Math investigation (bounces)
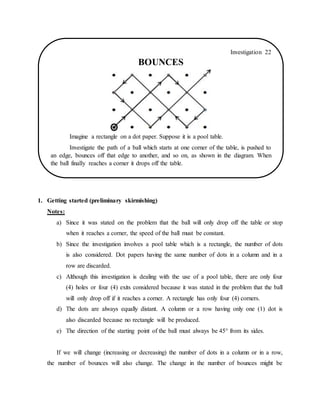
- 1. 1. Getting started (preliminary skirmishing) Notes: a) Since it was stated on the problem that the ball will only drop off the table or stop when it reaches a corner, the speed of the ball must be constant. b) Since the investigation involves a pool table which is a rectangle, the number of dots is also considered. Dot papers having the same number of dots in a column and in a row are discarded. c) Although this investigation is dealing with the use of a pool table, there are only four (4) holes or four (4) exits considered because it was stated in the problem that the ball will only drop off if it reaches a corner. A rectangle has only four (4) corners. d) The dots are always equally distant. A column or a row having only one (1) dot is also discarded because no rectangle will be produced. e) The direction of the starting point of the ball must always be 45° from its sides. If we will change (increasing or decreasing) the number of dots in a column or in a row, the number of bounces will also change. The change in the number of bounces might be Investigation 22 BOUNCES Imagine a rectangle on a dot paper. Suppose it is a pool table. Investigate the path of a ball which starts at one corner of the table, is pushed to an edge, bounces off that edge to another, and so on, as shown in the diagram. When the ball finally reaches a corner it drops off the table.
- 2. increasing or decreasing depending on the patterns that the investigator might discover. Consider the following illustrations. Illustration 1 Illustration 2 Illustration 3 Illustration 4 The observation was noted on a table. Illustration Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Number of Bounces 1 4 6 6 2 5 7 3 3 6 8 10 4 7 9 5 How many bounces can be made considering the number of dots in a column? How many bounces can be made considering the number of dots in a row? On what corner of the pool table will the ball drops off?
- 3. 2. Taking a break (gestating) What do you observe on the number of bounces if the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both odd? What do you observe on the number of bounces if the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both even? What do you observe on the number of bounces if the number of dots in a column is odd and the number of dots in a row is even? What do you observe on the number of bounces if the number of dots in a column is even and the number of dots in a row is odd? 3. Exploring systematically A. How many bounces can be made considering the number of dots in a column? In here, I consider the number of dots in a column to be constant. Thus, the number of dots in a row is only changing. Let us consider the lowest possible number of dots in starting this investigation. (Note: One is always not included. Equal number of dots in a row and in a column is also always excluded.) Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Number of Bounces 2 3 1 2 4 2 2 5 3 2 6 4 2 7 5 2 8 6
- 4. 2 9 7 B. How many bounces can be made considering the number of dots in a row? In here, I consider the number of dots in a row to be constant. Thus, the number of dots in a column is only changing. Let us consider the lowest possible number of dots in starting this investigation. (Note: One is always not included. Equal number of dots in a row and in a column is also always excluded.) Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Number of Bounces 3 2 1 4 2 2 5 2 3 6 2 4
- 5. 7 2 5 8 2 6 9 2 7 I had also done this with larger number of dots in a column and in a row. With this observation, I had concluded that the number of bounces is the same if the number of dots in a column and in a row is interchange. It seems that the figure was only rotated 90° to the right.
- 6. C. On what corner of the pool table or rectangle will the ball drops off? Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Corner that the Ball Drops Off 3 5 Adjacent Corner 4 6 Opposite Corner 5 8 Adjacent Corner 10 9 Adjacent Corner
- 7. 4. Making conjectures Conjecture A If the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both even, the ball drops off on the corner opposite to the corner where the ball started rolling. Conjecture B If the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both odd, the ball drops off on one of the corners adjacent to the corner where the ball started rolling. Conjecture C If the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both even, the number of bounces is always even. Conjecture D If either the number of dots in a column or in a row is odd or the numbers of dots in a column and in a row are both odd, the number of bounces is always odd. Conjecture E If the number of dots in a column is two (2), we can get the number of bounces by using the formula 𝑟 − 2 = 𝑏 where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture F If the number of dots in a column is three (3) and the number of dots in a row is odd, the number of bounces can be determined using the formula 𝑟 − 3 2 = 𝑏
- 8. where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture G If the number of dots in a column is three (3) and the number of dots in a row is even, the number of bounces can be determined using the formula 3𝑟 − (2𝑟 + 1) = 𝑏 where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture H If the number of dots in a column is four (4) and the number of dots in a row is any positive integer, the number of bounces is equal to the number of dots in a row except Z, Z+3, Z+3+3, Z+3+3+3…; where Z is 7. Conjecture I If the number of dots in a column is five (5) and the number of dots in a row is odd, the first digit of its product or area is the number of bounces if and only if the interval of the numbers of dots in a column and in a row is divisible by two (2) but not by four (4). If the product involves three (3) digits, the first two (2) digits is the number of bounces. Conjecture J If the number of dots in a column is five (5) and the number of dots in a row is even, the number of bounces can be determined using the formula 5𝑟 + 5 5 = 𝑏 where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture K
- 9. If the number of dots in a column is ten (10) and the number of dots in a row is any positive integer, we can get the number of bounces by using the formula 10𝑟+10 10 + 5 = 𝑏; except Z, Z+3, Z+3+3, Z+3+3+3,…; where Z is 4 where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture L If the number of dots in a column is equal to one less twice the number of dots in a row, then the number of bounce is always one (1). We can use the formula 2𝑐 − 1 = 𝑟 where 𝑟 = number of dots in a row b = number of bounces Conjecture M If the sum of the numbers of dots in a column and in a row is fifteen (15), then the number of bounces is always eleven (11). 5. Testing Conjectures Conjecture A Considering the numbers of dots in a column and in a row as both even, the ball always drops off on the corner opposite to the corner where the ball started rolling. Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Corner that the Ball Drops Off 2 4 Opposite Corner 2 6 Opposite Corner 2 8 Opposite
- 10. Corner 6 4 Opposite Corner 10 4 Opposite Corner Conjecture B Considering the numbers of dots in a column and in a row as both odd, the ball does not always drops off on one of the corners adjacent to the corner where the ball started rolling. Although most of the figures made agree with the conjecture, I had found a counter example. For instance, if the number of dots in a column is eleven (11) and the number Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Corner that the Ball Drops Off 3 5 Adjacent Corner
- 11. 5 7 Adjacent Corner 7 9 Adjacent Corner 11 3 Opposite Corner False Conjecture! Conjecture C Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Number of Bounces
- 12. 2 4 2 2 6 4 2 8 6 4 6 6 4 10 2 Conjecture D Considering that the numbers of dots in a column or in a row are both odd just even either of them. I came up with the following observation. I had found a counter example which is 11 and 3. Look at last row on the next page. This justifies that conjecture D is not true. Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Number of Bounces 3 5 1
- 13. 5 7 3 7 9 5 11 3 4 False Conjecture! Conjecture E If r = 3, then 3 – 2 = 1. If r = 4, then 4 – 2 = 2. If r = 5, then 5 – 2 = 3.
- 14. If r = 6, then 6 – 2 = 4. If r = 7, then 7 – 2 = 5. Conjecture F If r = 5, then 5−3 2 = 1. If r = 7, then 7−3 2 = 2. If r = 9, then 9−3 2 = 3. If r = 11, then 11−3 2 = 4. If r = 13, then 13−3 2 = 5. Conjecture G If r = 2, 3(2) – (2(2) + 1) = 1. If r = 4, 3(4) – (2(4) + 1) = 3. If r = 6, 3(6) – (2(6) + 1) = 5. If r = 8, 3(8) – (2(8) + 1) = 7. If r = 10, 3(10) – (2(10) + 1) = 9. Conjecture H If r = 2, then b = 2. If r = 3, then b = 3. If r = 5, then b = 5.
- 15. If r = 6, then b = 6. If r = 8, then b = 8. Conjecture I If r = 3, then 5(3) = 15. 1 is the first digit. Thus, 1 is the number of bounces. If r = 7, then 5(7) = 35. 3 is the first digit. Thus, 3 is the number of bounces. If r = 11, then 5(11) = 55. 5 is the first digit. Thus, 5 is the number of bounces. If r = 15, then 5(15) = 75. 75 is the first digit. Thus, 7 is the number of bounces. If r = 19, then 5(19) = 95. 3 is the first digit. Thus, 9 is the number of bounces. If the product involves three (3) digits, the first two (2) digits is the number of bounces. If r = 35, then 5(35) = 175. 17 is the first two digits. Thus, 17 is the number of bounces. Conjecture J If r = 2, then 5(2)+5 5 = 3. If r = 4, then 5(4)+5 5 = 5. If r = 6, then 5(6)+5 5 = 7. If r = 8, then 5(8)+5 5 = 9. If r = 10, then 5(10)+5 5 = 11. Conjecture K If r = 2, then 10(2)+10 10 + 5 = 8. If r = 3, then 10(3)+10 10 + 5 = 9. If r = 5, then 10(5)+10 10 + 5 = 11.
- 16. If r = 6, then 10(6)+10 10 + 5 = 12. If r = 8, then 10(8)+10 10 + 5 = 14. Conjecture L If c = 4 and r = 7, then 2(4) – 1 = 7. If c = 5 and r = 9, then 2(5) – 1 = 9. If c = 6 and r = 11, then 2(6) – 1 = 11. Since the examples above justifies the conditions of conjecture L, the number of their bounce is always one (1). Conjecture M If r = 11 and c = 4, then 11 + 4 = 15. Thus, the number of bounces is 11. If r = 10 and c = 5, then 5 + 10 = 15. Thus, the number of bounces is 11. If r = 9 and c = 6, then 6 + 9 = 15. Thus, the number of bounces is 11. 6. Reorganising Here are some of the data obtained from the investigation. Number of Dots in a Column Number of Dots in a Row Figure Number of Bounces Corner that the Ball Drops Off 2 3 1 Adjacent Corner 2 4 2 Opposite Corner 2 5 3 Adjacent Corner 2 6 4 Opposite Corner
- 17. 2 7 5 Adjacent Corner 2 8 6 Opposite Corner 2 9 7 Adjacent Corner 3 2 1 Adjacent Corner 3 5 1 Adjacent Corner 4 2 2 Opposite Corner 4 6 6 Opposite Corner 4 10 2 Opposite Corner
- 18. 5 2 3 Adjacent Corner 5 8 9 Adjacent Corner 6 2 4 Opposite Corner 7 2 5 Adjacent Corner
- 19. 8 2 6 Opposite Corner 9 2 7 Adjacent Corner 10 9 15 Adjacent Corner
- 20. 11 3 4 Opposite Corner 7. Elaborating Early in the investigation, several questions were recorded for possible consideration. These provide elaboration for the investigation. The questions involved the numbers of dots in a column and in a row and the path of the ball. The investigation involves dots on a rectangle. The situation could be varied by considering the number of dots on a rectangle. 8. Summarising In this investigation, some aspects were examined: a. the account of the aspect involving the numbers of dots in a column or/and in a row; b. the figures drawn for the cases considered; c. the table showing the data obtained from the investigation; d. the patterns observed e. the presentation of conjectures from A to M; f. the testing of conjectures from A to M, and; g. the elaboration of this investigation.
- 21. Extension: Investigate the number of regions inside the rectangle. Investigate the number of remaining dots not covered by the ball. Investigate the number of square inside the rectangle.
