TOPIC 18 : ACIDS AND BASES
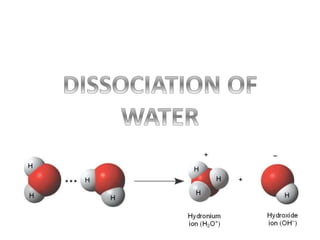
- 2. H2O + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH- Acid Base Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] Where, Kw: water dissociation constant for pure water at 25 ˚C
- 3. • [H3O+] = [OH-] = 1.0 × 10−7 mol dm-3 • Thus, Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] = (1.0 × 10−7 ) (1.0 × 10−7 ) mol2 dm-6 = 1.0 × 10−14 mol2 dm-6 • log [H3O+] + log[OH-] = log (1.0 × 10−14 ) log [H3O+] + log[OH-] = -14.0 -log [H3O+] + log[OH-]= 14.0 • Thus, pH + pOH = 14.0 or pH + pOH = pKw (-log = p)
- 4. THE pH of AQUEOUS SOLUTION • Calculate the pH of an aqueous solution of Ba(OH)2 0.25 mol dm-3
- 5. • Ba(OH)2 (aq) Ba2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) • pOH = -log [OH-] = -log (0.50) = 0.3 Initial molarity (mol dm-3) 0.25 0 0 Final molarity (mol dm-3) 0 0.25 0.50 pH = 14.0 – 0.3 = 13.7
- 6. What is the molarity of OH- in an aqueous solution of NaOH if its pH is 13.5? • pOH = 14.0 – pH = 14.0 – 13.5 = 0.5 • pOH = -log [OH-] 0.5 = -log [OH-] log [OH-] = -0.5 [OH-] = 0.3 mol dm-3 SOLUTION :
- 7. • Calculate the pH value of 1.0 × 10−8 mol dm-3 of HNO3 acid. Explain your answer. EXERCISE : (STRONG ACID)
- 8. • HNO3 H+ + NO2 - 1.0 × 10−8 1.0 × 10−8 1.0 × 10−8 • pH = -log [H+] = -log (1.0 × 10−8 ) = 8 • For acid, pH <7, [H3O+]> 1.0 × 10−7 consider [H3O+] from dissociation of water. • ∴ [H3O+] = [H3O+]w + [H3O+]acid = 1.0 × 10−7 + 1.0 × 10−8
- 9. • Anions derived from strong acids (such as Cl- from HCl) and cations from strong bases (such as Na+ from NaOH) do not react with water to affect the pH.
- 10. • Weak acid : CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) Acid Base
- 11. * CH3COO- (aq) + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH (aq) + OH-
- 12. • Ka . Kb = 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 [𝑂𝐻−] [𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂−]
- 13. To obtain the value of Kb for the anion derived from a weak acid • • , • For the hydrolysis of acetate ion (*), • Kb = 1.0 × 10−14 𝐾𝑤 1.8 ×10−5 𝐾𝑄 = 5.6 × 10−10
- 15. • The degree of dissociation of weak acids and bases, ∝ less than 1 (or less 100%). • The molarity of H3O+ ions is less than the molarity of the acid (HA). •
- 16. The molarity of H3O+ for weak acids (HA) can be calculated using equilibrium law. • HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq) Initial molarity (mol dm-3 ) : C 0 0 Reacted concentration : -X +X +X Equilibrium molarity (mol dm-3) ( C – X ) X X For a weak acid, X is small.
- 17. Acid dissociation constant, Ka • Each weak acid has an acid dissociation constant (Ka). • The relative strength of weak acids are deduced from the Ka values. • Strong acids have higher Ka (lower pKa) values than weaker acids. Example ; Methanoic acid (HCOOH); Ka = 1.6 × 10−4 mol 𝑑𝑚−3 pKa = 3.8 Is a stronger acid than ethanoic acid (C𝐻3COOH); Ka = 1.7 × 10−5 mol𝑑𝑚−3 pKa = 4.8
- 18. Example; Calculate (a) pKa, (b) pH, and (c) degree of dissociation , of 0.01 mol dm-3 nitrous acid, HNO2 [Ka = 5.1 × 10-4 mol dm-3]
- 19. Answers ; (a) pKa = - log Ka = - log (5.1 × 10-4) = 3.3 (b) HNO2 (aq) + H2O ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + NO2 - (aq) Initial : 0.01 mol dm-3 Reacted : - X X X At equilibrium : (0.01 – X) mol dm-3 X X
- 20. Ka = 𝐻3 𝑂 + [𝑁𝑂2 − ] [𝐻𝑁𝑂2 ] 5.1 × 10-4 M = 𝑋2 0.01 −𝑋 𝑀 , X is small ∴ (0.01 – X) ≈ 0.01 = 𝑋2 0.01 𝑀 X2 = 5.1 × 10−6 M2 X = 2.26 × 10−3 M ∴ [H3O+] = 2.26 × 10−3 M pH = -log [H+] = -log (2.26 × 10−3 ) = 2.6 X = 𝑲𝒂 . 𝑪 = 𝟓. 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟒(𝟎. 𝟎𝟏) = 𝟓. 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟔 = 2.26 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 M Or :
- 21. (c) degree of dissociation, ∝ ∝ = 𝑋 𝐶 × 100 𝐻3 𝑂+ 𝐻𝑁𝑂2 = 2.26 ×10−3 𝑀 0.01 𝑀 × 100 = 23 %
- 22. • The degree of dissociation of weak bases ∝ < 1 < 100% . • The molarity of OH- ion is less than the molarity of undissociated base. • The molarity of OH- from weak bases (B) can be calculated using equilibrium law.
- 23. • B (aq) + H2O ⇋ BH+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Initial molarity , moldm-3 C O O Reacted -X X X Equilibrium molarity , moldm-3 C – X X X
- 24. • Weak bases has a base dissociation constant, Kb. • The relative strength of weak bases can be deduced by comparing the Kb values. • Strong bases have higher Kb (lower pKb) values than weaker bases.
- 25. Example ; Ammonia, (NH3 ; Kb = 1.7 × 10−5 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑑𝑚−3 pKb = 4.8 ) Is a weaker base than methanamine ( CH3NH2; Kb = 4.2 × 10−4 moldm-3 pKb = 3.4)
- 26. Example ; Calculate (a) pKb, (b) pH and (c) degree of dissociation of 0.1 moldm-3 NH2OH. [Kb = 9.1 × 10−9 mold𝑚−3 ]
- 27. (a) pKb = -log Kb = -log ( 9.1 × 10−9 ) = 8.0 (b) NH2OH + H2O ⇋ NH3OH+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Initial : 0.1 0 0 Reacted : -X +X +X At equilibrium : (0.1 – X) +X +X
- 28. Kb = 𝑁𝐻3 𝑂𝐻+ 𝑂𝐻− 𝐵 9.1 × 10−9 M = 𝑋 2 0.1 −𝑋 𝑀 , X is small, (0.1 – X) ≈ 0.1 = 𝑋2 0.1 𝑀 𝑋2 = 9.1 × 10−10 M2 X = 9.1 × 10−10 M2 X = 3.02 × 10−5 M ∴ [OH-] = 3.02 × 10−5 M
- 29. POH = -log [OH-] = -log (3.02 × 10−5 ) = 4.5 pH = 14.0 – 4.5 = 9.5
- 30. (c) degree of dissociation, ∝ ∝ = 𝑋 𝐶 × 100% = [𝑂𝐻 − ] [𝑁𝐻2 𝑂𝐻] × 100% = 3.02 ×10−5 𝑀 0.1 𝑀 × 100% = 0.03 % NH2OH is a very weak base. ! NOTE : Both in (a) and (b)- neglected the contribution of the autoionization of water to [H+]and[OH-] because 1.0 × 10−7M is so small compared with 1.0 × 10−3 M and 0.040M.
- 31. Worked example :
- 32. Question 1 a) Calculate the pH of a 1.8× 10−2 M Ba(OH)2 solution. b) Calculate the pH of HNO3 0.001 moldm-3.
- 33. Answer a) Ba(OH)2 is a strong base. It ionise completely to form 1.8 x 10-2 moldm-3 OH- (aq). pOH = -log[OH-] = -log(1.8x10-2) = 1.74 pH + pOH = 14 pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 1.74 = 12.3
- 34. (b) HNO3 is a strong acid. It ionise completely to form 0.001 moldm-3 H+ (aq). pH = -log[H+] = -log(0.001) = 3
- 35. Question 2 The pH of rainwater collected in a certain region of north Malaysia on a particular day was 4.82. calculate the H+ ion concentration of the rainwater.
- 36. Answer pH = 4.82 pH = -log[H+] log[H+] = -pH log10[H+] = -pH [H+] = 10-pH [H+] = 10-4.82 = 0.000015 = 1.5 x 10-5 mol dm-3 logab = c b= ac
- 37. Question 3 The pH of a certain fruit juice is 3.33. calculate the H+ ion concentration.
- 38. Answer pH = 3.33 [H+] = ? pH = -log[H+] 3.33 = -log[H+] log[H+] = -3.33 log10[H+] = -3.33 [H+] = 10-3.33 = 0.000468 = 4.7 x 10-4 M
- 39. Question 4 In a NaOH solution, [OH-] is 2.9× 10−4 M. calculate the pH of the solution.
- 40. Answer pOH = -log[OH-] = -log(2.9 x 10-4) = 3.5 pOH + pH = 14 pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 3.5 = 10.5
- 41. Question 5 The OH- ion concentration of a certain ammonia solution is 0.88 M. What is the pH of the solution?
- 42. Answer pOH = -log [OH-] = -log(0.88) = 0.055517 = 0.06 pH + pOH = 14 pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 0.06 = 13.94
- 44. A. Strong acid and strong bases Example ; Calculate the pH of a) 1.0 × 10−3 M of HCl b) 0.020 M Ba(OH)2 solution
- 45. Answer a) HCl is a strong acid, completely ionized in solution : HCl(aq) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) HCl(aq) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) Initial (M) : 1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 M 0.0 0.0 Change (M) : -1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 M +1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 +1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 Final (M) : 0.0 1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 1.0 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑
- 46. ∴ [ H+] = 1.0 × 10−3 M pH = -log (1.0 × 10−3 ) = 3.00
- 47. (b) Ba(OH)2 is a strong base. Each Ba(OH)2 unit produces two OH- ions: Ba(OH)2 (aq) Ba2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) ∴ [OH-] = 0.040 M pOH = -log (0.040) = 1.40 pH = 14.00 – 1.40 = 12.60 Initial (M) : 0.020 0.00 0.00 Change (M) : - 0.020 + 0.020 + 2(0.020) Final (M) : 0.00 0.020 0.040
- 48. Exercise!!!
- 49. 1. What are the concentration of all species present in 1.00 M acetic acid at 25℃? For HC2H3O2, Ka is 1.8 × 10−5 . X = 4.2 × 10−3
- 50. 2. What are the concentration of all species present in a 0.10 M solution of HNO2 at 25℃. For HNO2 Ka is 4.5 × 10−4 . X = 6.5 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑
- 51. 3. Give the definition of pH. pH is a measure of hydrogenion concentration; a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of asolution
- 52. 4. a) What are [H+] and [OH-] in a 0.020 M solution of HCl. b) What are [H+] and [OH-] in a 0.0500 M solution of NaOH.
- 53. 5. a) What is the pH of a solution that is 0.050 M in H+? b) What is the pH of a solution for which [OH-] = 0.030 M ?
- 54. 6. What is [H+] of a solution with a pH of 10.60 ? 7. The pH of a 0.10 M solution of a weak acid HX is 3.30. what is the ionization constant of HX? (Ka = 2.5 × 10−6 )
- 55. 8. a) Propanoic acid, HC3H5O2 a weak monoprotic is 0.72% ionized in 0.25 M solution. What is the ionization constant for this acid? b) In 0.25 M solution of benzylamine, C7H7NH2, the concentration of OH- (aq) is 2.4 × 10−3 M. C7H7NH2 + H2O C7H7NH3 + + OH- what is the value of Kb for the aqueous ionization of benzylamine?
- 56. • Answer : a) Ka = 1.3 × 10−5 b) Kb = 2.3 × 10−5
