Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie Four Major Religions that Originated in India (20)
Mehr von Domenic Marbaniang (20)
Four Major Religions that Originated in India
- 1. © Domenic Marbaniang, 2014
marbaniang.com
FOUR RELIGIONS THAT ORIGINATED IN INDIA
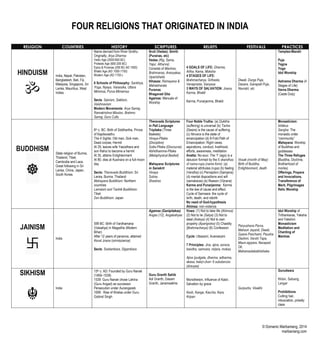
RELIGION COUNTRIES HISTORY SCRIPTURES BELIEFS FESTIVALS PRACTICES
HINDUISM
ॐ
India, Nepal, Pakistan,
Bangladesh, Bali, Fiji,
Malaysia, Singapore, Sri
Lanka, Mauritius, West
Indies
Name derived from River Sindhu
Originally, Arya Dharma
Vedic Age (2000-600 BC)
Protests Age (600-200 BC)
Epics & Puranas (200 BC-AD 1000)
Bhakti Age (AD 1000-1750)
Modern Age (AD 1750-)
6 Schools of Philosophy: Sankhya,
Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisesika, Uttara
Mimmsa, Purva Mimamsa
Sects: Saivism, Saktism,
Vaishnavism
Modern Movements: Arya Samaj,
Ramakrishna Mission, Brahmo
Samaj, Guru Cults
Sruti (Vedas); Smriti
(Puranas, etc)
Vedas (Rig, Sama,
Yajur, Atharva):
Consists of Mantras,
Brahmanas, Aranyakas,
Upanishads
Itihasas: Ramayana &
Mahabharata
Puranas
Bhagavad Gita
Agamas: Manuals of
Worship
4 GOALS OF LIFE: Dharma,
Artha, Kama, Moksha
4 STAGES OF LIFE:
Brahmacharya, Grihasta,
Vanaprasta, Sanyasa
3 WAYS OF SALVATION: Jnana,
Karma, Bhakti
Karma, Punarjanma, Bhakti
Diwali, Durga Puja,
Dasara, Ganapati Puja,
Navratri, etc
Temples-Mandir
Puja
Yagna
Yoga
Idol Worship
Ashrama Dharma (4
Stages of Life)
Varna Dharma
(Caste Duty)
BUDDHISM
☸
State religion of Burma,
Thailand, Tibet,
Cambodia and Laos.
Great following in Sri
Lanka, China, Japan,
South Korea.
6th c. BC: Birth of Siddhartha, Prince
of Kapilavasthu
The 4 Sights: Old man, Sick man,
Dead corpse, Hermit
At 29, leaves wife Yasodhara and
son Rahul to become a hermit
At 35, attains Enlightenment
At 80, dies at Kusinara on a full-moon
day
Sects: Theravada Buddhism: Sri
Lanka, Burma, Thailand
Mahayana Buddhism: Northern
countries
Lamaism and Tantrik Buddhism:
Tibet
Zen Buddhism: Japan
Theravada Scriptures
in Pali Language
Tripitaka (Three
Baskets)
Vinaya-Pitaka
(Discipline)
Sutta-Pitaka (Discourse)
Abhidhamma-Pitaka
(Metaphysical Basket)
Mahayana Scriptures
in Sanskrit
Vinaya
Sutras
Shastras
Four Noble Truths: (a) Dukkha
(suffering) is universal (b) Tanha
(Desire) is the cause of suffering
(c) Nirvana is the state of
emancipation (d) 8-Fold Path of
Emancipation: Right views,
aspirations, conduct, livelihood,
efforts, awareness, meditation
Anatta: No-soul. The “I” (ego) is a
delusion formed by the 5 skandhas
of nama-rupa (name-form): (a)
material attributes (rupa) (b) feeling
(Vendha) (c) Perception (Samjana)
(d) mental dispositions and will
(samskaras) (e) Reason (Vijnana)
Karma and Punarjanma: Karma
is the law of cause and effect.
Cycle of Samsara: the cycle of
birth, death, and rebirth
No need of God-hypothesis
Ahimsa: non-violence
Vesak (month of May):
Birth of Buddha,
Enlightenment, death
Monasticism:
bhikkus
Sangha: The
monastic order
“community”
Mahayana: Worship
of Buddhas and
goddesses
The Three Refuges
(Buddha, Doctrine,
Brotherhood of
monks)
Offerings, Prayers
and Invocations,
Transference of
Merit, Pilgrimages
Relic Worship
JAINISM
卐
India
599 BC: Birth of Vardhamana
(Vaisaliya) in Magadha (Modern
Bihar)
After 12 years of penance, attained
Keval Jnana (omniscience)
Sects: Svetambara, Digambara
Agamas (Ganipitakas)
Angas (12), Angabahyas
Vows: (1) Not to take life (Ahimsa)
(2) Not to lie (Satya) (3) Not to
steal (Asteya) (4) Not to own
property (Aparigraha) (5) Chastity
(Brahmacharya) (6) Confession
Cycle: Utsarpini, Avarsarpini
7 Principles: Jiva, ajiva, asrava,
bandha, samvara, nirjara, moksa.
Ajiva (pudgala, dharma, adharma,
akasa, kala)+Jiva= 6 substances
(dravyas)
Paryushana Parva,
Mahavir Jayanti, Diwali,
Gyana Panchami, Pausha
Dashmi, Varshi Tapa,
Maun-agiyara, Navapad
Oli,
Mahamastakabhisheka
Idol Worship of
Tirthankaras, Yaksha
and Yakshini
Monasticism
Meditation and
Chanting of
Mantras
SIKHISM
☬
India
15th c. AD: Founded by Guru Nanak
(1469–1539)
1539: Guru Nanak chose Lahina
(Guru Angad) as successor
Persecution under Aurangazeb
1699 : Rise of Khalsa under Guru
Gobind Singh
Guru Granth Sahib
Adi Granth, Dasam
Granth, Janamsakhis
Monotheism, Influence of Kabir,
Salvation by grace
Kesh, Kanga, Kaccha, Kara,
Kripan
Gurpurbs, Visakhi
Gurudwara
Kirtan, Satsang,
Langar
Prohibitions:
Cutting hair,
intoxication, priestly
class