Melden
Teilen
Downloaden Sie, um offline zu lesen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Dr.S.Sundarabalu
Dept.of LinguisticsThe Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)

The Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)Department of Linguistics,Bharathiar University
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Intro. to Linguistics_6 Phonetics (Organ of Speech, Segment, Articulation)

Intro. to Linguistics_6 Phonetics (Organ of Speech, Segment, Articulation)
Phonetics & phonology, INTRODUCTION, Dr, Salama Embarak

Phonetics & phonology, INTRODUCTION, Dr, Salama Embarak
Ähnlich wie Phonetics
Dr.S.Sundarabalu
Dept.of LinguisticsThe Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)

The Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)Department of Linguistics,Bharathiar University
Ähnlich wie Phonetics (20)
The Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)

The Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Production(Phonetics)
Csd 210 anatomy & physiology of the speech mechanism i

Csd 210 anatomy & physiology of the speech mechanism i
Mehr von Uludag University
Mehr von Uludag University (14)
Computer Assisted Language Learning - CALL by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University

Computer Assisted Language Learning - CALL by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University
Describing Language- by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University

Describing Language- by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University
Language and Language Learning by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University

Language and Language Learning by AYLİN AYDIN, Uludag University
Task Based Instruction by Aylin Aydın, Uludag University

Task Based Instruction by Aylin Aydın, Uludag University
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx

Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Phonetics
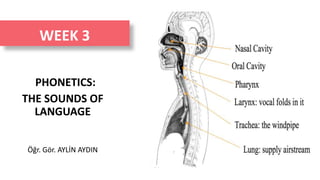
- 1. WEEK 3 PHONETICS: THE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE Öğr. Gör. AYLİN AYDIN
- 6. Speech Production Process Detailed / 1 The lungs In order to produce the majority of sounds in the world’s languages, we take air into the lungs and expel it during speech. A certain level of air pressure is needed to keep the speech mechanism functioning steadily. The pressure is maintained by the action of various sets of muscles coming into play during the course of an utterance. The muscles are primarily the intercostals (the muscles between the ribs) and the diaphragm (the large sheet of muscle separating the chest cavity from the abdomen). The intercostals raise the ribcage to allow air to flow into the lungs during inhalation, while the diaphragm helps to control the release of air during exhalation for speech so that we can speak for a reasonable period of time between breaths.
- 7. The larynx As air flows out of the lungs up the trachea (windpipe), it passes through a box-like structure made of cartilage and muscle; this is the larynx. As air passes through the space between the vocal folds, which is called the glottis, different glottal states are produced, depending on the positioning of the vocal folds. Sound is produced in the larynx. Speech Production Process Detailed / 2
- 8. Glottal States: space between the vocal folds • In the most basic terms, a sound produced while the vocal folds are vibrating is called a voiced sound. • A sound produced while the folds are not vibrating is called a voiceless sound. • All vowels are voiced, but consonants can be either voiced or voiceless. Speech Production Process Detailed / 3
- 9. Whispering is voiceless No vibration of the cords Vocal cords are almost completely closed Murmuring is voiced Vibration of the cords Vocal cords are relaxed i.e. Dense Tense Speech Production Process Detailed / 4
- 10. REVISION In most speech sounds, including all the soun producing ds used regularly in English, the air we use comes from the lungs. This air travels up from the lungs, passing through the trachea (windpipe), until it reaches the larynx, where it might be set into vibration. The larynx is commonly known as the voice box. The air passes through the larynx into the vocal tract, which is the air passages of the head and neck.
- 11. Vibration of the vocal folds The vocal folds do not stay in the same position all the time. A person can either keep the vocal folds wide apart (known as keeping them abducted), as happens during normal breathing, or shut them completely (known as keeping them adducted), as happens when coughing. When they are shut, they block the flow of air from the lungs, as happens when we hold our breath. During speech, the folds can either be kept far apart, or they can be narrowed, so that they vibrate when air from the lungs passes through them. Sound is produced when air is made to vibrate REVISION
- 12. REVISION
- 14. Lips Lips and teeth Between teeths Tongue – ridge Roof of the mouth Towards the velum Throaty
