Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Ähnlich wie Dna!
Ähnlich wie Dna! (20)
Streamlining DNA Preparation: Techniques and Applications

Streamlining DNA Preparation: Techniques and Applications
Mehr von amandayoung313
Mehr von amandayoung313 (20)
Dna!
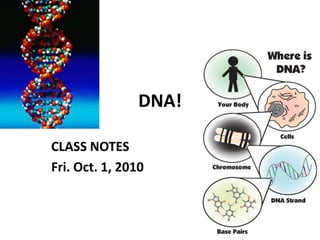
- 1. DNA! CLASS NOTES Fri. Oct. 1, 2010
- 2. What is DNA? Chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell have a code This code is a chemical called DNA (stands for: deoxyribonucleic acid) DNA is passed on and copied to new cells. It controls all activities in the cell
- 3. What does it look like? DNA is in the shape of a double helix Like a twisted ladder The ‘steps’ of the ladder are made up of molecules called NITROGENOUS BASES There are 4 types of bases: Adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine A, G, C and T A always pairs with T G always pairs with C
- 4. Base pairs These bases are important for the replication of chromosomes before mitosis The DNA double helix ‘unwinds’ and each side makes a new copy
- 5. Practice DNA sequencing For example, if you had a piece of DNA that is 10 bases long: A G C T T A G G C What is the sequence of the new DNA strand? REMEMBER: A always pairs with T G always pairs with C Answer:
- 6. MUTATIONS A mutation is ANY permanent changein the genetic information of a cell For example: Extra chromosome/missing a piece of a chromosome Incorrect matching of base pairs A + C instead of A + T An extra/missing base pair Mutations occur frequently but not all of them have harmful effects! Sickle cell anemia