Canine 2
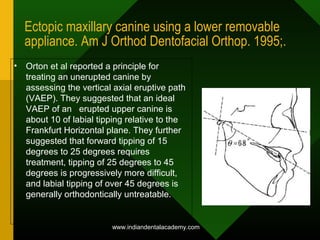
- 1. Ectopic maxillary canine using a lower removable appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995;. • Orton et al reported a principle for treating an unerupted canine by assessing the vertical axial eruptive path (VAEP). They suggested that an ideal VAEP of an erupted upper canine is about 10 of labial tipping relative to the Frankfurt Horizontal plane. They further suggested that forward tipping of 15 degrees to 25 degrees requires treatment, tipping of 25 degrees to 45 degrees is progressively more difficult, and labial tipping of over 45 degrees is generally orthodontically untreatable. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 2. Prevention of Impacted Teeth • Early detection and intervention • Removal of primary teeth and/or supernumeraries to prevent deflection and enhance the eruptive possibility of the permanent tooth • Space maintenance after early loss of deciduous teeth www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 3. TREATMENT PLANNING PRINCIPLES WITH IMPACTED TEETH • Prognosis is based on the extent of displacement and the surgical trauma required for exposure • Tooth should be pulled into the arch through keratinized tissue, not alveolar mucosa • Adequate space should be provided in the arch prior to attempting to pull the impacted tooth into positionwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 4. Indications for Serial Extraction • a significant arch length discrepancy exists • facial profile can support extraction treatment www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 7. Normalization of Mesially Inclined Canines with Extraction of Primary Canines • 91% normalize if the canines overlap the laterals <50% on the Panorex • 64% normalize if the canines overlap the laterals >50% on the Panorex Ericson & Kurol, Eur J Ortho, 1988 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 8. Indications for Primary Canine Extraction • 10-13 year age group • normal space conditions are present • no incisor root resorptions are found • Follow-up radiographs should be taken at 6 month intervals to follow the intra-bony eruptive movement of the permanent canines. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 9. IMPACTED TEETH TREATMENT OPTIONS • extraction of adjacent teeth to allow for eruption of impacted tooth (serial extraction) • extraction of impacted tooth • surgical exposure • no treatment- allow tooth to remain impacted • transplantationwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 10. Indications for Transplantation • otherwise well-aligned arch • adequate space exists for the impacted tooth • favorable access to the impacted tooth • Other issues contraindicate prolonged orthodontic treatment www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 13. Indications for Extraction of Impacted Teeth • Extreme malposition • Otherwise well aligned arch • Lengthy treatment contraindicated – medically compromised – poor cooperation – root resorption potential – periodontal problems • Ankylosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 14. • CAUSES FOR POOR PROGNOSISCAUSES FOR POOR PROGNOSIS • HorizontalHorizontal • high palatalhigh palatal • high labial (if above adjacent teeth)high labial (if above adjacent teeth) • Transalveolar (apex on one side, crown on theTransalveolar (apex on one side, crown on the other side of the alveolus)other side of the alveolus) • sclerotic bonesclerotic bone • closed apicesclosed apices • abnormal root configurationabnormal root configuration • older ageolder age • NOT ALL CUSPIDS CAN BE SAVEDNOT ALL CUSPIDS CAN BE SAVED www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 15. EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED TEETHwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 16. EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED TEETHwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 17. Surgical Exposure Procedures • Apically Positioned Flap • Closed Eruption • Open Eruption www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 18. SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS • Maintain adequate amount of attached gingiva • avoid excessive bone removal • do not expose CEJ • avoid damage to adjacent teeth • avoid movement, or excess movement www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 19. • Palatally inclined canines havePalatally inclined canines have adequate space, seldom erupt withoutadequate space, seldom erupt without surgical interventionsurgical intervention • Labial impactions have arch lengthLabial impactions have arch length discrepancy, erupt ectopicallydiscrepancy, erupt ectopically IMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINEIMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINE www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 20. SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FOR EXPOSING CANINES 1. Window approach 2. Apically repositioned flap 3. Flap closed eruption procedure 4. Tunnel traction ? what is the criterion for choosing the correct technique. THE LOCATION OF CANINE www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 21. LOCATION OF CANINE IMPACTION ************** LABIOPALATALLY VERTICALLY Labial Low Palatal Midalveolar High *************** www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 22. IMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINEIMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINE - LABIAL APPROACH- LABIAL APPROACH 1.Window approach 2. Gingiva Preservation (Vanarsdall & Corn 1977)2. Gingiva Preservation (Vanarsdall & Corn 1977) * Laterally Positioned Flap For High ImpactionsLaterally Positioned Flap For High Impactions * Apically Repositioned FlapApically Repositioned Flap 3. Flap closed eruption procedure 4. Tunnelling Method (Cresini 1994)Tunnelling Method (Cresini 1994)www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 23. IMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINEIMPACTED MAXILLARY CANINE - PALATAL APPROACH- PALATAL APPROACH • Plenty Of Keratinized GingivaPlenty Of Keratinized Gingiva • Full Thickness Palatal Flap, With Or Without Placement Of Button HoleButton Hole • Placement Of Button Hole Without Flap www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 24. IMPACTED MANDIBULARIMPACTED MANDIBULAR CANINE - LABIAL APPROACHCANINE - LABIAL APPROACH • Utilize Apically Repositioned Flap OrUtilize Apically Repositioned Flap Or Vestibular IncisionVestibular Incision • Watch For Mental NerveWatch For Mental Nerve • Labial Impactions Often Associated WithLabial Impactions Often Associated With Retained Primary DentitionRetained Primary Dentition www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 25. IMPACTED MANDIBULARIMPACTED MANDIBULAR CANINE - LINGUAL APPROACHCANINE - LINGUAL APPROACH • Full thickness flapFull thickness flap • no releasing incisionsno releasing incisions • very difficult accessvery difficult access • fortunately, rarefortunately, rare • watch for significant anatomywatch for significant anatomy • does pt have toridoes pt have tori • lingual impaction associated with shortage oflingual impaction associated with shortage of arch lengtharch length www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 26. IMPORTANCE OF CHOOSING THE CORRECT TECHNIQUE - The esthetic appearance - The periodontal health and - The longevity of the tooth depend on the technique used for exposing the tooth SURGICAL EXPOSURE MAKES THE PERIODONTAL APPARATUS VULNERABLE TO DESTRUCTION Kohavi , Vanarasdal Boyd, Vermette Bishara, Kokich www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 27. - ITS WIDTH IS MAXIMUM IN THE INCISOR REGION AND MINIMUM IN THE CANINE-PREMOLAR REGION Alveolar mucosa Attached gingiva ATTACHED GINGIVA For proper periodontal health, the tooth must have a collar of attached gingiva measuring at least 2-3 mm in width . www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 28. IN THE ABSENCE OF ATTACHED GINGIVA, THE MUSCLES OF FACE CAN DETACH THE MARGINAL PERIODONTAL TISSUE FROM TOOTH CAUSING MARGINAL BONE LOSS AND GINGIVAL RECESSION www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 29. THE CREATION AND PRESERVATION OF A FUNCTIONAL BAND OF ATTACHED GINGIVA MUST BE AN IMPORTANT OBJECT IN THE SURGICAL EXPOSURE OF LABIALLY IMPACTED CANINE ************* THE PALATE HAS A WIDE ZONE OF ATTACHED GINGIVA www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 30. WINDOW APPROACH Main considerations- AFTER THE PROPOSED GINGIVECTOMY ,THE TOOTH MUST HAVE A RESIDUAL COLLAR OF ATTACHED GINGIVA MEASURING AT LEAST 2-3 mmwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 32. APICALLY POSITIONED FLAP • split thickness pedicle reflected from edentulous area • bone covering the enamel is removed • flap sutured back to periosteum, leaving 1/2 - 2/3 of the crown exposed • surgical dressing placed for 1 week post-op to prevent tissue overgrowth • 2 weeks post-op: bond an attachment on the toothwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 34. SURGICAL PROCEDURE Local infiltration anesthesia is given. An incision is made along the ridge area in the edentulous space. The incisogingival dimension to this keratinized band of tissue will be determined by the amount of attached gingiva that exists on the adjacent teeth or its antimere in the arch. Vertical releasing incisions are made, and the attached gingiva is freed. The connective tissue is removed from the labial aspect of the tooth, and bone is removed beyond the height of contour of the crown. Bone removal is not performed beyond the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) area. The CEJ area is not disturbed because it is here that we would like to establish the dentogingival attachment to the tooth Robert L. Vanarsdall, and Herman Corn, 1977 ajodo www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 35. PLACEMENT OF ATTACHED GINGIVA • It is essential that the graft be placed to cover the cementoenamel junction area and 2 to 3 mm of the crown • The dressing is retained in position for 7 to 10 days to afford the tissue time for reattachment to the tooth and for epithelization to occur in the area. Upon removal of the dressing, a direct bond bracket is attached to the tooth, and tooth movement is begun immediately with light force. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 37. INDICATIONS – 1 . CANINES WHICH ARE HIGH, SUPERFICIAL & LABIALLY PLACED LIMITATIONS – 1. CANNOT BE DONE IF CANINE IS VERY HIGH 2. CANNOT BE DONE IF CANINE IS MIDALVEOLAR APICALLY REPOSITIONED FLAP www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 38. APICALLY REPOSITIONED FLAP FULL THICKNESS SPLIT THICKNESS Technique easier to do. Technique more difficult Thick graft, Thin graft More scarring Less scarring Hence poor appearance Better appearance Injury to flap can cause necrosis. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 39. Complications of APF • thick gingiva • rolled margin • long clinical crown • vertical relapse www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 40. CLOSED ERUPTION • Elevate A Flap At Midcrestal Region • Remove Enough Bone To Bond An Attachment • Ligature Wire Or Gold Chain Is Hung From The Attachment • Flap Returned To Original Position For Complete Closure With The Chain Or Ligature Wire Passing Under The Flap And Exiting At The Midcrestalwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 41. INDICATIONS- 1. Very high canines 2. Midalveolar canines FLAP CLOSED ERUPTION PROCEDURE STEPS- www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 45. APF vs CE surgical technique for labially impacted teeth Vermette et al, Angle Ortho, 1995;65(1):23-34 • APF – more post-op recession – more unesthetic (gingival scarring) (90% vs 6% with CE) – significant vertical relapse (intrusion) (61% vs 0% with CE) • CE – narrower post-op zone of attcached gingiva • HYPOTHESIS – CE duplicates more of a “natural” tooth eruptionwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 46. Uncovering labially impacted teeth: apically positioned flap and closed-eruption techniques Michael E. Vermette, Vin.. Angle Orthodontist 1997 . • The purpose of this study was to examine the esthetic and periodontal differences between two methods of uncovering labially impacted maxillary anterior teeth: the apically positioned flap and closed-eruption techniques. • The sample consisted of 30 patients who were recalled a minimum of three months after orthodontic treatment of a unilateral labially impacted maxillary anterior tooth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 47. • . In the CE group, clinical examination showed less width of attached gingiva on the distal surface and increased probing bone level on the facial surface of the uncovered teeth relative to their contralateral controls. Uncovered teeth in the APF group showed more apical gingival margins on the mesial and facial surfaces; greater crown length on the midfacial surface; increased probing attachment level on the facial surface; increased width of attached gingiva on the facial surface; increased probing bone level on mesial, facial, and distal surfaces; and gingival scarring. Radiographic examination showed shorter roots on the uncovered teeth in both groups. Photographic examination revealed vertical relapse of the uncovered teeth in the APF group. • labially impacted maxillary anterior teeth uncovered with an apically positioned flap technique have more unesthetic sequalae than those uncovered with a closed- eruption technique. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 48. Indications for Apically Positioned Flap on labially positioned impactions •Labially positioned impacted canine (not mid-alveolus) •Tooth positioned slightly apical to the muco-gingival junction or coronal to it •There is insufficient gingiva in the area of the impacted canine •The crown of the impacted canine is positioned mesially over the root of the adjacent lateral incisor Kokich , AJODO; 126:278-283 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 49. Indications for Closed Eruption on labially positioned impactions • Any mid-alveolus impaction • Labially positioned impacted canine IF: » Tooth positioned well above the muco-gingival junction » There is sufficient gingiva in the area of the impacted canine » The crown of the impacted canine is not positioned too far mesially or distally Kokich , AJODO; 126:278-283 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 51. OE vs CE surgical technique for palatally impacted teeth Burden et al, AJODO, 1999;115:634-9 • Equal long-term periodontal health of ectopic canines • Repeat surgery was more often associated with CE • Treatment times were equal if ortho traction was applied soon after surgery • Treatment time was increased for OE if the canine was allowed to erupt naturally before orthodontic appliances were fitted.www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 52. Problems with traditional OE or CE for palatally impacted canines Most orthodontists usually wait to uncover the palatally impacted canines 6 – 9 months after starting mechanics to open space for the tooth. By this time the crown of the impacted tooth has often come in intimate contact with the roots of the incisors – this makes it difficult for the surgeon to remove adequate bone around the crown – this makes it much more difficult to move the tooth through bone. And then after it is exposed they begin traction within just a few weeks. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 53. Alternate OE Technique for Palatally Impacted Cuspids Kokich and Mathews offer an alternative technique: Uncover the impacted tooth prior to ortho treatment, even in the late, mixed dentition. The canine will erupt without orthodontic forces and be at the level of the occlusal plane before it is bonded. Because they are getting to the impacted teeth earlier, before they are in intimate contact with the roots of the adjacent incisors, they can easily remove all bone around the crown. This facilitates the eruptive potential of the impacted tooth. Kokich and Mathews, Orthodontic and dentofacial orthopedics, Ann Arbor: Needham Press; 2001 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 54. Full thickness muco-periosteal flap All palatal bone removed down to cej Flap replaced with a “window” Canine erupted without orthodontic forces When the cusp tip is level with the occlsual plane,it is bracketed Kokich and Mathews, Orthodontic and dentofacial orthopedics, Ann Arbor: Needham Press; 2001 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 55. Open Eruption Palatally Impacted Canines www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 57. Chain attached to the impacted tooth & taken to oral cavity through tunnel & socket of ‘c’ www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 58. Tooth exposed through window & a tunnel created Probe through tunnel During treatment Post treatment www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 59. Chain through tunnel Post treatment www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 60. THE DESIRABLE BIOMECHANICAL SEQUELAE * Canine moves through cancellous bone. *Erupts through the socket of ‘C’. *Erupts at the centre of the alveolar crest. *Better coverage by bone and attached gingiva, labially and palatally. ************** www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 63. * Located in the anterolateral curvature of maxillary alveolus. * Overlying labial cortical bone is very thin. ∴ Avoid pulling the canine further labially or laterally Canine position is ‘unique’ www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 64. ARF FCET UNDESIRABLE BIOMECHANICAL SEQUELAE IN ARF & FCET www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 65. UNDESIRABLE BIOMECHANICAL SEQUELAE IN ARF & FCET * CANINE EXPERIENCES AN OUTWARD PULL * * CANINE IS DRAGGED OVER THE LABIAL CORTEX* * LABIAL CORTEX THINS OUT AND RESORBS * * THE CANINE ERUPTS AT THE BUCCAL EXTREMITY OF THE ALVEOLAR RIDGE AND NOT AT THE CENTRE* * PHYSOLOGIC ERUPTION IS NOT SIMULATED * www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 67. CAN BALLISTA SPRING OVERCOME THIS PROBLEM ? NOT COMPLETELY. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 68. PALATALLY IMPACTED CANINE - FCET www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 69. PALATALLY IMPACTED CANINE - FCET www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 70. SIMPLY REFLECTING A FLAP TO EXPOSE AN IMPACTED TOOTH BY ITSELF CAN DAMAGE THE EPI. ATTACHMENT AND THE PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT OF AN ADJACENT TOOTH Adams 1988 FLAP DESIGN IN ‘FLAP CLOSED’ - A Disadvantage - www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 71. MODIFIED FLAP DESIGN IN T .T FCET T.T www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 72. METHODS OF ATTACHMENT • Pin placed into hole created in crown of impacted tooth • Stainless steel crown • Wire ligature around the crown • Direct bonding of a bracket/button www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 73. ATTACHMENTS FOR THE EXPOSED TOOTH Extensive bone resorption Circumferential wire ligation External root resorption Ankylosis. Bands Extra coronal caps Necessitate extensive bone Gold caps with cleats removal Cast gold inlays www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 74. Indications for Stainless Steel Crown • Inability to attain an adequately dry field for direct bonding • Compromised enamel for bonding (amelogenesis imperfecta) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 78. MAGNETS – POSITIONING IS VERY DIFFICULT BONDING - REQUIRES ONLY MINIMAL BONE REMOVAL (4-5mm) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 79. Bur hole at cuspid tip www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 80. Ligation Vs. Bonding • increased chance of ankylosis/external resorption with ligation relative to bonding • Increased loss of periodontal attachment with ligation relative to bonding www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 84. PIN ATTACHMENT Threaded pins - Can damage pulp www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 85. Attachment bonding to impacted teeth at the time of surgical exposure A. BeckerN. Shpack and A. Shteyer European Journal of Orthodontics, October 1996. • The results showed that bonding at the time of exposure is superior to its performance at a later date, that the use of an eyelet attachment has a lower failure rate than the use of a conventional bracket, that the palatal aspect offers the poorest bonding surface and that pumicing the exposed tooth offers no advantage over immediate etching of the exposed enamel. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 86. MECHANICAL APPROACHES FOR ALIGNING UNERUPTED TEETH • elastomeric material tied from a heavy base arch to the exposed tooth • alignment spring either soldered to heavy base archwire or bent into a light archwire (delivers more constant force over a longer range) • Direct light-wire (NiTi memory wire) to the tooth • magnetic forcewww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 87. Orthodontic Principles • light forces for canine extrusion • continuos tie or stop of the teeth mesial and distal to the canine area • rectangular archwire should be present before extrusion mechanics are started (resists the deformation caused by the extruding forces) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 90. The Wave Spring VOGT jco2004 • The Wave Spring* is a new type of ortho-dontic retraction spring that takes the shape of a wave when extended • A superelastic nickel titanium alloy delivers a relatively large amount of activation-about 90g of force-from an extremely compact spring-only 6mm long in its resting statewww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 91. • When a closed-coil spring is activated. the ends of the spring twist in opposite directions; as the spring returns to its resting state, it unwinds, creating torque on the attached teeth. • The Wave Spring stretches in a linear direction and thus produces no unwinding torque. • Because the spring has no coils, it lies flat instead of protruding into the buccal vestibule, making it more comfortable and hygienic. • Also, its attachment eyelets are integral to the spring, which elimi-nates the problem of the eyelets loosening and falling off. • The Wave Spring's greatest attribute is its ability to fit into a small space yet remain active over a long distance www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 92. Kilroy Spring Bowman s The Kilroy Spring is a pre-formed module that is simply slid onto a rectangular continuous arch wire at the site of an impacted tooth. The vertical loop of the Kilroy Spring extends perpendicularly from the occlusal plane in its passive state. A stainless steel ligature is then placed through the helix at the apex of the vertical loop of the Kilroy and then this loop is directed toward the impacted tooth. The ligature is tied either directly to the helix of the loop button or to the loop of the Monkey hook that is in-turn linked to the loop button attachment. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 93. • The Kilroy Spring is supported by 1) the rectangular base arch wire, 2) reciprocal force from the incisal one-third of the adjacent teeth where contacted by the lateral extensions of the Kilroy Spring • The Kilroy I Spring was designed to produce both vertical and lateral eruptive forces for palatally impacted canines. The Kilroy II Spring produces more vertical forces and was created for buccally- impacted teeth. Due to the multiple helices and cantilever design of the Kilroy II, there is a chance of tissue impingement adjacent to the impacted tooth therefore, more frequent visits to monitor progress are recommended www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 95. "Ballista Spring" (1979 ajodo) • The "Ballista Spring" system developed by Harry Jacoby • used for marsupialization of unerupted teeth consists of a spring made from the Wilcock special plus wire www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 96. • The Ballista spring system uses a spring which creates a vertical traction on the impacted tooth along its long axis thus separating the impacted tooth from the roots of the adjacent tooth. • The Ballista spring is easily inserted, ligated and is independent of other parts of the appliance. • In general most systems require full bonded arches at the beginning of the treatment while the ballista spring does not require any bonding of anterior teeth till the crown of the impacted tooth erupts completely. • It can be used for buccally as well as palatally impacted canines. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 97. • A Double backed portion entering the double tube on the molar around which the wire is twisted. • b. Coil to increase the wire length, thus increasing the resiliency. • c. Vertical arm with a loop to be tied to the canine www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 98. An Extrusion Spring for Palatally Impacted Cuspids OPPENHUIZEN jco aug 2003 Before placing the extrusion spring, stabilize the arch with a rectangular wire, and bring the maxillary incisors into reasonable alignment The extrusion spring is made from a prefabricated .018 s.s arch using ant curvature to generate extrusive component For unilateral correction cut opposite distal to lateral incisor opposite to impactionwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 99. • Bend the wire over space created for cuspid. bend a tight helix at the point of eyelet attached to impacted cuspid • For bilateral impaction bend the wire on both sides over the spaces created for the cuspids, and form helices at both ends • To activate the extrusion spring, bend the wire inferiorly so It points straight down perpendicular to the occlusal plane www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 100. Cantilever Mechanics for Treatment of Impacted Canines FISCHER, ZIEGLER, DMDCHRISTOPHER LUNDBERG, 2000 JCO, A cantilever made from .0175" × .025" TMA* can generate the 25-30g of force needed to extrude a canine over a wide range of activation. The cantilever is tied into the auxiliary molar tube or welded directly to the continuous archwire To prevent the generation of a second couple, the cantilever should be attached to the canine with a single- point contact; an alternative is a compensating bend that allows a passive angle of entry into the canine bracket www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 101. Management of Palatally Impacted Canines Cantilever between .032" bracket, welded lingually to molar tube, and single-point attachment to palatally impacted canine. Occasionally, a palatally impacted canine will require buccal root torque for proper axial inclination. This problem can be solved by bonding a mandibular second bicuspid bracket with 22° of built-in torque to the labial surface and using a full-size rectangular wire.www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 102. In cases requiring more anchorage, such as bilaterally impacted canines, an .0175" × . 025" TMA composite cantilever can be welded directly to an . 032" × .032" TMA transpalatal arch between the .032" lingual molar brackets . As with the unilateral cantilever, activations can be made to generate extrusive forces followed by buccal movement. The combination of a stiff buccal archwire and the transpalatal arch provides superior control of the reactive forces and excellent anchorage. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 103. The K-9 Spring for Alignment of Impacted Canines VARUN KALRA, JCO/OCTOBER 2000 – The K-9 spring is made of . 017" × .025" TMA* wire, – The horizontal arm of the spring is inserted into the first molar buccal tube and the premolar – About 7mm mesial to the first premolar bracket, the horizontal arm is bent 90° downward to form a vertical arm, which is about 11mm long and ends in a helix .www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 104. • While the spring is held with a plier just distal to the vertical arm, the vertical arm is bent about 20° inward, toward the palate. • To activate the spring after it is engaged in the buccal segment , the vertical arm is swung upward and ligated to the bonded attachment on the impacted canine www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 105. – . This provides a gentle extrusive force on the canine; the spring also has a buccal component of force due to the arcial pattern of activation and deactivation. – The force needed to distalize the canine is achieved by cinching the spring back about 2mm after it has been ligated to the canine. – Alternatively, the distalization force can be provided by bending the vertical arm distally prior to its ligation to the canine www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 106. The Monkey Hook: An Auxiliary for Impacted, Rotated,and Displaced Teeth BOWMAN, ALDO CARANO, JCO/JULY 2002 • The Monkey Hook* is a simple auxiliary with an open loop on each end for the attachment of intraoral elastics or elastomeric chain, or for connecting to a bondable loop- button. The hook can be closed with a plier to prevent disengagement. A combination of Monkey Hooks and bondable loop-buttons allows the production of a variety of different directional forces to assist in the correction of impacted, rotated, or displaced teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 107. • The loop should be positioned parallel to the roots of the adjacent teeth to allow subsequent attachment of more hooks for production of a variety of forces . The Monkey Hook can extend through the gingival tissue after surgical exposure If the tooth is deeply impacted, a second Monkey Hook can be linked to the first. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 109. Monkey Hooks can be attached to intermaxillary elastics, with anchorage derived from the opposing dental arch . The hooks provide more rigid support for intermaxillary elastics than is produced by twisting a steel ligature into a hook. Although elastic thread or chain can be tied from a ligature hook to a base archwire, the forces produced by these materials will decay dramatically over time. If patients are asked to change the intermaxillary elastics daily, thus avoiding the diminution of forces to the impacted tooth, the variable of patient compliance is introduced. An alternative is to place a continuous superelastic archwire through the Monkey Hook to direct tooth eruption. Later this archwire can be passed directly through the lumen of the loop button to continue the processwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 110. If anchorage is unavailable from the opposing arch, vertical intra-arch eruptive forces can be produced using superelastic coil springs www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 111. Eruption of Impacted Canines with an Australian Helical Archwire • Elastic force modules have the disadvantages of rapid force decay and the need for stiff main archwires to avoid side effects on the adjacent teeth. If a superelastic nickel titanium wire is inserted directly into the canine bracket, the wire must be deflected, and archform can become distorted. This can result in tipping or intrusion of adjacent teeth, canting of the occlusal plane, and a consequent lateral or anterior open bite. J Clin Orthod. 2000 Sep;34(9):538-41.www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 112. • An overlay or piggyback wire avoids these side effects, but delays the forced eruption of the impacted canine, since the rest of the dentition must be fully aligned before a sufficiently rigid main archwire can be placed. Furthermore, the stiff primary archwire prevents the flexible nickel titanium archwire from sliding freely through the brackets. The Australian wire is bent with helices that serve as stops against the brackets of the adjacent teeth to maintain space for the erupting canine. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 113. An additional incisal helix increases the resilience of the system and anchors the stainless steel ligature running to the canine attachment. The force vector for the canine can be altered by changing the transverse position of the incisal helix. The appliance is activated by twisting the steel ligature. This force also maintains space for the erupting tooth. The amount of force can be varied by using different archwire designs www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 116. In contrast with overlay or piggyback techniques, the Australian helical archwire provides a virtually friction- free system. It also avoids the side effects associated with superelastic nickel titanium archwires. Unlike a rectangular arch, a round arch has no torquing effect on the adjacent teeth. The stiffness of the Australian wire resists deformation by the forces applied to it and reduces intrusive reciprocal forces on the adjacent teeth. If intrusive forces are a concern, however, vertical elastics can be used. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 117. Nickel Titanium Closed-Coil Spring for Extrusion of Impacted Canines • Cut a 16mm Jones Jig spring in half. Pull out one end slightly to form a small hook • Slip the hook through the link of elastomeric chain (from the impacted canine) nearest the gingiva, and twist it a couple of times www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 118. Activate the spring, and wrap several links around a stable rectangular archwire with an occlusal step. Be sure to leave a "tail" of chain for reactivation. At the next visit, unwrap, reactivate, and rewrap the spring . This will take only a few minutes www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 120. Alignment of Impacted Canines with Cantilevers and Box LoopsJCO-2003 • The use of TMA box loops to produce 1st- and 2nd- order corrections while continuing vertical eruption. • Initial extrusion mechanics with a cantilever. • Use of a box loop to continue canine extrusion and to make 1st- and 2nd-order corrections. • Incorporation of the canine into a continuous archwire for finishing. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 121. A cantilever constructed from .017" × .025" TMA wire is inserted into the auxiliary tube of the first molar and connected by a one-point contact to the active unit The magnitude of the force (F) used to extrude the canine should not exceed 70g www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 122. • A box loop produces a statically indeterminate force system.5 When used for canine alignment, it is constructed of .017" × .025" TMA. The activation of the box loop depends on the desired position of the canine in both the sagittal and horizontal planes of space www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 123. Magnetic Force (Vardman, AJO, 1991) • magnetic bracket bonded to an impacted tooth and an intraoral magnet linked to a Hawley-type retainer • attraction was initiated 1-2 weeks after healing • stated advantages: – less invasive – effective forces at short distances – controlled spatial guidancewww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 125. Direct NiTi wire to the tooth www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 126. Wire placed directly to the tooth www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 128. Treatment Time Stewart et al, AJODO 2001;119:216-25 • 3 groups : – unilaterally impacted group – bilaterally impacted group – control group matched with similar characteristics but without the impacted canine • Avg. duration of treatment: – Control group: 22.4 months – Unilateral group: 25.8 months – Bilateral group: 32.3 monthswww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 129. Treatment Outcomes D’Amico et al, Angle Orthod 2003;73:231-238 • Subjects followed 3.5 years post-ortho • Canine rise occurred more often on working sides with normally erupted canines than with impacted canines www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 130. SUCCESS OF ADULT TREATMENT with palatally impacted canines • Sample of 19 adults (mean age 28.8 y, range 20 -47y) with 23 impacted teeth • Control sample (mean age 13.7 y, range 12 – 16y) – matched for positions of the impacted teeth in the 3 planes of space • Success rate: – Control:100% – Adults: 69.5% - unsuccessful treatment defined as failure to erupt (5 teeth) or partially extruded but not aligned with the arch (2 teeth). All 7 failed canines occurred in patients > 30 years old. • Equal length of treatment – BUT adult patients had significantly more visits and visits were significantly longer in duration Becker et al, AJODO 2003;124:509-14 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 131. Pulpal and periodontal reactions to orthodontic alignment of palatally impacted canines (Angle Orthodontist 1994 ) • The purpose of this study was to evaluate differences in periodontal and pulpal status, root length, and tooth alignment between contralateral maxillary lateral incisors, canines, and premolars in patients treated for unilateral impaction of maxillary canines • Clinical examinations were performed on 32 patients, average age 22 years 11 months and average posttreatment observation period 3 years 7 months • Probing attachment level was lower at the mesial and distal aspect of the previously impacted canine and at the distal aspect of the adjacent lateral incisor. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 132. • Crestal bone height was lower at the mesial aspect of the previously impacted canine and at the distal aspect of the adjacent lateral incisor. The roots of the lateral incisors and premolars adjacent to the previously impacted canines were shorter. Pulpal obliteration was observed in six previously impacted canines (21%), and pulp necrosis in one previously impacted canine. The pulps of the remaining teeth appeared normal radiographically. A negative response to electric pulp testing was observed in eight previously impacted canines. Approximately 40% of the previously impacted canines exhibited noticeable relapse and were judged to be intruded, lingually displaced, mesially rotated, as well as discolored. Of the contralateral canines, 91% were normal in appearance. The previously impacted canine could be identified on posttreatment color slides in approximately 75% of the cases. www.indiandentalacademy.com
