8 monsaccharide-gluconeogenesis
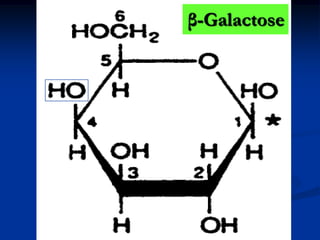
- 1. β-Galactose
- 2. Galactose Found in milk sugar (lactose) H H OH lactase OH
- 3. Glycolysis
- 4. (Active Galactose) Lactose Glycolysis In lactating M.G.
- 5. Pathways for utilizing galactose into G –6–P, lactose, glycogen, GAGs, glycolipids, and in glycolysis Glycolipids Glycogen 2 Lactose + Glucose In lactating Lactose synthase Mammary Gland (Active Galactose) 1 Into Glycolysis
- 6. Galactose metabolism: 1. Galactokinase 2. Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase 3. UDP-galactose-4-epimerase 4. Pyrophosphorylase
- 7. Disorders of Galactose Metabolism • Galactosemia is a group of disorders, which can be defined as a congenital disease due to deficiency of an enzyme in galactose metabolism, leading to accumulation of galactose in blood and its reduction into the sugar alcohol “galactitol” by: • NADPH-dependent galactose reductase that is present in neural tissue and in the lens of the eye • A high concentration of galactitol (hygroscopic) in the lens causes osmotic swelling, with the formation of cataract • The principal treatment of these disorders is to eliminate lactose from the diet
- 8. Clinical Significance of Galactose Metabolism Galactosemia Classic Galactosemia Galactose-1-phosphate UDP-galactose-4- uridyl transferase defect epimerase defect Galactokinase Deficiency Galactosaemia Galactokinase defect
- 9. Clinical Symptoms of Galactosemia 1. A failure of neonates to thrive (to develop well and to be healthy) 2. Vomiting and diarrhea occur following ingestion of milk, hence individuals are termed lactose intolerant 3. Impaired liver function 4. Elevated blood galactose (Hypergalactosemia) 5. Metabolic acidosis 6. Urinary galactitol excretion and hyperaminoaciduria
- 10. Clinical Symptoms of Galactosemia 7. If Galactosemia is not treated, it will produce: • cataract (Lens obeique) , المياه البيضاء • blindness and • fatal liver damage (Cirrhosis) • Glucoma (increased intraocular pressure, )المياه الزرقاء
- 12. Fructose Metabolism • People eating diets containing large amounts of sucrose, can utilize fructose as a major source of energy • The pathway for utilization of fructose differs in muscle and liver • Muscle which contains only hexokinase can phosphorylate fructose into F-6-P which is a direct glycolytic intermediate
- 13. Glyceraldehyde Fructose Fructose-1- phosphate Fructose-1- phosphate DHAP
- 14. Entry of fructose carbon atoms into the glycolytic pathway (Fructolysis) in hepatocytes B
- 15. Conversion of Fructose into Glucose
- 16. Synthesis of Fructose in Seminal Vesicles NADPH NADP+ NAD+ NADH Glucose Aldose reductase Sorbitol Sorbitol DH Fructose Estimation of seminal fructose is used as a Male Fertility Test Deficiency of aldolase B (Hereditary Fructose Intolerance) leads to: 1. Accumulation of Fructose & F–1–P 2. F–1–P inhibits glycogen phosphorylase enzyme leading to hypoglycemia especially after ingestion of fructose
- 18. Reduction of Glucose to Sorbitol Aldose Reductase
- 20. Metabolism of Sorbitol NADPH NADP+ NAD+ NADH Glucose Aldose reductase Sorbitol Sorbitol DH Fructose Aldose reductase (NADPH-linked) reduces glucose into Sorbitol Sorbitol dehydrogenase converts Sorbitol into fructose
- 21. Metabolism of Sorbitol Aldose reductase is found in significant amounts in: 1. Liver 2. Seminal vesicle 3. Epithelium of the eye lens 4. Schwann cells of peripheral nerves 5. Papillae of the kidney While Sorbitol dehydrogenase is present only in: 1. liver 2. Seminal vesicle
- 22. In Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose enters tissues listed above freely (requires no insulin) In hyperglycemia large amounts of glucose enter these tissues & converted into sorbitol which is dead metabolite in the retina, kidney & peripheral nerves, due to absence of Sorbitol DH Sorbitol will accumulates in these cells, causing many physiologic & pathologic manifestation including: 1. Cataract 2. Retinopathy of eye lens 3. Peripheral neuropathy of peripheral nerves 4. Nephropathy of kidney 5. Vascular problems (Atherosclerosis)
- 23. Gluconeogenesis • Definition: It is the formation of glucose from non- carbohydrate sources • Site: Only in Liver & Kidney • It occurs partly in cytoplasm & partly in mitochondria • Importance of Gluconeogenesis: 1. It is the chief source of blood glucose after the first 18 hours-fasting 2. It removes blood lactate produced by RBCs & muscles and blood glycerol produced by adipose tissue or absorbed by intestine
- 24. Enzymes of Gluconeogenesis 1. Pyruvate Carboxylase: • Converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate 2. Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEP Carboxykinase): • Converts oxaloacetate to PEP 3. Fructose–1,6–diphosphatase: • To reverse F–1,6–diP into F–6–P 4. Glucose–6–phosphatase: • To reverse Glucose–6–P into Glucose
- 25. & Kidney
- 26. • Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase enzyme is present in the cytoplasm • Oxaloacetate cannot diffuse through the mitochondrial membrane to the cytosol In Cytoplasm • This problem can be solved by the dicarboxylic acid shuttle In Cytoplasm In Mitochondria In Mitochondria
- 27. a In mitochondria b 1 In cytoplasm 2 Steps of Gluconeogenesis 3
- 28. Sources of Gluconeogenesis 1.Blood Lactate: • From RBCs and exercising muscles 2.Glycerol: • From adipose or absorbed from intestine 3.Odd chain fatty acids: • From ruminants 4.Glucogenic Amino acids
- 29. Substrates for Gluconeogenesis 2 3 4 1
- 30. 1 & RBCs
- 31. 2 (10 % of Fat) • Incorporation of Glycerol into Glycolysis in Liver Glycerol kinase Glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase
- 32. 3 Odd chain fatty acids • Conversion of Propionyl CoA to Succinyl CoA -Oxidation From Ruminants
- 33. 3 Conversion of Propionyl CoA to Succinyl CoA
- 34. 4 Glucogenic Amino acids • Proteins are the most important sources of glucose during fasting after the liver glycogen is depleted • 58% of proteins are convertible to glucose. This is proved by the D/N ratio • D/N ratio is the ratio between the amount of Dextrose (D) or glucose and Nitrogen (N) in urine. it is zero in normal animals due to absence of glucose in urine
- 35. 4 Glucogenic Amino acids • An animal starved for 2 – 3 days, pancreatectomized and given phlorizin • The D/N ratio of this animal is 3.65/1, i.e., proteins which contain one gram nitrogen give 3.65 grams of glucose • Since 100 grams of proteins contain 16 grams of nitrogen, therefore, 100 grams of proteins can give 16 X 3.65 = 58.4 grams glucose
- 36. 4
- 37. 4 Glucogenic Amino acids < TD>
- 39. Regulation of Gluconeogenesis 1. After carbohydrate diet, Insulin inhibits the synthesis of enzymes of gluconeogenesis 2. During starvation, glucocorticoids, growth hormone, glucagon and adrenaline stimulate the synthesis of enzymes of gluconeogenesis 3. Acetyl CoA is an allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase, so oxaloacetate accumulate 4. Citrate & ATP stimulate fructose–1,6–diphosphatase 5. Fructose diphosphate & AMP inhibit fructose–1,6– diphosphatase
