I. Population change
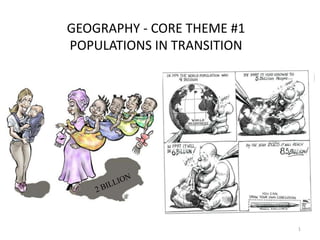
- 1. GEOGRAPHY - CORE THEME #1 POPULATIONS IN TRANSITION 1
- 2. Population growth since the Stone Age Population growth since 1750 Watch an animated dot map showing the evolution of the human population for the last 2000 years: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4BbkQiQyaYc 2
- 3. The Malthusian Projection Thomas Malthus, An Essay on the Principle of Population (England, 1798) [There is a] constant effort towards an increase in population [which tends to] subject the lower classes of society to distress and to prevent any great permanent amelioration of their condition. The way in which these effects are produced seems to be this: we will suppose the means of subsistence in any country just equal to the easy support of its inhabitants. The constant effort towards population (…) increases the number of people before the means of subsistence are increased. The food therefore, which before supplied seven millions, must now be divided among seven millions and half or eight millions. The poor consequently must live much worse, and many of them be reduced to severe distress (…). The power of population is so superior to the power of the earth to produce subsistence for man, that premature death must in some shape or other visit the human race. The vices of mankind are active and able ministers of depopulation. They are the precursors in the great army of destruction, and often finish the dreadful work themselves. But should they fail in this war of extermination, sickly seasons, epidemics, pestilence, and plague advance in terrific array, and sweep off their thousands and tens of thousands. Should success be still incomplete, gigantic inevitable famine stalks in the rear, and with one mighty blow levels the population with the food of the world. Paul Ehrlich, The Population Bomb, 1968 Population control – or race to oblivion? Overpopulation is now the dominant problem in all our personal, national and international planning. No one can do rational planning, nor can public policy be resolved in any area unless one first takes into account the population bomb (…). The battle to feed all of humanity is over. In the 1970s and 1980s hundreds to millions of people will starve to death in spite of any crash programs embarked upon now (…). Population control is the conscious regulation of the numbers of human beings to meet the needs not just of individual families, but of society as a whole. 3
- 4. MAIN DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATORS Type of indicator Indicator Definition Limitations Number of live births per 1,000 people per Affected by age-sex structure Crude Birth Rate (CBR) year Fertility of an imaginary woman who passes Not based on the fertility of any through her reproductive life real group of women (15-49) subject to all the age-specific fertility rates for ages 15–49 that were recorded for a Total Fertility Rate (TFR) BIRTH given population in a given year To see how it is calculated, go to: www.ined.fr/en/everything_about_population/ animations/fecondity/ TFR needed to achieve demographic Doesn’t take into account Replacement Fertility Rate equilibrium (stable population): 2.1 to 2.3 (up migratory gains/losses to 3.0 for high CMR) Number of deaths per 1,000 people per year Affected by age structure Crude Death Rate (CDR) Number of infants who died before the age of Can be affected when counting Infant mortality Rate (IMR) 1 per 1,000 live births mortality linked to infanticides or sometimes miscarriages MORTALITY Number of children who died before the age of Child mortality Rate (CMR) 5 per 1,000 live births Average number of years of life remaining at a Life Expectancy at Birth (LEB) given age. depends highly on IMR or CMR, Life expectancy To see how it is calculated, go to: so demographers sometimes www.ined.fr/en/everything_about_population/ prefer Life Expectancy at Five animations/life_expectancy/ (LEF) Natural gain per 1,000 people per year Doesn’t take into account NATURAL GROWTH Rate of Natural Increase (RNI = CBR – CDR) migratory gains/losses 4
- 5. Birth and Mortality and Sweden and Mexico (1735-2000) CBR Sweden CBR Mexico CDR Sweden CDR Mexico CBR: Crude Birth Rate (= live birth / 1000 people / year) CDR: Crude Death Rate (= death / 1000 people / year) 5
- 6. Birth and Mortality In the Middle East (1950-2004) 6
- 7. North America Europe Russia China East Asia Mexico India Brazil South Central-South Africa Asia Latin America Caribbean Sub-Saharan North Africa Africa Middle East Oceania 7
- 8. DEMOGRAPHIC SITUATIONS: PATTERNS AT A GLOBAL SCALE 20% Pop. 80% Wealth 80% Pop. 20% Wealth MEDCs (“North”) LEDCs (“South”) Developed Countries Main Oil Exporters (OPEC) Post-Communist Transition Emerging Powers Intermediary Countries Least Developed Countries (LDCs) North/South Limit © 2011 Antoine Delaitre
- 9. DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITIONS (1950-2050) WORLD SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA 2010 2010 2010 2010 EAST ASIA EUROPE 9
- 10. AFRICA The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) ASIA EUROPE 10
- 11. 4 STAGES OF THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL DTM stage Pre-Transition Early Transition Middle Transition Post-Transition High and stable CDR/CBR Moderate increase of Decreasing CDR (20- Very low CDR (<10) (40-50) CDR 10 CDR / CBR 30) Decreasing CBR (20- (“accidents”: famine, High CBR (40-50) 30) Low CBR 10 epidemics) Very high and High but declining Low RNI Low or negative RNI RNI increasing RNI RNI < 10 -5 to 10 >20 10-20 Rapid but declining Slow growth or Growth Stable or slow growth Very rapid growth growth decline? Latin America, Middle Europe, North East, South Asia Examples No examples today Sub Saharan Africa America, East Asia (India) (China) World average 11
- 12. First, watch this animation about fertility: www.ined.fr/en/everything_about_population/animations/birth/ IMPACTING FACTORS MORTALITY FERTILITY Education (linked to healthcare/revenue) Gender equality and status of women (measured by Age structure: lower CDR in younger populations (see CDR GDI – Gender Development Index) Sub-Saharan African 1950-2050) vs higher CDR in older Female education (linked to revenue/healthcare/birth populations (see CDR in Europe 1950-2050) control/professional ambition) Age of marriage: couples (particularly women) tend to start procreating only once they are married Residence can contribute to higher CBR: SOCIOCULTURAL o Rural areas: rigid social pressures on women, FACTORS less state control (China), fewer educational opportunities for women o Slums: young/poor population from rural background Religion: most religions are opposed to birth control or contraception, but limited impact on actual behavior (ex: Algeria v Yemen, Brazil vs Poland) Revenue (affects nutrition, education, healthcare). Ex: Revenue: people with no retirement plans or social Blacks vs Whites in South Africa security in some countries see large families as able a Nutrition (2500 cal/day recommended) (linked to means to increase the family’s workforce (farmers), revenue) and a protection for their old age ECONOMIC FACTORS Industrialization and technology (linked to better farming Standard of living: raising a child is costly in countries outputs) with a high standard of living Residence: slums (pollution, poverty: Rio de Janeiro), poor Professional ambition of women can be incompatible rural areas (low farm productivity: Nordeste Brazil) with repeated pregnancies Hazardous occupations: soldiers, miners, farmers, etc ENVIRONMENTAL Pollution (respiratory diseases), heat (infants and seniors) Pollution may affect fertility (uncertain) FACTORS Healthcare, primarily for infants (see IMR) or older people Use of birth control, contraception, abortion (linked (see LEB) (linked to revenue/education) to education/healthcare) Infectious diseases (LEDC: malaria, diarrhea, cholera, AIDS, Longer breastfeeding -> lower TFR HEALTH FACTORS etc) and degenerative conditions (MEDC: cancer, stroke, Child’s survival rate (linked to healthcare/revenue): heart disease, obesity) low survival rate may encourage women to have Access to clean water more children to compensate for their losses. Wars, political instability, man-made famines (Sudan) Non coercitive pro-natalist policies: Western Europe POLITICAL FACTORS (limited impact) Strict anti-natalist policies: China, India 12
- 13. 13
- 14. FERTILITY AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Source: www.gapminder.org Sub-Saharan Africa South Asia / Middle East Latin America Europe / North America East Asia 14
- 15. Regional level TFR CMR LEB Europe 1.50 9 75.1 (East/West) North America 2.26 7 79.3 East Asia 1.72 28 74 Latin America 2.04 28 73.4 North Africa / 2.94 45 70 Middle East South Asia 2.60 50 66 Sub-Saharan Africa 5.08 148 51.5 World 2.56 71 67.6 National/State TFR IMR LEB level Washington 1.80 5.1 79.4 Mississippi 2.26 10.7 73.9 USA 2.09 5.9 79.2 Uttar Pradesh 3.80 67 58.4 Kerala 1.70 12 73.5 India 2.76 54.6 63.5 15
- 16. TOTAL FERTILITY RATE (TFR) TFR <2 2-3 3-5 5-6 >6 Niger: 7.19 Taiwan: 1.14 2010 averages: World = 2.49 / MEDC = 1.65 / LEDC = 2.62 16
- 17. INFANT MORTALITY RATE (IMR) Japan: 3.3 Angola: 193 2010 averages: World = 47 / MEDC = 6 / LEDC = 52 17
- 18. LIFE EXPECTANCY AT BIRTH Japan: 82.1 Angola: 38.2 To estimate how many more years an average person like YOU is expected to live (note: it’s only an average!),18 go to http://calculator.livingto100.com/calculator
- 19. EXAMPLES OF POPULATION PYRAMIDS 2008 19
- 20. AGE-SEX IMBALANCES Age-sex ratios Definition Impact The sex ratio can sometimes be very imbalanced, for sociocultural or economic reasons, with problematic consequences: High sex ratio at birth (cultural preference for boys, abortions: % of men for 100 women 120% in China): shortage of brides, lower TFR Sex ratio (human biological sex ratio: 105% at High sex ratio adults (immigration of young men): Saudi Arabia birth) 129% for age 15-64 Low sex ratio of adults (emigration of young men, alcohol, cancer): shortage of husbands: loneliness of widows, depression. Russia: 92% at age 15-64, 44% for 65+ An ageing ratio too low or too high reveals future strains on public finances (education, retirement, health care) Low ageing ratio (France, Japan): the population is too old -> # or % of people under 20 challenge for health care and retirement Ageing ratio compared to people over 65 Moderate ageing ratio (USA, Thailand, China): the population is balanced High ageing ratio (Kenya, Niger): the population is too young -> challenge for education High dependency ratio = burden on the working class to educate the young and/or support the elderly. Ex: Kenya, Niger= very high number of children % of dependents (children+retirees) Low dependency ratio = there is a sufficiently large work force Dependency compared to productive population to support young/elderly. ratio (15-64) Ex: China, Thailand = large work force France, Japan or USA have a moderate dependency ratio = the growing number of elderly is offset by the declining number of children The age that divides the population Measure the age of a population: SEE TABLE WITH IMPACT OF AGE Median age into two groups of equal size World median age in 2010 = 29.1 (ie: 50% are younger than 29.1) 20
- 21. TYPICAL POPULATION PYRAMIDS 21
- 22. TYPICAL POPULATION PYRAMIDS Pyramids Developing countries (LEDC) Developed countries (MEDC) Shape Triangular pyramid Cylinder or spinning top Wide base: Narrow base: Base Poverty + poor education -> high TFR Affluence + good education -> low TFR (TFR = 2.73, Africa = 7) (TFR = 1.64) Narrow top: Widen top: Top Poor health care -> low life expectancy Good health care -> high life expectancy (LEB = 66) (LEB = 77) “Population contraction” “Population explosion” High median age + ageing ratio -> challenge for shrinking Low median age + ageing ratio -> Large work force in young generations who have to support a growing 10-20 years. This can be beneficial ONLY IF that number of retirees (Germany, Japan) + risk of population population can be educated and later find contraction UNLESS fertility increases to allow the professional opportunities (ex: China), but replacement of generations (>2.1) OR unless the country represents a major challenge in very poor countries opens to immigration (double benefit: influx of young (ex: Niger, Uganda: 50% < age 15). Significance pop + immigrants are usually poorer, less educated and therefore tend to have a higher fertility rate) (ex: USA) Confronted to those challenges, these countries usually Confronted to those challenges, these countries try to adopt pro-natalist policies or push back the usually try to adopt anti-natalist policies. But the retirement age (ex: legal retirement age 60 -> 62 in poorest countries are also the ones who have the France 2010?), while opening to immigration often least government control to enforce any efficient remains a sensitive political issue (Japan, Western policy (lack of funds, corruption, civil unrest) Europe) 22
- 23. IMPACT OF AGE ON A POPULATION Youthful population Ageing population (median age < 25) (median age > 35) Young, dynamic, creative population -> progressivism Opposite of challenges of youthful Large work force in the short term future population: good infrastructures, resources, food supplies, low unemployment, abundant Opportunities resources, less social tension and crime. New market (“third age”, “seniors”) -> active healthy population with free time (need for recreation, artistic or health care jobs) Pressure on infrastructures: housing shortage, slums, Lack of dynamism and creativity -> roads, water, sewage, etc conservatism Pressure on services: education (crowded classrooms, Pressure on retirement plans (high ageing low schooling rate, high illiteracy rate), health care ratio) -> reduced benefits, higher taxes, (high infant mortality and low life expectancy, rapid extension of working age spread of epidemics), transportation, police, etc Pressure on health care (high life Pressure on food supplies -> malnourishment leading expectancy) -> increasing medical costs to occasional famine when coupled with civil unrest or Pressure on to allow immigration -> sensitive climate accident political issue Pressure on working population (high dependency ratio) -> public debt Challenges Pressure on job market -> unemployment, emigration (males) sometimes leading to unbalanced sex ratio, higher crime rates Pressure on resources -> smaller farming lots, desertification, lack of water Pressure on future generations (high population momentum) -> the challenges above will go on for at least a generation Pressure on idle young men -> “youth bulge” leading to civil unrest, war or terrorism? (controversial theory of Gunnar Heinsohn, 2003) 23
- 24. MEDIAN AGE Japan: 44.7 Uganda: 15 Japan: 44.7 China: 34.2 Kenya: 18.4 France: 40.1 India: 25.0 Uganda: 15.0 USA: 36.6 Egypt: 23.9 World: 29.1 24
- 25. Dependency ratio: Ageing ratio: • DR < 50%: low • AR < 3: low •DR 50-80%: moderate •AR 3-5: moderate •DR > 80: high •AR > 5: high 25
- 26. Population Momentum Factor: PMF < 1: negative momentum = snowballing effect of ageing population will lead to a decline without immigration PMF = 1: no momentum = no snowballing effect of youthful/ageing and population can reach equilibrium if nothing changes PMF > 1: positive momentum = snowballing effect of the youthful population which will contribute to continued growth even with low TFR 26
- 27. POPULATION EXPLOSION, EQUILIBRIUM OR CONTRACTION? See how fertility (TFR) and life expectancy (LEB) impact the future of a population using your own simulation: www.ined.fr/en/everything_about_population/play_population/population_simulator/ 27
- 28. Food intake (1964-2030) Wheat yields in developing countries Recommended: 2,500 calories/day (1950-2004) 28