Ccpa catheter basics07medicine
- 2. What is a Swan? • Full name: Swan-Ganz Catheter • Pulmonary Artery (PA) Catheter = right heart catheter • Used it to monitor a patient’s hemodynamics when we cant answer the question using noninvasive/clinical measures • Useful to measure right atrial, pulmonary artery, right ventricular pressures and indirectly measure left atrial pressures, cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance
- 3. Why use a Swan? • Differentiation between causes of shock>cardiogenic, hypovolemic, septic • Differentiation between causes of pulmonary edema>cardiogenic versus noncardiogenic • Diagnosis of pericardial tamponade • Diagnosis of intracardiac shunt • Evaluation/Management of pulmonary hypertension • Diagnosis of lymphangitic spread of tumor and fat embolism • Management of complicated MI, HF • Determine need for vasopressor/inotropic therapy • Fluid Status>in GI bleed, renal failure, sepsis • Ventilator management>determining the best PEEP
- 4. Some history… • First pulm catheters were placed in 1940s • 1970-William Ganz and Harold Swan introduced this catheter. Pulmonary artery Catheter that is balloon-tipped and flow directed, placed bedside • Revolutionized catheters>moved from diagnosis only to help in management. No clinical trials were done to see if they improved mortality. Benefit was assumed • 1987- nonrandomized trials:showed mortality was higher in patients with an acute MI who had a Swan placed • 1990s-Ontorio Intensive Care Group attempted a RCT for use of Swans>not done b/c many clinicians felt unethical to withhold Swan placement because accurate diagnosis=accurate treatment=better prognosis????
- 5. Is it unethical to withhold Swan Placement? And are they better at predicting clinical outcomes? • 1996 observational study of RHC in first 24 hours said NO. • Placement led to worse patient outcomes b/c of complications of placement or misinterpretation of data • Use of catheter might be a marker of more aggressive care, which is associated with higher mortality • Changes in therapy in response to the information might have led to high mortality (i.e. using pressors) • Study might not have adequately adjusted for confounding factors • Only looked at SGC placed in first 24 hours. • Connors AF Jr, Speroff T, Dawson NV, et al. The effectiveness of right heart catheterization in the initial care of critically ill patients. JAMA 1996;276:889-897
- 6. Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Use of Pulmonary-Artery Catheters in High-Risk Surgical Patients. Sandman et al. NEJM- Jan, 2003 • 1994 high-risk surgical patients underwent randomization for PA catheters (RCT) • Preop placement, for elective or urgent surgery • Looked at 6mo and 12 mo mortality • No difference b/t PA catheter group from placebo in terms of mortality and length of hospitalization • Increased risk of PE in the catheter group and thus, PA catheters may be associated with increased morbidity
- 7. Escape Trial • The value of Swan-Ganz catheterization to guide tailored therapy in heart failure patients is an area of controversy. • The randomized ESCAPE trial showed no benefit on a primary end point of the number of days alive and out of the hospital at six months JAMA. 2005;294:1625-1633.
- 8. To Swan or Not to Swan? INDIVIDUALIZE CARE Understanding Swan Ganz Catheters= Understanding Hemodynamics
- 10. Basic Catheter Features • Made of polyvinylchloride and has a pliable shaft that softens at body temperature • Catheter is 110 cm and external diameter is either 5 or 7 French (1 French=0.0335mm) • Balloon is fastened 1-2mm from the tip and when inflated it guides the catheter (using fluid dynamic drag) from greater intrathoracic veins through tight heart into pulmonary artery • Thermistor-4cm proximal to the tip, measures temperature>important for determining cardiac output
- 11. • Typically catheters have 4 ports: 2. White port with blue wire is the proximal port> terminates at 30cm from tip of catheter and is used to measure right atrium pressures 3. White port, yellow wire is the PAD distal port 4. White port with red wire is for balloon inflation 5. Last port has the connection to the thermodilution cardiac output computer> contains the electrical leads for thermistor.
- 12. Insertion Techniques • Average time from decision to use PA catheter until onset of catheter based treatment is 120 minutes • Goal: get the catheter to the pulmonary artery • Cordis into right internal jugular vein or left subclavian allows easiest passage • Swan should be oriented ex-vivo to approximate the course in the body • Catheter goes through an introducer and into the vein. The balloon stays closed until we reach the right atrium. • When we reach the right atrium (20cm), balloon should be inflated to reduce possibility of injury to the myocardium. • Then the balloon should be moved quickly through the right ventricle (30cm)> and then pulmonary artery (40cm) and PCWP (50cm) FROM SUBCLAVIAN/IJ APPROACH
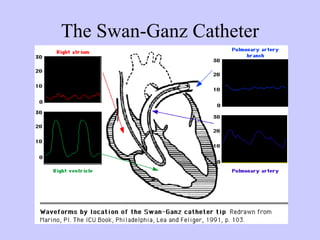
- 13. How do you know you are in the Right Atrium?>>20 cm Normal right atrial presssure is 0-6mmHg. Normal oxygen content 15% Normal O2 saturation 75% a=atrial contraction. c=sudden motion of the AV ring toward the right atrium x descent=atrial relaxation v=pressure generated by venous filling of the right atrium y descent=rapid emptying of the RA into RV
- 14. What Elevates the Right Atrial Pressure? • RV infarct • Pulmonary hypertension • Pulmonary stenosis • Left to right shunt • Tricuspid valvular disease • Left heart failure
- 15. Prominent RA pulsations • Prominent a wave: • Tricuspid stenosis • Cannon a wave: • AV dissociation or Ventricular tachycardia • Prominent v wave: • Tricuspid regurgitation or VSD
- 16. How do you know you are in the right ventricle? 30cm RV systolic=17-30 RV diastolic=0-6 RV O2 content=15% RV O2 saturation 75%
- 17. What Increases RV Pressures? • RV failure • Pulmonary hypertension • Pulmonary stenosis • Pulmonary Embolism • Cardiomyopathy • Cardiac tamponade • Cardiac constriction
- 18. How do you know you are in the pulmonary artery? Normal PA pressure, systolic 15-30 Normal PA pressure, diastolic 5-13 O2 content 15% O2 saturation 75%
- 19. What Elevates PA pressure? • Volume Overload (backflow) • Primary lung disease • Primary pulmonary hypertension • Pulmonary Embolism • Left to right shunt • Mitral Valve Disease
- 20. THE WEDGE: What is the Pulmonary Artery Wedge Pressure? The measurement is obtained when the inflated balloon impacts into a slightly smaller branch of the pulmonary artery. This is where the arterial pressure exceeds the venous pressure and the venous pressure exceeds the alveolar pressure, thereby creating a continuous column of blood from the catheter tip to the left atrium when the balloon is inflated. Pulmonary venous pressure is the best indicator of left atrial pressure except when there is venoocclusive disease. AND ONLY WHEN THE PA CATHETER IS IN ZONE 3 of the lung.
- 21. Inflation of the Balloon for PCWP Tracing Pulmonary artery wedge 2-12 PCWP tracing looks like RA tracing Pulmonary vein O2 content 20% except that the v wave is slightly higher Pulmonary vein O2 sat 98% than the a wave (opposite of RA). Also, b/c of the time required for LA mechanical events, PAWP waveforms are further delayed when recorded by EKG
- 22. What Increases PCWP? • PEEP (minimally) • LV failure • Cardiac tamponade • Aortic Insufficiency • Mitral regurgitation • VSD
- 23. Prominent PCWP Tracings • Prominent a waves: -mitral stenosis -LV systolic dysfunction -LV overload -Decreased LV compliance • Prominent v waves -mitral regurgitation -VSD
- 25. Calculation of Cardiac Output Thermodilution versus Ficks method •Thermodilution: Add an indicator substance (5ml of dextrose or saline) that is cooler than blood. Indicator in injected through the proximal port of the PA catheter and mixes with the blood in the RV. The mixing lowers the temperature of the flowing blood which is carried to the distal thermistor port. The thermistor records the temperature change and electronically displays a temperature/time curve. The area under the curve is inversely proportional to the flow rate in the pulmonary artery which equals the cardiac output in absence of intracardiac shunt -sources of error with thermodilution are seen with tricuspid regurgitation and intracardiac shunts
- 26. Fick’s Method • General principle: the release or uptake of a substance by an organ equals the product of the bloodflow through that organ times the difference of arteriovenous concentrations of that substance. • CO= O2 consumption (ml/min) --------------------------------------------------------------- arterial O2 content(PCWP)-mixed venous (PA) O2 content • O2 consumption varies according to individual, by age and sex. Usually estimated as being 250mL for a 70kg male. Generally estimated at 130mL x BSA • Blood O2 content=% saturation X Hb x 1.39 ml O2/gm Hb • Errors: assumptions of O2 consumption, wont work at all with intracardiac shunts. But works better with TR
- 27. Cardiac Output/Index • What is cardiac output? • What is normal cardiac output? • What is normal cardiac index?
- 28. Effects of PEEP • Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure — Alveolar pressure will not return to atmospheric pressure at end-expiration in the presence of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), a change that can affect the measurement of intravascular pressures. • The effects of PEEP are generally felt not to be clinically significant. • PEEP does affect right sided pressures (i.e. RA or CVP).
- 29. Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) • Refers to the resistance to blood flow offered by all of the systemic vascular resistance, excluding the pulmonary vasculature. • This is sometimes referred as total peripheral resistance (TPR). • Mechanisms that cause vasoconstriction increase SVR, and those mechanisms that cause vasodilation decrease SVR. • SVR can be calculated if cardiac output (CO), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and central venous pressure (CVP) are known. • SVR = 80 X (MAP - CVP) ÷ CO • Normal Systemic Vascular Resistance is 800-1200 (dyne*sec)/cm5
- 30. Zeroing is performed by opening the system to air to establish atmospheric pressure as zero. Referencing (or leveling) is accomplished by placing the air-fluid interface of the catheter (or the transducer) at a specific point to negate the effects of the weight of the catheter tubing and fluid column
- 31. Not an Entirely Benign Lign… •Insertion of an introducer to provide venous access>Pntx, bleeding, infection •Passage of the Swan through the introducer>minimized by inflating the balloon tip after entering the right atrium -Sustained ventricular arrythmias, occur in 0-3% pts -RBBB develops in about 5% of catheter insertions, placing pts with a preexisting LBBB in complete heart block. RBBB is usually temporary. -Knotting catheter-can occur during insertion if loops are allowed to form in one of the cardiac chambers. When knotting occurs, can usually remove transvenously but some require venotomy or surgical extraction. •Maintenance of the catheter>Inflating balloon when catheter has moved distally>causing pulmonary artery perforation. Mortality >30%, usu requires thoracotomy
- 32. Not Without Risks??? •Don’t leave balloon inflated in wedge position for extended period of time>can cause pulmonary infarction • Thromboembolic events can occur with the catheter acting as a nidus for thrombus formation. Less common with heparin bonded catheters •Misinterpretation of the data •Mural thrombi can be induced by inflammation of infection of a vessel wall, seen in 33% of patients at autopsy •Sterile vegetations, seen in 90% of patients •Endocarditis of the pulmonic valve •Rupture of the catheter balloon and consequent air embolism
- 33. THINK HARD BEFORE YOU STICK
- 34. Sample Questions • BP 80/40 HR 120 • RA 20 • RV 50/23 • PA 70/30 • PCWP 28 • CO 2.0 • SVR 1600
- 35. • BP 80/40 HR 120 • RA 20 • PA 70/33 • PCWP 12 • CO 2.0 • SVR 1200
- 36. • BP 80/40 HR 120 • RA 5 • RV 18/5 • PA 25/15 • PCWP 10 • CO 2.0 • SVR 1600
- 37. • BP 80/40 HR 120 • RA 12 • PA 25/12 • PCWP 14 • CO 9 • SVR 500
- 38. Case Scenario •55 yo male comes into the ED. •
- 41. Cath showed 100% RCA occlusion. Treated with O2, heparin, MSO4 and his condition improves. 48 hours later, he becomes pale, diaphoretic and oliguric. Vitals: HR 120bpm, RR 24/min and BP 88/55. PE: JVP+ angle of jaw, +RUQ tenderness, lungs clear. +S3, Grade ¼ holosystolic murmur at LLSB. +LE edema
- 42. EKG: unchanged Right heart cath placed which showed: RA 20 mmHg RV 40/18 mmHg PAP 25/15 mmHg PCWP 12 mmHg CO 2L/min RA tracing:
- 43. WHAT DOES THIS PT HAVE? c. Papillary muscle rupture d. Massive PE e. Cardiac Tamponade f. Rupture of the IV septum g. RV infarct
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Several studies show that clinicians are poor at correlating clinic status with hemodynamic assessment. In a general ICU population, clinicians could correlate correlate PCWP and cardiac index only 30-70% of the time. And 60-85% of the time in CCUs. People then argued that more frequent and accurate diagnosis of the conditions that can be treated would improve patient outcome. So in the 1970s, with Swan-Ganz, it became the standard of care in hemodynamically unstable patients. Differentiation between causes of shock>cardiogenic, hypovolemic, septic Differentiation between causes of pulmonary edema>cardiogenic versus noncardiogenic Diagnosis of pericardial tamponade Diagnosis of intracardiac shunt Evaluation/Management of pulmonary hypertension Diagnosis of lymphangitic spread of tumor and fat embolism Management of complicated MI, HF Determine need for vasopressor/inotropic therapy Fluid Status>in GI bleed, renal failure, sepsis Ventilator management>determining the best PEEP
- First pulm catheters were placed in 1940s. pUT in lab, just for dx. 1970-William Ganz and Harold Swan introduced this catheter. Pulmonary artery Catheter that is balloon-tipped and flow directed, placed bedside Revolutionized catheters>moved from diagnosis only to help in management. No clinical trials were done to see if they improved mortality. Benefit was assumed 1987- nonrandomized trials:showed mortality was higher in patients with an acute MI who had a Swan placed 1990s-Ontorio Intensive Care Group attempted a RCT for use of Swans>not done b/c felt unethical to withhold Swan placement. They felt that anything that helped with “MORE ACCURATE” hemodynamic monitoring had to help.
- In 1996, Connors et al did an observational study of PA catheters. They evaluated people who had a RHC put in within 24 hours of admission to the ICU. End point was pt survival. Pts who underwent RHC had an increased 30 day mortality compared to those who did not undergo the procedure. Subgroup analysis did not show any group who was assoc with improved outcome. WHY? Placement led to worse patient outcomes b/c of complications of placement or misinterpretation of data Use of cathether might be a marker of more aggressive care, which is associated with higher mortality Changes in therapy in response to the information might have led to hight mortality (i.e. using pressors) Study might not have adequately adjusted for confounding factors Only looked at SGC placed in first 24 hours and maybe no indication in first 24 hours, and later when all else fails, actually improves mortality.
- 1994 high-risk surgical patients underwent randomization for PA catheters (RCT) Preop placement, for elective or urgent surgery Looked at 6mo and 12 mo mortality No difference b/t PA catheter group from placebo in terms of mortality and length of hospitalization Increased risk of PE in the catheter group and thus, PA catheters may be associated with increased morbidity
- To Swan or Not to Swan? Each patient think hard…lots of comlications which I will get into. Tammy Cannon With that caveat in mind…lets get into the nuts and bolts of swan placement.
- Made of polyvinylchloride and has a pliable shaft that softens at body temperature Polyvinylchloride is thrombogenic so they are usually coded with heparin. Studies have shown that this is more effective in prevent catheter related thrombogenicity Catheter is 110 cm and external diameter is either 5 or 7 French (1 French=0.0335mm) Balloon is fastened 1-2mm from the tip and when inflated it guided the catheter (using fluid dynamic drag) from greater intrathoracic veins through tight heart into pulmonary artery. The balloon when it is fully inflated, is designed to protrude above the catheter tip. And distributes force over large area, minimizing chances for endocardial damage. Thermistor-4cm proximal to the tip, measures temperature>important for determining cardiac output
- Typically catheters have 4 ports: White port with blue wire is the proximal port> terminates at 30cm from tip of catheter and is used to measure simultaneous right atrium and pulmonary artery pressure White port, yellow wire is the PAD distal port White port with red wire is for balloon inflation Thermistor-4cm proximal to the tip, measures temperature Last port has the connection to the thermodilution cardiac output computer> contains the electrical leads for thermistor. 6. Some catheters now available have a 5th lumen allowing passage temporary pacemaker
- Average time from decision to use PA catheter until onset of catheter based treatment is 120 minutes Goal: get the catheter to the pulmonary artery Cordis into right internal jugular vein or left subclavian allows easiest passage Swan should be oriented ex-vivo to approximate the course in the body Catheter goes through an introducer and into the vein. The balloon stays closed until we reach the right atrium. When we reach the right atrium (20cm), balloon should be inflated to reduce possibility of injury to the myocardium. Then the balloon should be moved quickly through the right ventricle (30cm)> and then pulmonary artery (40cm) and PCWP (50cm) FROM SUBCLAVIAN/IJ APPROACH The balloon is inflated with air. But filtered CO2 should be used in any situation in which balloon rupture might cause air to get into arterial system>like if there is an intracardiac shunt or pulmary A-V fistula.
- a=atrial contraction. A wave peak follows the electrical p wave by about 80msec c=sudden motion of the AV ring toward the right atrium. x descent=atrial relaxation v=pressure generated by venous filling of the right atrium. The peak of the v wave occurs at the end of ventricular systole when atrium is maximally filled. This occurs near the end of the t wave y descent=rapid emptying of the RA into RV Normal right atrial presssure is 0-6mmHg. Normal oxygen content 15% Normal O2 saturation 75%
- We just said that a wave is atrial contraction. And we are looking at the right atrial side…so What gives a prominent a wave?
- Two pressures are measured in the RV. The peak of the RV systolic pressure and the RV end diastolic pressure, right after the a wave. The ventricular diastole is made up of early rapid filling phase (60%) and a slow phase (25%) filling and an atrial systolic phase which produces an a wave in the RV tracing.
- PA waveform is characterized by a systolic peak and diastolic trough with a dictrotic notch due to closure of the pulmonic valve. PA systolic pressure occurs within T wave of EKG similar to the systemic arterial pressures.
- The measurement is obtained when the inflated balloon impacts into a slightly smaller branch of the pulmonary artery. In this position, the balloon stop flows and catheter tip senses pressure transmitted backward through the static column of blood from the next pulmonary bed, the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary venous pressure is the best indicator of left atrial pressure except when there is venoocclusive disease The PCWP only indicates the LAP if the pressure in the surrounding capillaries exceeds the mean alveolar pressure. That is ZONE 3. This concept is based on the idea tha the lung can divided into 3 physiologic zones of blood flow which are based upon the relationship b/t alveolar pressure, PAP and pulm capillary pressure. In ZONE 1, the alveolar pressure is greater than the capillary pressure. In Zone 3, the most dependent portion of the lung, vascular pressures are the highest d/t gravity. So again PCWP is only accurately a measure of LAP IF PCP exceeds mean alveolar pressure. So how do you know you are in Zone 3? 60% of catheter insertion are only in the right place. You can look at the CXR and the catheter should be below the left atrium. If there is marked respiratory vairation in the PAWP tracing you are likely not in Zone 3 and if PAD> PCWP then you are likely not in zone 3.
- Inflation of the balloon changes the tracing of the pulmonary artery. Goes from having a dicrotic notch to having more of a,c,v wave pattern like we saw in the right atrium. This is because we are measure left atrial pressure. Pulmonary artery wedge 2-12 PCWP tracing looks like RA tracing except that the v wave is slightly higher than the a wave (opposite of RA) B/c of the time required for LA mechanical events, PAWP waveforms are further delayed when recorded by EKG. The peak of the A wave follows the the peak of the EKG p wave by 240 ms and the peak of the v wave occurs after the EKG t wave. A wave=atrial systole C wave=reflecting closure of the mitral valve V wave=represents both ventricular systole and passive atrial filling in atrial diastole. Pulmonary artery wedge 2-12 Pulmonary vein O2 content 20% Pulmonary vein O2 sat 98% Confirmation of the PCWP position is done be withdrawing blood from the distal lumen and measureing the O2 aturation. If >95% are considered satisfactory.
- Thermodilution: Add an indicator substance (5ml of dextrose or saline) that is cooler than blood. Indicator in injected through the proximal port of the PA catheter and mixes with the blood in the RV. The mixing lowers the temperature of the flowing blood which is carried to the distal thermistor port. The thermistor records the temperature change and electronically displays a temperature/time curve. The area under the curve is inversely proportional the the flow rate in the pulmonary artery=cardiac output in absence of intracardiac shunt sources of error with thermodilution are seen with tricuspid regurgitation and intracardiac shunts. In TR, there will be an attenuated peak and a prolonged washout phase of the temperature-time curve. This is d/t cold injectate refluxing back into the vena cava and so you have resultant decreased pulm artery cooling and delayed appearance of the injectate that has moved retrograde into the vena cava and then is recirculated. Result is an underestimated cardiac output. Intracardiac shunt> both r>l and l>r intracardiac shunts can produce falsely elevated CO measurements by the thermodilution technique. R>L intracardiac shunts produce shunting of the cold injectate into the left heart and thus, decreased PA cooling, lowers the peak of the temperature-time curve and overestimates CO . L>R shunt result in increases right heart volumes, dilutes the injectate and attenuates the height under the temp-time curve and falsely elevated estimate of CO .
- . If the respiratory variation seen in the PAWP tracing exceeds that seen in the pulmonary artery tracing, then the PAWP may be unreliable due to non-zone 3 conditions. By definition, in zone 3, no airway pressure should be transmitted to the vasculature The intravascular pressure is the pressure ostensibly transmitted back from the left atrium. PEEP can alter intravascular pressures, but those PEEP-altered pressures are the "effective" filling pressures for the patient under those clinical circumstances. An estimate of the true transmural filling pressures can be made in the presence of PEEP by subtracting one-half of the PEEP level from the PAWP if lung compliance is normal, or one-quarter of the PEEP level if lung compliance is reduced [ 19 ]. Since 10 cmH2O pressure is approximately 7.7 mmHg, the effects of PEEP on PAWP are usually small, and rarely affect clinical management During normal spontaneous ventilation, alveolar pressure (relative to atmospheric pressure) decreases during inspiration and increases during expiration. These changes are reversed with positive pressure ventilation: alveolar pressure increases during inspiration and decreases during expiration. The changes in pleural pressure are transmitted to the cardiac structures and are reflected by changes in pulmonary artery and PAWP measurements during inspiration and expiration. At end-expiration, pleural and intrathoracic pressures are equal to atmospheric pressures, regardless of the mode of ventilation. Thus, the true transmural pressure and therefore the PAWP should be measured at this point. Most intensive care units use electronic pressure monitors that are designed to measure pressure in time intervals of four seconds and to display three different pressures: systolic (peak); diastolic (trough); and electronic mean pressure. The wedge pressure can be followed serially by selecting the systolic pressure for those breathing spontaneously, and by selecting the diastolic pressure for those on positive pressure ventilation. Use of these settings avoids false depression or elevation of intravascular pressure measurements due to superimposed fluctuations in pressure during respiration. Alternatively, many ICU monitors allow manual selection of the pulmonary artery wedge pressure via a cursor.
- Just to go over the risks in more details….