Topic 3.2
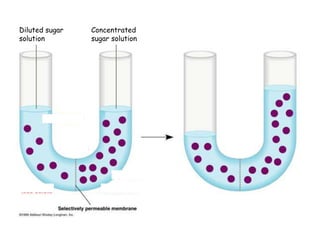
- 1. Diluted sugar Concentrated solution sugar solution
- 2. Hypotonic solution Hypertonic solution
- 3. A B Balance the concentration on both sides If solute is of large molecules Only water molecules can diffuse through In order to balance, we need to add water on the more concentrated side (B) So, water molecules from A (more dilute) will diffuse to B (more concentrated) Before After A B A B Water 10 5 5 10 Solute 5 10 5 10
- 4. A B If solute is of small molecules Both water and solute molecules can diffuse through the semi-permeable membrane Diffusion of both molecules occur until A and B are isotonic Before After A B A B Water 11 5 8 8 Solute 5 11 8 8
- 5. By now, you should know that: Movement of substances across plasma membrane depends on the concentration of the solutions. Water diffuse from more dilute solution (hypotonic) to more concentrated solution (hypertonic).
- 6. Terms to take note and remember!! Hypertonic – solution with higher concentration of solutes than cell Hypotonic – solution with lower concentration of solutes than cell Isotonic – solution of equal solute concentration with cell Which one has high solute concentration and low water concentration? Hypertonic The process where water diffuses across plasma membrane from hypotonic soln. to hypertonic soln. is ...? Osmosis
- 7. Effects of hypertonic, hypotonic & isotonic solutions on plant cells Hypertonic solution H2O diffuses out from cell by osmosis H2O lost from vacuole & cytoplasm Vacuole shrinks Cytoplasm & plasma membrane shrinks and is pulled away from the cell wall Cell becomes flaccid. Plant wilts. Process : Plasmolysis If immersed in a hypotonic solution, H2O diffuse into the cell, making it turgid. Process : Deplasmolysis
- 8. Effects of hypertonic, hypotonic & isotonic solutions on plant cells Hypotonic solution H2O diffuses into the cell by osmosis Vacuole gains water, expands and exert pressure outwards on the cell wall This pressure (tugor pressure) causes the cell to be turgid (firm) Turgidity gives plant mechanical support Isotonic solution No net movement of water across plasma membrane Water diffuses across the plasma membrane at the same rate in both directions Cell’s volume and shape maintains
- 9. Effects of hypertonic, hypotonic & isotonic solutions on animal cells Hypertonic solution H2O diffuses out of cell by osmosis H2O is rapidly lost Red blood cells shrivel and probably die Process : Crenation Hypotonic solution H2O diffuses into the cell by osmosis Red blood cells gain water and swell and finally burst (because have no cell wall) Process : Haemolysis For other animal cells, the process is known as lysis
- 10. Effects of hypertonic, hypotonic & isotonic solutions on animal cells Isotonic solution No net movement of water across plasma membrane Water diffuses at the same rate in both directions Red blood cells maintain their shape
- 11. Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Flaccid No change Turgid
- 12. Osmosis in everyday life 1. Wilting plants Excess use of chemical fertilisers which dissolve in soil Soil becomes hypertonic to the root cells Water diffuses out from root cells into soil Root cells becomes flaccid and undergo plasmolysis Wilt and may eventually dies 2. Preservation of food Salted fish Preserved fruits
