Trigeminal nerve-ambika - Copy.ppt
- 1. Trigeminal Nerve Seminar presented by: Dr.Ambika Bhandari 1st year PG
- 2. contents Introduction Nerve root The sensory nuclei The gasserian ganglion The ophthalmic nerve The maxillary nerve The mandibular nerve Applied anatomy
- 3. THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE It is the Fifth and Largest Cranial nerve. Also called: Nerve Trigeminus Trifacial nerve This nerve contains both motor and sensory fibers
- 4. Sensory supply to the scalp, teeth ,skin of the face,forehead ,mucous membranes of oral and nasal cavity,floor of the mouth ,teeth ,the anterior two third of tounge and extensive portions of the cranial dura Motor supply to muscles of the first branchial arch Propioceptive nerve fiber from masticatory and facial muscles.
- 6. Nerve root It is attached to the ventral surface of pons by a large sensory root and small motor root. The two roots enter the middle cranial fossa. The motor root lies ventro-medial to the sensory root.
- 8. Sensory root These fibers arise from the posteromedial margin of Semilunar Ganglion or the gasserian ganglion. The ganglion forms central and peripheral branches . The central branches are sensory roots of trigeminal nerve and the periphral branches form the ophthalmic ,maxillary and mandibular nerve
- 9. The sensory root leaves the ganglion, passes back and enter pons . The fibers divide into ascending and decending groups . From here these fibers terminate into different sensory nuclei of trigeminal nerve.
- 10. ASCENDING FIBRES DESCENDING FIBRES Terminate in UPPER sensory nucleus In pons lateral to motor nucleus. Terminate in SPINAL nucleus extending caudally from upper sensory nucleus to 2nd cervical segment. Conveys:: · Light touch · Tactile discrimination · Sense of position · Passive movement Conveys:: Pain Temperature CENTRAL BRANCHES (SENSORY ROOTS OF NERVE)
- 11. Motor Root The fibers of the motor root arise from two nuclei, the superior and the inferior motor nucleus located in upper pons. The motor root runs in front of and medial to the sensory root, and passes beneath the ganglion; it leaves the skull through the foramen ovale, and, immediately below this foramen, joins the mandibular nerve.
- 13. The fibers from the superior nucleus constitute the mesencephalic root: they descend through the mid-brain, and, entering the pons, join with the fibers from the lower nucleus, and the motor root, thus formed, passes forward through the pons to its point of emergence. It is uncertain whether the mesencephalic root is motor or sensory.
- 14. The Sensory nuclei Sensory nuclei are arranged in 3 groups: • Mesencephalic Nucleus • Principal Sensory Nucleus • Spinal Nucleus of 5th nerve
- 16. Mesencepalic nucleus This nucleus serves as a sensory station that recieves proprioceptive impulses from the TMJ ,the periodontal ligament ,and the hard palate Also it recieves affrent impulses from the stretch receptors of the muscles of mastication ie these fibers are concerned with perfect synchronization in controlling the biting force
- 17. Principal sensory nucleus Also called the main sensory or the upper nucleus . This nucleus gives rise to the dorsal trigeminothalmic tract . Sensory fibers from this tract ascend upwards .
- 18. Spinal nucleus this nucleus is also called the bulbospinal nucleus. Spinal nucleus extends from the main sensory nucleus to the second cervical segment This gives rise to the ventral trigeminothalmic tract
- 19. Gasserian Ganglion Also known as semilunar ganglion it is developed from the neural crest cells Contains unipolar neurons. Crescent shaped, with its convexity directed forward and medially Located in Meckel's cavity in the upper part of apex of petrous temporal bone.
- 21. Arterial supply of trigeminal ganglion by the ganglionic branches of 1. Internal carotid artery 2. Middle meningeal artey 3. Accesory meningeal artery
- 22. The ganglion receives, on its medial side, filaments from the sympathetic carotid plexus . It gives off minute branches to the tentorium cerebelli, and to the dura mater in the middle fossa of the cranium.
- 24. Functional component of trigeminal nerve Special visceral effrent fibers They arise from the motor nucleus of nerve and supply the muscles of mastication Because they supply muscles developing in branchial arch, so they are also known as branchiomotor fibres
- 25. General somatic afferent fibers These nerve fibres can be divided into 2 groups 1.Nerve fibres carrying sensation of touch,pain,temperature from the skin of face and mucous membrane of mouth and nose 2.Another group of general somatic afferent neurons carry proprioceptive impulses from the muscles of mastication.
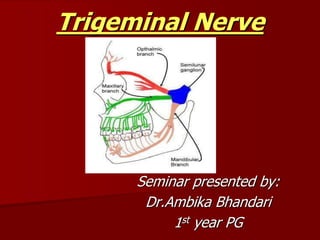
- 27. From convex border of the trigeminal ganglion three large nerves proceed, viz., the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The ophthalmic and maxillary consist exclusively of sensory fibers; the mandibular is joined outside the cranium by the motor root.
- 28. Peripheral Branches Ophthalmic nerve Maxillary nerve Mandibular nerve
- 29. Ophthalmic Nerve This is the first division of the trigeminal nerve . It is the smallest division of the trigeminal nerve. It is a pure sensory nerve. Route: Leaves from the upper part of the Ganglion and passes forward through the lateral wall of cavernous sinus , it enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure, it divides into three branches.
- 30. Fibres are afferent to: In the middle cranial fossa the nervous tentori branches supply the dura. Scalp Skin of forehead Conjunctiva of eyeball Lacrimal gland Skin of lateral angle of the eye Sclera of eyeball Lining of ethmoid cells
- 31. Subdivisions of Ophthalmic Nerve: Lacrimal nerve Frontal nerve Nasociliary nerve
- 33. Lacrimal nerve it is the smallest of the three nerves It enters the orbit through the narrowest part of the superior orbital fissure. In the orbit it runs along the upper border of the lateral Rectus, with the lacrimal artery, and communicates with the zygomatic branch of the maxillary nerve.
- 34. SUPPLIES - Lacrimal Gland, Adjacent conjunctiva, & lateral portion skin of the upper eyelid.
- 35. Frontal Nerve: (Largest of three) In middle of the orbit, nerve divides into: Supra orbital nerve: Larger branch from supraorbital foramen Supplies middle portion of skin of upper eyelid and skin of forehead & scalp Supratrochlear Nerve: Smaller of the two Supplies the skin of the lower part of forehead & medial portion of skin of upper eyelid and conjunctiva.
- 36. Nasocilliary nerve this nerve is more deeply placed it passes through the anterior ethmoidal foramen, front part of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, and runs down, through a slit at the side of the crista galli, into the nasal cavity.
- 37. NASOCILIARY NERVE:: BRANCHES IN ORBIT: · Long root of cilliary ganglion · Long cilliary nerves:iris & cornea · Posterior ethmoid nerve:post. Ethmodal cell. · Anterior ethmoid nerve BRANCHES IN THE NASAL CAVITY Supplies the mucous membrane of the cavity. BRANCHES ON THE FACE:- · Skin of medial part of both eyelids · skin over the side of bridge of the nose.
- 39. MAXILLARY DIVISION 2nd sensory division of the Trigeminal nerve.
- 40. Transmits afferent impulses from: Upper lip Lower eyelid Side of the nose Hard and soft palate Lining of maxillary sinus All maxillary teeth and gingiva Mucous membrane of most the nasal cavity
- 41. Course Intracranial part:: Originates from the middle part of semilunar ganglion Passes forward through the lateral wall of cavernous sinus Exits through foramen rotundum.
- 42. Extracranial part:: Enters pterygopalatine fossa. Enters inferior orbital fissure to enter orbital cavity. Occupies infraorbital groove and enter infra orbital canal. Emerges through infra orbital foramen.
- 44. MAXILLARY NERVE In the Cranium In the Pterygopalatine Fossa In the Infra- orbital Canal On the Face Middle meningeal nerve · Zygomatic. · Sphenopalatine. · Posterior superior alveolar. · Anterior superior alveolar. · Middle superior alveolar. · Inferior palpebral. · External nasal. · Superior labial Lateral nasal Superior labial
- 45. Middle meningeal nerve Travels with middle meningeal artery. it is given off from the maxillary nerve directly after its origin from the semilunar ganglion Sensory innervation to the duramater of anterior half of middle cranial fossa.
- 46. Pterygopalatine branches 2 short nerve twigs that unite at the pterygopalatine ganglion. fibres pass through the ganglion without synapse. Serves as a communication between pterygopalatine ganglion and maxillary nerve.
- 48. 1.Pharyngeal branch To mucosa of nasopharynx 2.Palatine branches Middle and posterior palatine these innervate soft palate and tonsil Anterior Or Greater palatine branch To the mucosa of the palate
- 49. 3. nasal branches Posterior superior lateral nasal Sensory to the mucous membrane of nasal septum and possterior ethmoidal cells Medial or septal branch It innervates the mucous membrane over the vomer as this continues downward and forward,reaches the floor of the nasal cavity,decsnding from there into the incisal canal to the mucous membrane of the premaxilla. This nerve is the nasopalatine nerve
- 51. Zygomatic nerve 4. orbital branches These branches are sensory for the periosteum of the orbit Emerges in the pterygopalatine fossa. Passes anteriorly and laterally through inferior orbital fissure into orbit. Conveys post ganglionic parasympathetic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion to lacrimal gland.
- 53. DIVIDES INTO 2 PARTS:: ZYGOMATICOFACIAL NERVE: It perforates the facial surface of zygomatic bone. sensory to skin over the prominence of the zygomatic bone
- 54. ZYGOMATICOTEMPORAL NERVE: It perforate temporal surface of zygomatic bone through temporal fascia. Supplies sensory fibres to skin over the anterior temporal fossa region.
- 55. Posterior superior alveolar nerve Usually 2-3 in number. Descends from the main trunk.Pass downward over posterior surface of maxilla.One branch remains external to the bone. Other branch enter through posterior alveolar canal on the infratemporal surface of maxilla and passing from behind forward in the substance of bone to the posterior wall of maxillary sinus and innervating the maxillary molars.
- 56. Supplies: Mucous membrane of sinus, alveolus ,periodontal ligament and pulpal tissue of the maxillary molars except the mesio buccal root of maxillary first molar
- 57. Middle superior alveolar nerve originates in the infra orbital canal. Supplies maxillary sinus, premolars, mesiobuccal root of Molar, buccal soft tissue in premolar region. This nerve forms a ganglion situated at the junction of posterior superior alveolar nerve and middle superior alveolar nerve called the ganglion of valentine It is present above the second premolar teeth.
- 58. Anterior superior alveolar nerve Origin 6-10 mm before its exit from incisal foramen. It descends in a canal in the anterior wall of maxillary sinus and divides into branches which supply the incisor and canine teeth the canal is called canalis spinosus a gangilon at the junction of anterior superior alveolar nerve and middle superior alveolar nerve is called the ganglion of bockdalek
- 59. Supplies: Incisors and cuspid, Anterior Part of maxillary sinus, Labial gingiva of incisors and cuspid
- 61. Inferior palpebral nerve • 2 or 3 in number. • Pass upwards & supply sensory fibres to skin of lower eyelid and its conjunctiva.
- 62. Lateral nasal nerve • Pass to skin of the side of the nose. Superior labial nerve • 3 or more in number. • Distributed to the skin & mucous membrane of the upper lip.
- 64. Mandibular division Largest division of trigeminal nerve. Formed by large sensory root & small motor root
- 65. Sensory root Supplies: Duramater External ear Parotid gland TMJ articulation Lower teeth and gingiva Scalp over temporal region Ant. 2/3rd of the tongue. Skin and mucous membrane of chin, cheek & lower lip.
- 66. Motor root supplies Muscles of mastication masseter Temporalis Medial and lateral pterygoid Mylohyoid & Ant. Belly of digastric Tensor tympanii Tensor palatini
- 67. course and distribution Motor root is located in middle cranial fossa Sensory root emerges from semilunar ganglion 2 roots pass alongside in cranium. Emerging from foramen ovale, they unite.
- 69. MANDIBULAR NERVE Branches from undivided nerve Anterior Trunk Posterior Trunk Nervous Spinosus Nerve to Medial Pterygoid Masseteric Deep Temporal Nerve to Lateral Pterygoid Buccal Auriculotemporal Lingual Inferior Alveolar
- 71. Branches from the undivided nerve a.) Nervous spinosus arises outside the skull and then passes in the middle cranial fossa through foramen spinosum to supply duramater and mastoid cells. b.) Nerve to medial pterygoid it sinks into the deep surface of the muscle . A branch supplies tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani muscles
- 72. ANTERIOR DIVISION This is the smaller division It recieves both motor and sensory supply Of the muscles of mastication,mucous membrane of cheek,buccal gingiva and lower molars. .A.) Lateral Pterygoid Nerve: Enters the medial side of lateral pterygoid muscle for its motor supply.
- 73. B.) Masseter Nerve: Passes above the lateral pterygoid to traverse the mandibular notch and enter the deep side of masseter muscle. Its gives of branch to TMJ C.) temporal branches: ANT. DEEP TEMPORAL NERVE:: passes above the upper head of lat. pterygoid, enters the anterior deep part of the temporalis muscle.
- 74. POST. DEEP TEMPORAL NERVE:: Passes Upwards To Enter The Deep Posterior Part Of The Temporal Muscle.
- 75. D.) BUCCAL NERVE: Passes downwards, anteriorly and laterally between the two heads of lateral pterygoid muscle. AT THE LEVEL OF OCCLUSAL PLANE, Sensory innervation to cheek ,Sensory fibres passes to retromolar triangle,Sensory fibres to buccal gingivae
- 77. Posterior division 1. Auriculotemporal nerve: Course:Passes posteriorly, Deep to external pterygoid muscle.Between sphenomand. Ligament & neck of condyle.Traverses upper deep part of parotid
- 79. Supplies: Temporomandibular joint Parotid fascia Skin of the temple Tympanic membrane
- 80. 2.LINGUAL NERVE It lies Medial to lateral Pterygoid In pterygomandibular space. Lies medial and anterior to inferior alveolar nerve.enters at the side of the base of the tongue,medial to third molar. Proceeds anteriorly winding around submandibular duct. Then reaches the deep surface of sublingual gland.
- 82. INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE: Largest branch of the posterior division.Passes downwards, (medial side of lateral pterygoid and ramus) Enters mandibular foramen,Distributed throughout mandible Reaches mental foramen,2 terminal branches Mental nerve and incisive nerve
- 83. Supply inscive nerve:sensory to the teeth incisors and canine mental nerve: sensory to skin of lower lip ,chin
- 84. MYLOHYOID NERVE Both sensory & motor fibres. It is given before the inferior alveolar nerve enters the mandibular foramen Continues downward & forward in mylohyoid groove. Motor fibres Supply:Mylohyoid muscle and anterior belly of digasric Sensory fibres supply:chin and Mandibular incisors.
- 86. Four major autonomic ganglion associated with trigeminal nerve
- 87. Ganglions roots The cilliary ganglion The pterygopal atine ganglion The Otic ganglion The submandi bular ganglion Preganglionic / parasympathetic Occulomotor nerve Greater petrosal nerve Glosopharyn geal nerve via the lesser petrosal nerve via chorda tympani and lingual nerve postganglionic/ parasympathetic Short cilliary nerves Via zygomatic n to lacrimal nerve Auriculotemp oral nerve Secretomot or fibers to salivary glands Postganglionic /Sympathetic Internal carotid plexus Deep petrosal nerve/ carotid plexus Plexus around middle meningeal artery --------------
- 88. Thank you
- 90. Contents Orofacial pain Nerve injuries Trigeminal neuralgia Nerve involvement in mid face fractures Nerve involvement in mandibular fractures Nerve involvement in carcinoma Superior orbital fissure syndrome Frey’s syndrome Branches of trigeminal nerve encountered during various surgical procedures
- 91. OROFACIAL REGION PAIN Pain: - An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.
- 92. Classification of orofacial pain:- Typical orofacial pain of extracranial origin:- Dental cause: - pulpitis, dentine hypersensitivity, periapical lesion, impacted third molar. Periodontal: - primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
- 93. Mucosal:-ulcerations, herpetic etc. Salivary gland: - sialolithiasis. TMJ: - dysfunctions and others. Primary neuralgias Vascular origin Referred pain Psychogenic origin
- 94. pain pathway MEDIATED FROM THE SENSORY ROOT INTO THE PONS DESCENDIN G FIBERS PAIN PONS BY SPINAL TRACT FIBERS OF TRIGEMINAL NERVE MEDULLA SECOND CERVICAL SEGMENT ASCENDING FIBERS GENERAL TACTILE SENSATION STIMULUS IN THE REGION OF TRIGEMINAL NERVE CONDUCTED AS IMPULSE ALONG AFFERENT FIBERS GASSERIAN GANGLION
- 96. Nerve Injuries NEUROPRAXIA AXONOTMESIS NEUROTMESIS SUNDERLAND CLASSIFICATION 1degree 2,3,4, degree 5 degree NERVE SHEATH Intact Intact Intrerrupted AXONS Intact interrupted interrupted WALLERIAN DEGENERATION None Yes, partial Yes, complete CONDUCTION FALIURE Transitory Prolonged Permanent SPONTANEOUS RECOVERY Complete Partial Poor to none TIME OF RECOVERY Within 4 weeks Months Begin by 3 months, if any
- 98. ETIOLOGY OF NERVE INJURY Wisdom tooth removal Facial trauma Endosseous Dental implant placement Orthognathic surgery Salivary gland surgery Treatment of benign and malignant lesion of head and neck Endodontic and periradicular surgeries
- 99. CLINICAL TESTING 1. Subjective Assessment : Visual Analog Scale 2. Objective Assessment : Level A : Static 2 point discrimination Brush-Stroke directional discrimination Level B : Contact detection Level C : Pinprick nociception Thermal discrimination
- 100. PARESTHESIA: Paresthesia is defined as persistent anaesthesia or altered sensation well beyond the expected duration of anaesthesia. Patient complains of:- Numbness Sensation of swelling, tingling Itching Oral dysfunction
- 101. Causes: Injection of LA contaminated with alcohol Trauma to nerve sheath during extraction Haemmorhage around the nerve mandibular implants Resolves in approximately 8 weeks without treatment .
- 102. TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA Also known as: tic douloureux DEFINITION: - It is sudden, usually unilateral, severe, brief, stabbing, recurring pain in one or more branch of fifth cranial nerve.
- 103. Etiology basilar artery superior cerebellar artery compress sensory root demyelination of nerve fibres trigeminal neuralgia
- 104. CLINICAL FEATURES: Occurs frequently in patients over 50 yrs. Pain is unilateral (rarely bilateral)and occurs in paraoxysms for 1-2 minutes No pain between episodes During pain patient grimaces with pain, clutches his hand over to the affected side of the face, stops all activity. Common trigger zones include:Lips,Cheek,Ala of nose,Lateral brow,,Intraoral sites including teeth, gingivae, or tongue.
- 106. TREATMENT MODALITIES Medical: • Carbamazepine 100mg TDS • Phenytoin 100mg TDS • Sodium Valproate 600mg/day • Clonazepam 1.5mg/day
- 107. Surgical: • Peripheral injection of a long acting anesthetic agent • Peripheral injection of alcohol • Peripheral neurectomy • Cryosurgery • Selective radiofrequency thermocoagulation
- 108. Microvascular nerve root decompression Posterior fossa approach separation of superior cerebellar artery from the sensory root of trigeminal nerve placement of alloplastic material between the artery and sensory root
- 109. Newer Approaches: – Acupuncture; – Physiologic inhibition of pain by TENS (transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation) Psychological approach counselling
- 110. Superior orbital fissure syndrome Ophthalmic nerve and its branches may rarely undergo transient degenerative response to ischemia caused by hematoma and edema pressures exerted at the superior orbital fissure This condition is known as superior orbital fissure syndrome in which ophthalmoplegia, Pupillary constriction, proptosis,peri orbital edema, and ptosis of eyelid can be seen
- 112. Frey’s syndrome During healing of a penetrating injury in the region of parotid gland the secretomotor fibers of the Auriculotemporal nerve grow out and join the distal end of the great auriclar nerve This leads to formation of beads of sweat on the skin covering the parotid gland called gustatory sweating
- 113. Treatment options 1. Topical agents- antiperspirants and anticholinergics 2. Radiation therapy-50 gy 3. Surgical procedures- Auriculotemporal nerve section Tympanic neurectomy Skin excision
- 114. Myofacial pain dysfunction syndrome (MPDS) – History of pain: the patient complains of unilateral or bilateral insidious, chronic, dull, and aching type of pain. – Pain is continuous in MPDS – Palpation: In MPDS the patient complains of muscle tenderness – Trigger points when palpated patients give a positive jump sign
- 115. Treatment Medical -Nsaids like aspirin 0.3- 0.6 gm/4 hr piroxicam 10 -20 mg/3-4 /day ibuprofen 200-600 mg tds diazepam 5-10 mg/2-3 /day amitriptyline 10-25mg tds or at bed time Physiotherapeutic modalities Heat application TENS Ultrasound occlusal splints Cryotherapy counterirritants
- 116. Nerve involvement in midface fractures Zygomatico complex fractures The injury may produce ecchymosis about the orbit and anaesthesia in the distribution of the infraorbital nerve
- 117. Le fort 2 & 3 fractures Ophthalmic division may be injured resulting in anesthesia or parasthesia in the region of innervation
- 118. Nerve involvement in mandibular fractures Sensory nerve injury, particularly of the inferior alveolar and mental nerves,commonly occurs with mandibular fractures Causes of inferior alveolar or mental nerve injury are displaced fractures, delay in treatment, and improper use of drill or screws. Closed reduction is associated with lower incidence of nerve dysfunction
- 120. Nerve involvement in carcinomas The clinical history begins with the present illness and includes the duration and location of symptoms such as non-healing ulcer, mass in the oral cavity Or neck, pain, bleeding, and any symptoms of cranial nerve deficits. A complete examination is performed, emphasizing sensation over the chin for mandibular nerve deficit.
- 121. Paresthesia of the chin suggests extensive mandible invasion and inferior alveolar nerve involvement by oral carcinoma The lip is a common site for oral cancer. Large lesions may invade the mandible or the mental nerve
- 122. Branches of trigeminal nerve encountered during surgical procedures
- 123. When opthalmic nerve is not involved in trigeminal neuralgia, surgical section of the inferolateral part of sensory root interrupts the fibres of maxillary and mandibular divisions but preserve the opthalmic division which occupy the superomedial part of root Thereby the corneal sensations are retained and formation of corneal ulcer is avoided
- 124. Damage to the inferior alveolar nerve may occur as it runs from mandibular to mental foramen during visor osteotomy ,cyst removal, genioplasty, mandibular resection, causing anaesthesia or paraesthesia in the area. Damage to the infra orbital nerve can occur at the time of orbital osteotomy and if retraction during caldwell luc procedure goes too high.
- 125. Preauricular incision sometimes may damage auriculotemporal nerve Temporal extension of the skin incision should be located posteriorly so that the main distribution of nerve is dissected and retracted forward with in the flap patients rarely complain about sensory disturbances that result from damage of this nerve
- 126. The lingual nerve, the submaxillary ganglion and the hypoglossal nerve are situated close to the gland, disruption of these nerves is to be avoided during excision of the submandibular gland .
- 127. The lingual nerve usually crosses the duct at approximately 2nd molar level and is a helpful point of orientation during floor of the mouth surgery such as vestibuloplasty and sialothotomy and tumor excision
- 128. While removing lower impacted third molar, the distal releasing incision should be given from the distal most point of 3rd molar across external oblique ridge into buccal mucosa The incision should not be taken on the lingual aspect of the ridge, as the lingual nerve can be found at or above the crest of alveolar ridge, in approximately 17% of the population
- 129. the normal position of the lingual nerve is 2mm inferior to the crest and 0.5mm lingual to the lingual cortex of the mandible in the 3rd molar region
- 130. NERVE INJURY DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT: According to Peterson: • a minimum distance of 2 mm from the superior aspect of the bony inferior alveolar canal • 5mm from the mental foramen There will be a sharp pain and sudden increase in bleeding if perforated Nerve repositioning can be done to avoid this condition
- 132. refrences Greys anatomy Monheims local anaesthesia and pain control in dental practice B.D.chaurasia textbook of anatomy Contemparary oral surgery by peterson Atlas of human anatomy Essentials of human anatomy A K dutta Malamad handbook of local anesthesia Fractures of mid face and mandible by killey and kay
- 133. Thank you