altering principle verbal behavior write-out/review term
- 20. • A learned reinforcer that is a • Elements of a stimulus reinforcer • have their value or function • because it has been paired • only when they are with a variety of other combined; reinforcers. • otherwise, the individual elements may be relatively neutral. • A system of generalized • A stimulus that is a learned reinforcers reinforcer • in which the organism that • because it has been paired receives those generalized with another reinforcer. reinforcers can save them • and exchange them for a variety of backup reinforcers later. • A stimulus • The pairing of a neutral • that is aversive stimulus with • because it has been paired • a reinforcer or aversive with another aversive stimulus. stimulus. • The behavioral term for • The pairing procedure language • converts a neutral stimulus into • a learned reinforcer • or learned aversive stimulus.
- 21. 12 12 Concept: Concept: discriminative stimulus (SD) stimulus discrimination write-out/review term (stimulus control) 12 12 Concept: Concept: S-delta (S∆) incidental teaching write-out/review term 12 12 Criteria for diagraming Concept: Discriminated Contingencies: Prompt S∆ contingency test write-out/review term 12 12 Concept: Concept: discrimination training operandum (manipulandum) procedure write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 22. • The occurrence of a response • A stimulus in the presence more frequently in the of which presence of one stimulus • a particular response will be • than in the presence of reinforced or punished. another, • usually as a result of a discrimination training procedure. • The planned use of • A stimulus in the presence • behavioral contingencies, of which • differential reinforcement, • a particular response will not and be reinforced or punished. • discrimination training • in the student’s everyday environment. • A supplemental stimulus • Is there also an S∆? • that raises the probability of • (If not, then you also don’t a correct response. have an SD). • That part of the environment • Reinforcing or punishing a • the organism operates response (manipulates). • in the presence of one stimulus • and extinguishing it • or allowing it to recover • in the presence of another stimulus.
- 23. 12 12 Criteria for diagramming Criteria for diagramming discriminated contingencies: discriminated contingencies: same before condition test different before condition test 12 12 Criteria for diagramming Criteria for diagramming discriminated contingencies discriminated contingencies: response test operandum test 12 13 Criteria for diagramming Concept: discriminated contingencies: stimulus generalization extinction/recovery test write-out/review term 13 13 Concept: Concept: stimulus class concept training write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 24. • Does the SD differ from the • Is the before condition the before condition? same for both the SD and the S∆? • Does the SD differ from the • Is the response the same for operandum? both the SD and the S∆? • The behavioral contingencies • Is the S∆ contingency • in the presence of one stimulus always extinction or • affect the frequency of the recovery? response • in the presence of another stimulus. • Reinforcing or punishing a response • A set of stimuli, • in the presence of one stimulus • all of which have some class common physical property. • and extinguishing it • or allowing it to recover • in the presence of another stimulus class.
- 25. 13 13 Concept: Concept: matching to sample Subjective measure write-out/review term 13 13 Concept: Concept: conceptual stimulus control Objective measure (conceptual control) write-out/review term 13 13 Concept: Concept: stimulus-generalization stimulus dimensions gradient 13 13 Concept: Concept: fading procedure errorless write-out/review term discrimination procedure
- 26. • The criteria for • Selecting a comparison measurement are not stimulus completely specified in • corresponding to a sample physical terms stimulus. • or the event being measured is a private, inner experience. • Responding occurs more • The criteria for measurement often in the presence of one are completely specified in stimulus class physical terms • and less often in the • and the event being measured presence of another stimulus is public and therefore class observable by more than one • because of concept training. person. • The physical properties of • A gradient of responding a stimulus. showing • a decrease in responding • as the test stimulus • becomes less similar to the training stimulus. • The use of a fading • At first, the S∆ and the SD procedure differ along at least two • to establish a stimulus dimensions. discrimination, • Then the difference between • with no errors during the the S∆ and the SD is reduced training. along all but one dimension, D ∆ • until the S and S differ along only the relevant dimension.
- 27. 14 14 Concept: Concept: Imitation physical prompt write-out/review term (physical guidance) 14 14 Concept: Concept: generalized imitation verbal prompt write-out/review term 14 14 Concept: Theory: imitative reinforcers the theory of write-out/review term generalized imitation 15 15 Concept: Concept: avoidance contingency avoidance-of-loss contingency write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 28. • The form of the behavior of • The trainer physically moves the imitator the trainee's body • is controlled by • in an approximation of the • similar behavior of the desired response. model. • A supplemental verbal • Imitation of the response stimulus • of a model • that raises the probability of • without previous a correct response. reinforcement of • imitation of that specific response. • Generalized imitative • Stimuli arising from the responses occur match between • because they automatically • the behavior of the imitator produce imitative reinforcers. • and the behavior of the model. • Response-contingent • Response-contingent • prevention of • prevention of • loss of a reinforcer • an aversive condition • resulting in an increased • resulting in an increased frequency of that response. frequency of that response.
- 29. 15 16 Concept: Concept: warning stimulus Differential reinforcement of write-out/review term other behavior (DRO) write-out/review term 16 16 Concept: Concept: punishment-by-prevention- punishment-by-prevention-of- of-a-reinforcer removal contingency contingency write-out/review term 17 17 Concept: Concept: Intermittent Reinforcement fixed-ratio responding write-out/review term write-out/review term 17 17 Concept: Concept: continuous reinforcement variable-ratio (VR) (CRF) schedule of reinforcement write-out/review term
- 30. • A reinforcer is presented • A stimulus that precedes • after a fixed interval of time • an aversive condition • if the response of interest and thus becomes a learned has not occurred during that aversive stimulus. interval • Response-contingent • Response-contingent • prevention of removal of • prevention of • an aversive condition • a reinforcer • resulting in a decreased • resulting in a decreased frequency of that response frequency of that response. • After a response is reinforced, § A reinforcer follows the • no responding occurs for a response period of time, § only once in a while. • then responding occurs at a high, steady rate • until the next reinforcer is delivered. • A reinforcer follows • A reinforcer follows each • after a variable number of response. responses.
- 31. 17 17 Concept: Concept: schedule of reinforcement variable-ratio responding 17 18 Concept: Concept: fixed-ratio (FR) fixed-interval (FI) schedule of reinforcement schedule of write-out/review term reinforcement write-out/review term 18 18 Concept: Principle: fixed-interval scallop variable-interval write-out/review term responding write-out/review term 18 18 Concept: Concept: fixed-time schedule resistnce to extinction of reinforcer delivery write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 32. • Variable-ratio schedules • The way reinforcement occurs produce • because of the number of • a high rate of responding, responses, • with almost no • time between responses, and postreinforcement pausing. • stimulus conditions. • A reinforcer is contingent on • A reinforcer follows • the first response, • a fixed number of • after a fixed interval of time, responses. • since the last opportunity for reinforcement. • A fixed-interval schedule often produces a scallop: • Variable-interval schedules • a gradual increase in the rate of produce responding, • a moderate rate of • with responding occurring at a high responding, rate, • just before reinforcement is • with almost no available. postreinforcement pausing. • No responding occurs for some time after reinforcement. • The number of responses or • A reinforcer is delivered, • the amount of time • after the passage of a fixed • before a response period of time, extinguishes. • independently of the response.
- 33. 18 18 Concept: Principle: superstitious behavior resistance to extinction write-out/review term and intermittent reinforcement write-out/review term 18 19 Concept: Concept: variable-interval (VI) concurrent contingencies schedule of write-out/review term reinforcement write-out/review term 19 19 Concept: Erroneous Principle: differential reinforcement symptom substitution of incompatible behavior (DRI) write-out/review term 19 19 Principle: Concept: matching law Intervention/treatment package
- 34. • Intermittent reinforcement • Behaving as if the response • makes the response causes • more resistant to extinction • some specific outcome, • than does continuous • when it really does not. reinforcement. • More than one contingency • A reinforcer is contingent on of reinforcement or • the first response, punishment • after a variable interval of • is available at the same time. time, • since the last opportunity for reinforcement. • Problem behaviors are • Reinforcement is contingent symptoms of an underlying on a behavior that is mental illness. • incompatible with another • So if you get rid of one problem behavior behavior (“symptom”), • another will take its place, • until you get rid of the underlying mental illness. • The addition or change of • When two different responses several independent are each reinforced with a different schedule of variables reinforcement, • at the same time • the relative frequency of the two • to achieve a desired result, responses • without testing the effect of • equals the relative value of each variable individually. reinforcement on the two schedules of reinforcement.
- 35. 20 20 Concept: Concept: total-task forward chaining presentation 20 20 Principle: Concept: dual-functioning behavioral chained stimuli chain write-out/review term write-out/review term 20 20 Concept: Concept: backward chaining differential reinforcement write-out/review term of low rate (DRL) write-out/review term 21 21 Concept: Concept: unconditioned response conditioned stimulus (UR) (CS) write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 36. • The establishment of the • The simultaneous training of first link in a behavioral • all links in a behavioral chain, chain. • with the addition of successive links, • until the final link is acquired • A sequence of stimuli and • A stimulus in a behavioral responses. chain • Each response produces a • reinforces the response that stimulus that precedes it • reinforces the preceding • and is an SD or operandum response for the following response. • and is an SD or operandum • for the following response. • Reinforcement • The establishment of the • for each response following final link in a behavioral the preceding response chain, • by at least some minimum • with the addition of delay. preceding links, • until the first link is acquired. • A stimulus that has acquired • An unlearned response its eliciting properties • elicited by the presentation • through previous pairing with • of an unconditioned stimulus another stimulus.
- 37. 21 21 Concept: Concept: unconditioned stimulus conditioned response (US) (CR) write-out/review term write-out/review term 21 21 Concept: Concept: operant conditioning respondent conditioning write-out/review term write-out/review term 21 21 Concept: General Rule: higher-order conditioning SD / CS test write-out/review term 21 21 Concept: Concept: respondent extinction systematic desensitization write-out/review term write-out/review term
- 38. • A learned response • A stimulus that produces the • elicited by the presentation unconditioned response • of a conditioned stimulus. • without previous pairing with another stimulus. • A neutral stimulus • Reinforcing consequences • acquires the eliciting • following the response properties • increase its future frequency; • of an unconditioned stimulus and • through pairing the • aversive consequences unconditioned stimulus • following the response • with a neutral stimulus. • decrease its future frequency. • To determine if a stimulus is an • Establishing a conditioned SD or CS, stimulus • look at its history of conditioning: • by pairing a neutral stimulus • look for a plausible US -- UR relation; • with an already established • and alternatively, look for a conditioned stimulus. plausible SD -- R -- SR contingency. • Combining relaxation with • Present the conditioned • a hierarchy of fear-producing stimulus • without pairing it stimuli, • with the unconditioned • arranged from the least to stimulus, the most frightening. • or with an already established conditioned stimulus, • and the conditioned stimulus will lose its eliciting power.
- 39. 22 22 Concept: Concept: direct-acting rule contingency write-out/review term 22 22 Concept: Concept: rule-governed analog to rule control a behavioral contingency write-out/review term 22 22 Concept: Concept: ineffective contingency rule-governed behavior write-out/review term 22 22 Concept: Concept: contingency control indirect-acting write-out/review term contingency write-out/review term
- 40. • A description of a • A contingency in which behavioral contingency. • the outcome of the response • reinforces or punishes that response. • The statement of a rule • A change in the frequency • controls the response of a response • described by that rule. • because of a rule describing the contingency. • Behavior under the control • A contingency that does not of a rule. control behavior. • A contingency that controls • Direct control of behavior the response, • by a contingency, • though the outcome of that • without the involvement of response rules. • does not reinforce or punish that response.
- 41. 22 22 Principle: Concept: (Optional-not on quiz) (Optional-not on quiz) Immediate reinforcement a contingency that is not direct acting 22 23 (Optional-not on quiz) General Concept: Rule: feedback rule control write-out/review term 23 23 Concept: Review Concept: process vs. product Covert behavior write-out/review term 23 23 Concept Review: Principle: task analysis shifting from rule-control write-out/review term to contingency control
- 42. • Either an indirect-acting • The effect of the reinforcement contingency or procedure decreases • as the delay between the • an ineffective contingency. response and the outcome increases. • Reinforcers delayed more than 60 seconds • have little or no reinforcing effect. • Nonverbal stimuli • Start looking for rule • or verbal statements control, • contingent on past behavior • if behavior is controlled by • that can guide future an outcome behavior. • that follows the response by more than 60 seconds. • Private behavior (not visible • Sometimes you need to make to the outside observer). reinforcers and feedback • contingent on the component responses of the process, • not just the product (outcome). • With repetition of the • An analysis of complex response, behavior • control often shifts from • and sequences of behavior control by the rule describing • into their component a direct-acting contingency responses. • to control by the direct-acting contingency itself.
- 43. 23 24 Concept: Concept: multiple baseline performance contract design (behavioral contract or contingency contract) 24 24 False Principle: Principle: the mythical cause of rules that are easy to follow poor self-management write-out/review term 24 24 Model: Principle: the three-contingency model the real cause of of performance-management poor self-management write-out/review term 24 25 Principle: Principle: rules that are hard to follow the deadline principle write-out/review term
- 44. • A written rule statement • An experimental design describing • in which the replications • the desired or undesired involve baselines behavior, • the occasion when the behavior • of differing durations and should or should not occur, and • interventions of differing • the added outcome for that starting times. behavior. • Describe outcomes that are • Poor self-management • both sizable occurs • and probable. • because immediate • The delay isn't crucial. outcomes control our behavior • better than delayed outcomes do. • Poor self-management results • The three crucial contingencies from are: • poor control by rules describing • the ineffective natural • outcomes that are either contingency, • too small (though often of • the effective, indirect-acting cumulative significance) performance-management • or too improbable. contingency, and • The delay isn't crucial. • the effective, direct-acting contingency. • If an indirect-acting • Describe outcomes that are contingency either • is to increase or maintain • too small (though often of performance, cumulative significance) • it should involve a deadline. • or too improbable. • The delay isn't crucial.
- 45. 25 25 Concept: General Rule: pay for performance The it-is-probably-rule-control write-out/review term rule 25 26 Principle: Concept: the analog to avoidance spiritualistic mentalism principle 26 26 Concept: Concept: the simplistic biological- the simplistic cognitivist error determinist error 26 26 Concept: Concept: the simplistic behaviorist error methodological behaviorism write-out/review term
- 46. • It is probably rule control, if • Pay is contingent on specific • the person knows the rule, achievements • the outcome is delayed, or • the performance changes as soon as the person hears the rule. • The doctrine that the mind • If an indirect-acting is contingency • spiritual (nonphysical). • is to increase or maintain performance, • it should be an analog to avoidance. • Rats think • Analogous behaviors are • homologous behaviors. • An approach that restricts the • People don’t think. science of psychology to • only those independent and dependent variables • that two independent people can directly observe.
- 47. 26 26 Concept: Concept: mentalism mind 26 26 Concept: Concept: materialism spiritualism 26 26 Concept: Concept: radical behaviorism cognitive structure write-out/review term 26 26 Concept: Concept: cognitive behavior modification materialistic mentalism
- 48. • An entity or collection of • The doctrine that the mind entities causes behavior to occur. • assumed to cause behavior to occur. • It may be either material or nonmaterial, • but it is not the behavior itself. • The doctrine that the world is • The doctrine that physical divided into two parts, (material) world • material and spiritual. • is the only reality. • An entity • An approach that • assumed to cause action; addresses all psychology • the way the organism sees the • in terms of the principles of world, behavior. • including the organism's beliefs and expectations. • It is material, but not behavior. • The doctrine that the mind is • An approach that attempts • physical, not spiritual. to modify behavior • by modifying the cognitive structure.
- 49. 26 26 Concept: Concept: Values goal-directed systems design 26 26 Concept: Concept: legal rule control moral (ethical) rule control 27 27 Concept: Principle: performance maintenance behavior trap write-out/review term write-out/review term 28 29 Concept: Review Principle: transfer of training the law of effect write-out/review term
- 50. • First you select the ultimate • Learned and unlearned goal of a system, reinforcers • then you select the various • and aversive conditions. levels of intermediate goals needed to accomplish that ultimate goal, • and finally, you select the initial goals needed to accomplish those intermediate goals. • Control by rules specifying • Control by rules specifying added analogs to added analogs to behavioral behavioral contingencies. contingencies • Such rules specify social, • and added direct-acting religious, or supernatural behavioral contingencies outcomes. • based on material outcomes. • Add a reinforcement • The continuing of contingency performance • to increase the rate of • after it was first established behavior. • Then the behavior will frequently contact • built-in reinforcement contingencies, • and those built-in • contingencies our actions The effects of • Performance established determine whether we will • will maintain that behavior. • at one time repeat them. • in one place • now occurs in a different time and place.
- 51. 29 29 Concept: Concept: subjective evaluation external validity of experts 29 29 Concept: Concept: obtrusive assessment duration 29 29 Concept: Concept: unobtrusive assessment force 29 29 Concept: Concept: products of behavior interobserver agreement
- 52. • The extent to which the • Experts’ evaluation conclusions of an experiment • of the significance of • apply to a wide variety of • the target behavior and the conditions. outcome. • The time from • Measuring performance • the beginning • when the clients or subjects • to the end are aware • of a response. • of the ongoing observation. • Intensity of a response. • Measuring performance • when the clients or subjects • are not aware • of the ongoing observation. • Agreement between • Record or evidence • observations of • that the behavior has • two or more independent occurred. observers.
- 53. 29 29 Review Concept: Review Concept: confounded variables baseline 29 29 Concept: Concept: case study simple baseline design 29 29 Concept: Concept: internal validity reversal design 29 29 Concept: Review Concept: research design multiple-baseline design
- 54. • The phase of an • Two or more possible experiment or intervention independent variables have • in which the behavior is changed at the same time, measured • so it is not possible to • in the absence of an determine which of those intervention. variables caused the change in the dependent variable. • An experimental design • The evaluation of the results • in which the baseline data of are collected • an applied intervention or • before the intervention. • a naturally changing condition • that involves confounded variables. • An experimental design • The extent to which a • in which the intervention research design (experimental) and baseline • eliminates confounding conditions variables. • are reversed • to determine if the dependent variable changes as • those conditions (independent variable) change. • An experimental design • The arrangement of the • in which the replications various conditions of an involve experiment or intervention • baselines of differing • to reduce the confounding of durations independent variables. • and interventions of differing starting times.
- 55. 29 29 Concept: Review Concept: changing-criterion functional assessment design 29 29 Concept: Concept: alternating-treatments social validity design 29 29 Concept: Concept: Experimental interaction target behavior 29 Concept: social comparison
- 56. • An analysis • An experimental design • of the contingencies • in which the replications responsible for involve • behavioral problems. • interventions with criteria of differing values. • The goals, • An experimental design • procedures, • in which the replications involve • presenting the different values of • and results of an the independent variable intervention • in an alternating sequence • are socially acceptable to • under the same general the conditions • client, • or in the same experimental • the behavior analyst, phase, • and society. • while measuring the same • The behavior being • dependent variables. One experimental condition measured, • affects the results of • the dependent variable. another. • A comparison of the performance of clients • exposed to the intervention • with an equivalent or "normal" group.
