vam.ppt
•Als PPT, PDF herunterladen•
0 gefällt mir•13 views
PPT on Vogel's Approximation Method
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie vam.ppt
Ähnlich wie vam.ppt (20)
Substation grounding grid design using Alternative Transients Program-ATP and...

Substation grounding grid design using Alternative Transients Program-ATP and...
Lecture 7 transportation problem finding initial basic feasible solution

Lecture 7 transportation problem finding initial basic feasible solution
Generalized Logistic Regression - by example (Anthony Kilili)

Generalized Logistic Regression - by example (Anthony Kilili)
IRJET- Developed Method for Optimal Solution of Transportation Problem

IRJET- Developed Method for Optimal Solution of Transportation Problem
Mehr von debmahuya
Mehr von debmahuya (8)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph

Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph
Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx

Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode

Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
Web & Social Media Analytics Previous Year Question Paper.pdf

Web & Social Media Analytics Previous Year Question Paper.pdf
vam.ppt
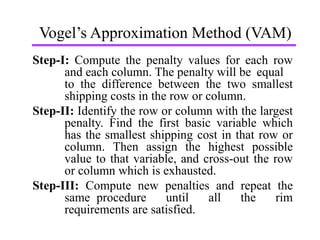
- 1. Vogel’s Approximation Method (VAM) Step-I: Compute the penalty values for each row and each column. The penalty will be equal to the difference between the two smallest shipping costs in the row or column. Step-II: Identify the row or column with the largest penalty. Find the first basic variable which has the smallest shipping cost in that row or column. Then assign the highest possible value to that variable, and cross-out the row or column which is exhausted. Step-III: Compute new penalties and repeat the same procedure until all the rim requirements are satisfied.
- 2. An example for Vogel’s Method Find the IBFS of the following transportation problem by using Penalty Method. Supply 6 7 8 15 80 78 D1 D2 D3 15 5 5 10 15 O1 O2 Demand
- 3. Step 1: Compute the penalties in each row and each column . Supply Row Penalty 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 80-7=73 78-8=70 7-6=1 78-15=63 15 5 5 10 15
- 4. Step 2: Identify the largest penalty and choose least cost cell to corresponding this penalty Supply Row Penalty 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 80-7=73 78-8=70 7-6=1 78-15=63 15 5 5 10 15
- 5. Step-3: Allocate the amount 5 which is minimum of corresponding row supply and column demand and then cross out column2 Supply Row Penalty 5 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 80-7=73 78-8=70 7-6=1 78-15=63 15 5 5 10 15
- 6. Step-4: Recalculate the penalties Supply Row Penalty 5 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 78-8=70 8-6=2 78-15=63 15 X 5 5 15
- 7. Step-5: Identify the largest penalty and choose least cost cell to corresponding this penalty Supply Row Penalty 5 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 78-8=70 8-6=2 78-15=63 15 X 5 5 15
- 8. Step-6: Allocate the amount 5 which is minimum of corresponding row supply and column demand, then cross out column3 Supply Row Penalty 5 5 6 7 8 15 80 78 Demand Column Penalty 15-6=9 8-6=2 78-15=63 15 X X 5 15
- 9. Step-7: Finally allocate the values 0 and 15 to corresponding cells and cross out column 1 Supply 0 5 5 6 7 8 15 15 80 78 Demand X X X X X D3 O1 O2 D1 D2
- 10. Solution of the problem Now the Initial Basic Feasible Solution of the transportation problem is X11=0, X12=5, X13=5, and X21=15 and Total transportation cost = (0x6)+(5x7)+(5x8)+(15x15) = 0+35+40+225 = 300.