Elements principles
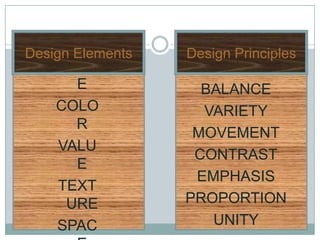
- 1. LINE Design Elements Design Principles SHAP E BALANCE COLO VARIETY R MOVEMENT VALU CONTRAST E EMPHASIS TEXT URE PROPORTION SPAC UNITY
- 2. Elements of Design Are the seven basic building blocks of art & design. Without these building blocks the principles are meaningless. Without the principles the elements can not be used to their best ability.
- 3. Design Elements LINE SHAPE COLOR VALUE TEXTURE SPACE FORM
- 4. Line A mark. Lines have thickness, direction, and movement; they can be interrupted and can show emotion in an artwork.
- 5. Line
- 6. Line Contour lines- outline the edges of forms or shapes Gestural lines- indicate action and physical movement
- 7. Shape When line curves or corners around and crosses over itself it becomes a shape.
- 8. Shape SHAPES CAN BE DESCRIBED AS: GEOMETRIC square, triangle, rectangle, rhombus, circle, cone ORGANIC free form shapes, shapes in nature for example: leaves, trees, clouds, animals
- 9. Color Color has three main properties: 1. Hue 2. Value 3. Intensity
- 10. Color Color has three properties: 1. The first is HUE. (this is the name of the colors) 2. The second property of color is value, which refers to the lightness or darkness of a hue. 3. The third property of color is intensity, which refers to the purity of the hue (called “chroma”)
- 11. Neutral Colors These colors are made by adding a complimentary color (opposite on the color wheel) to a hue. Neutralized hues are called tones.
- 12. Tints and Shades Tints-adding the color white. Shades- adding the color black.
- 13. Warm and Cool Colors
- 14. Value The lightness or darkness of a hue.
- 15. Value Value contrasts help us to see and understand a two-dimensional work of art. Value describes form and value defines space.
- 16. Texture The quality of a surface: Smooth, rough, bumpy, hairy, etc.
- 17. Hatching and Cross Hatching Line can be used to create value and textures Hatching Cross Hatching
- 18. Texture Textures are all around us in our environment. Actual texture – texture that you can feel with your sense of touch. Implied texture – texture that has been simulated in drawing and painting on a smooth surface to appear as if it is textured.
- 19. Space The amount of depth in both 2D and 3D artworks. Around, above, inside, outside, help describe space
- 20. Space The feeling of space in a drawing or painting is always an illusion. Artists combine the use of light and dark value with other techniques. Some of these are: simple overlapping, ladder perspective, linear perspective, and atmospheric perspective. Linear perspective “Snow in New York”
- 21. Form In 3D artworks it is the quality of the shape. Ex. Cubes, spheres and cones
- 22. Form Form describes volume and mass, or the three-dimensional aspects of objects that take up space. Forms can be realistic, abstract, geometric, organic etc… Form is considered three-dimensional showing height, width and depth. It can be illustrated or constructed.
- 23. Principles of Design The basic rules of aesthetics that guide in the organization of elements in a work of art.
- 24. Design Principles Balance Emphasis Variety Movement Proportion Contrast Unity
- 25. Balance An appearance of evenness in an artwork. There are two kinds: Symmetry & Asymmetry
- 26. Balance Balance refers to the distribution of visual weight in a work of art This is an example of This is an example of symmetrical balance in which asymmetrical balance the design is the same on both because the object is not the sides of the center axis. same on both sides.
- 27. Balance An appearance of evenness in an artwork. There are two kinds: Symmetry & Asymmetry
- 28. Symmetry In composition it is an arrangement of elements using order or disorder.
- 29. Vertical symmetry A composition with identical or similar elements arranged on both the right and left halves of an image.
- 31. Horizontal symmetry A composition with identical or similar elements arranged on both the top and bottom halves of an image.
- 33. Radial symmetry A composition with a center point from which the arrangement of elements radiate around in a circular format. Imagine: Cut a piece of “pie” out of an empty circle. Create a design on the piece of pie. Repeat the pie piece to finish off the “pie.”
- 34. Radial symmetry
- 35. Asymmetry A composition with a heavy and light amount of elements. Asymmetry uses disorder to create balance.
- 36. Asymmetrical
- 37. Contrast A large difference between elements. Green and Red, dark and light, large and small, thin and thick, bright and dull.
- 38. Contrast Contrast refers to differences in values, colors textures, shapes and other elements.
- 39. Emphasis Where an artist draws attention to one or more parts of a design.
- 40. Emphasis Emphasis is used by artists to create dominance and focus in their work. Artists often use focal areas (centers of interest) to place emphasis on the most important aspect of art.
- 41. Movement The path the viewer’s eye is directed to take by the artist’s choice of elements such as line.
- 42. Movement Visual movement is used by artists to direct viewer through their work, often to focal areas.
- 43. Variety The differences in any element in a work of art give it variety. Ex: A variety of shape sizes or a variety of the same hue
- 44. Rhythm Rhythm is repetition of visual movement of the elements-colors shapes, lines, values, forms, spaces, and textures. Movement and rhythm work together to create the visual equivalent of a musical beat..
- 45. Pattern Pattern uses the art elements in planned or random repetitions to enhance surfaces of paintings or sculptures.
- 46. Unity A sense that all of the parts belong together as one piece of artwork.
- 47. Unity Unity provides the cohesive quality that makes an art work feel complete and finished. All the principles work together to create unity and therefore a successful design. Salvador Dali Andy Warhol
- 48. Proportion – aka – Scale The relationships of size in artworks in relation to how they are normally viewed. Ex. A perfectly drawn person in proportion or a perfectly drawn person with a tiny head
- 49. Proportion This picture uses the idea of proportion to illustrate the size difference between the fish and the boat.
- 50. Proportion – aka – Scale
